Archaeologists in southern Mexico have uncovered an ancient hilltop ceremonial center where enigmatic rock carvings and monumental platforms reveal centuries of ritual activity tied to the sun, water, and fertility.
The site, known locally as Piedra Letra and hidden for centuries in the rugged hills of Guerrero’s Costa Chica region, was recently investigated by specialists from Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH). Their findings suggest that the sanctuary, used for nearly 800 years, was a vital spiritual hub for the Amuzgo and Mixtec peoples, where ceremonies sought rain, honored the solar calendar, and reinforced agricultural cycles.
Rediscovering a Hidden Center of Worship
The Piedra Letra complex was recorded by INAH specialists Cuauhtémoc Reyes Álvarez and Miguel Pérez Negrete as part of a cultural heritage survey linked to the Plan of Justice and Development for the Amuzgo People. Local officials had alerted researchers to the presence of little-known vestiges scattered across the municipality, prompting a systematic reconnaissance of six communities: Huehuetónoc, Limón Guadalupe, Jicayán de Tovar, Santiago Yoloxóchitl, San Cristóbal, and Guadalupe Mano de León.
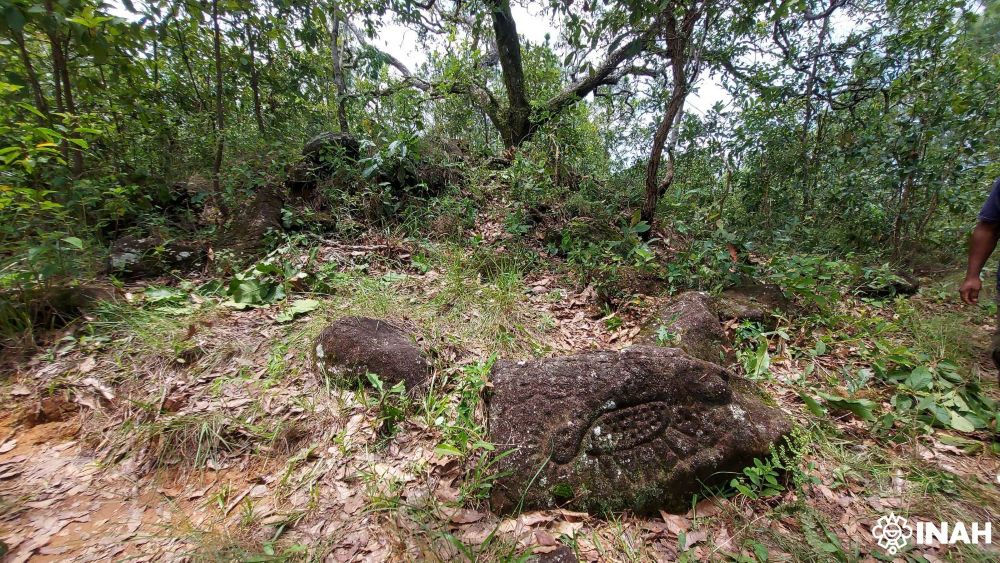
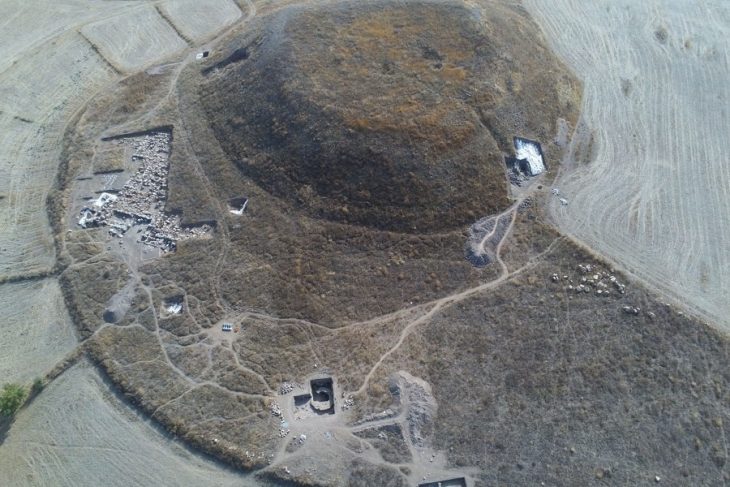
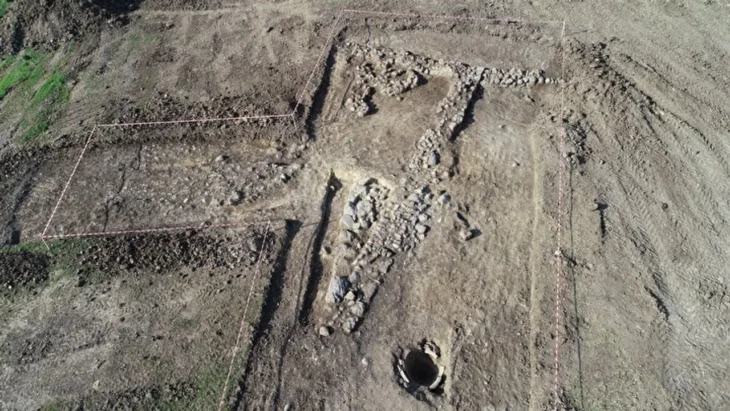
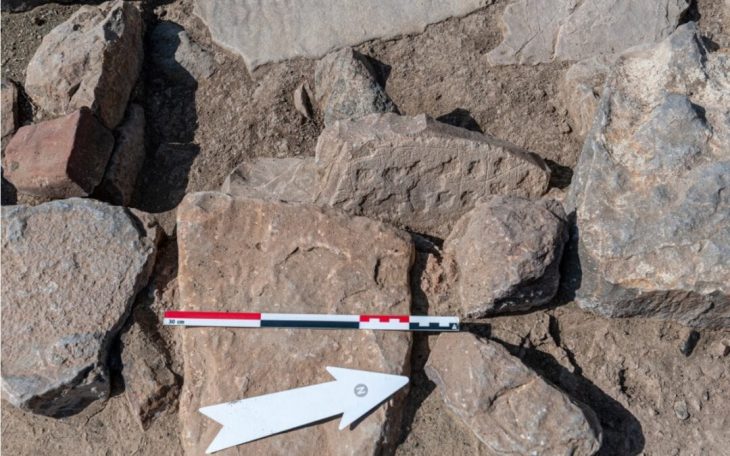
During their survey, archaeologists identified 11 pre-Hispanic sites featuring surface ceramics, rock art, and architectural remains. The most striking was Piedra Letra, where an expansive platform, two main bases, and smaller structures surround a rocky outcrop covered with petroglyphs. These carvings, dating from the Epiclassic–Early Postclassic period (AD 650–1150) to the Late Postclassic (AD 1150–1521), suggest the hilltop sanctuary remained in use for nearly eight centuries.
