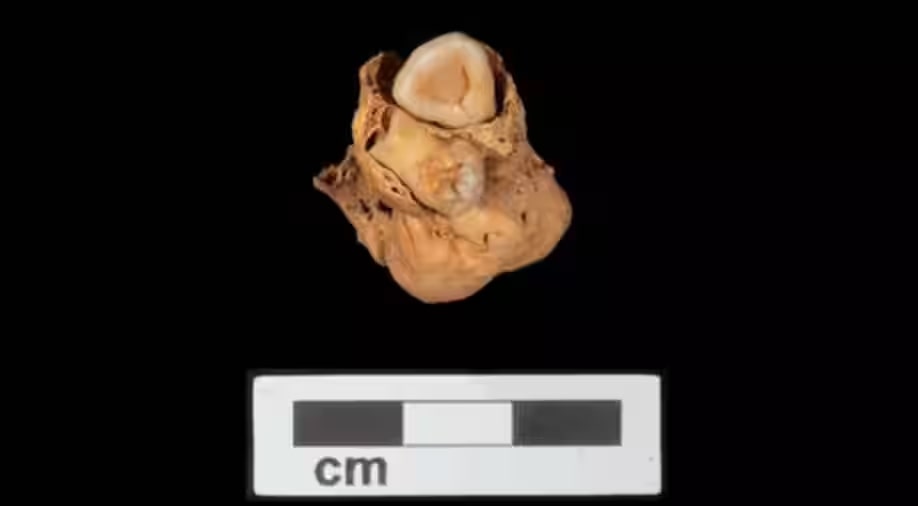
Archaeologists have unearthed the oldest documented example of a teratoma discovered within the 3,000-year-old burial chamber of a young woman in an ancient Egyptian cemetery.
Teratoma is a rare type of tumor which typically grows in testicles or ovaries. Teratomas can present as hair, teeth, bones and, in the most extreme cases, partial limbs and underdeveloped organs, which is perhaps where the tumor form got its name “teratoma,” derived from the Greek word “teras,” meaning monster.
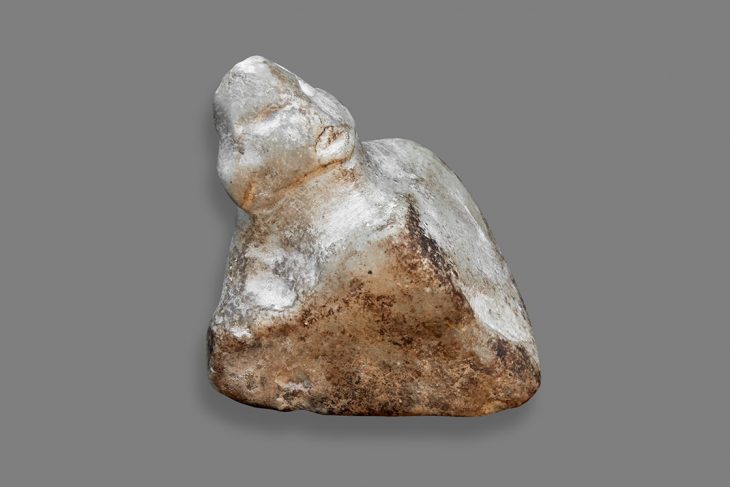
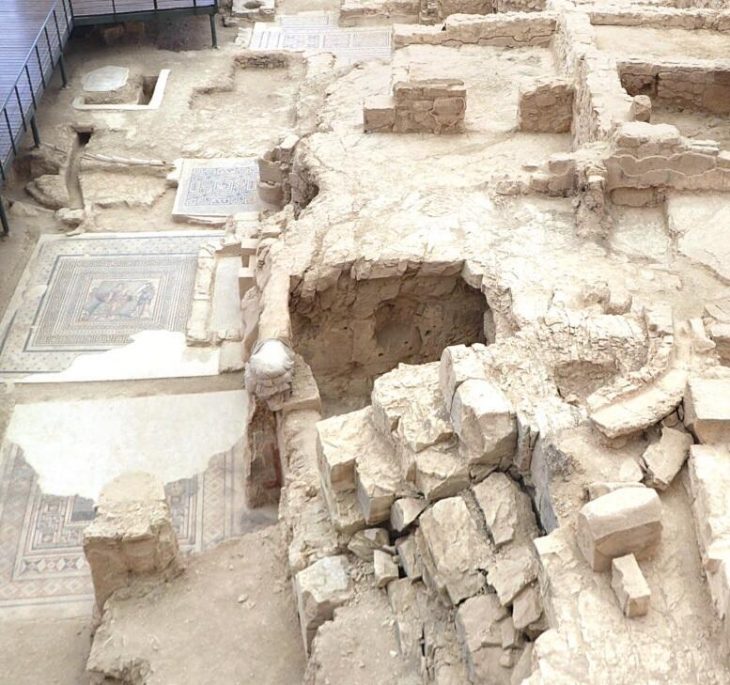
The ovarian tumour was found in the pelvis of a woman who had died over 3,000 years ago and was believed to be between the ages of 18 and 21.
Till now, archaeologists have found only four archaeological examples of teratomas, out of which three were in Europe and one was found in Peru. The latest teratoma discovered in the New Kingdom period cemetery in Amarna, Egypt, is the fifth archaeological case published so far.
The woman’s remains were found by Anna Stevens from the University of Cambridge and Gretchen Dabbs from Southern Illinois University, who have headed the project researching Amarna cemeteries since 2005.

In a paper, “A mature ovarian teratoma from New Kingdom Amarna, Egypt,” published in the International Journal of Paleopathology, the researchers detail the archaeological discovery of a mature ovarian teratoma in Amarna, Egypt, dating to the mid-14th century BCE
The skeleton was wrapped in a plant fibre mat and it was buried along with various grave goods, which included a deity related to childbirth, a ring decorated with the figure of Bes, fertility, and protection.
“The presence of a gold ring decorated with the god Bes on Individual 3051′s [the label given to the woman] left hand, and perhaps the positioning of the hand and ring close to the mass, may suggest the teratoma was not asymptomatic and Individual 3051 was attempting to invoke Bes to protect her from pain or other symptoms, or aid in her attempts to conceive and birth a child,” the study explains, as per Science Direct.
It is unclear what was known of the woman’s condition at the time, though the young age at the time of death could indicate that she died from an infection associated with the condition. Today, such a condition would be visible in an X-ray and likely treatable by surgery.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpp.2023.10.004
Cover Photo: Image of ovarian tumor found in the skeleton of Egyptian woman. Photo: Amarna Project