Petroglyphs of Time, Water, and the Cosmos
The motifs at Piedra Letra are rich with symbolism. Early carvings depict spirals, circular beads believed to mark cycles of time, water drops, and even a schematic ballcourt. Figures include a person wearing a feathered headdress and circular chest ornament, alongside the profile of a jaguar decorated with dotted spots.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
One later carving—a sun with a human face—belongs stylistically to the Late Postclassic and reinforces the interpretation that ceremonies tied to the solar calendar, rain petitions, and fertility rites took place on the hill. Archaeologists argue that the imagery reflects a worldview in which water, the sun, and agricultural abundance were interconnected forces crucial for community survival.
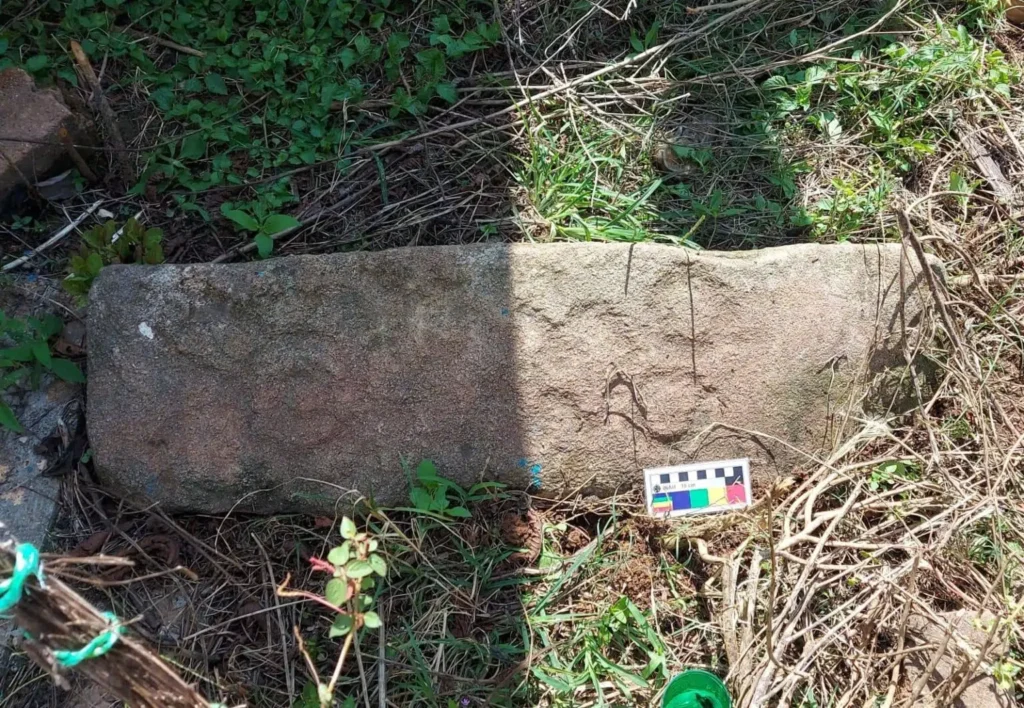

Monumental Sites Beyond Piedra Letra
The inspection also revealed monumental architecture at other sites. At San Cristóbal, researchers documented granite stelae rising nearly two meters, plain but imposing markers accompanied by carved stones bearing spirals and concentric circles. At Guadalupe Mano de León, they recorded a platform with remnants of walls and a carved stone axe. These discoveries, previously unknown in Tlacoachistlahuaca, expand the archaeological map of the Costa Chica and highlight the municipality’s role as a cultural hub in pre-Hispanic times.
A Cultural Crossroads in the Costa Chica
Tlacoachistlahuaca, known in the Amuzgo language as sei’ chue (“plain of the opossums”), has long been a melting pot of cultures. The Amuzgo people remain concentrated in Huehuetónoc and surrounding villages, while Mixtec groups inhabit northern communities such as Limón Guadalupe and Santiago Yoloxóchitl. Historically, the region also hosted the now-extinct Ayacatecan population and maintains connections with Nahua communities from nearby Xochistlahuaca.
For archaeologists, the findings provide an opportunity to move beyond fragmented oral traditions and colonial-era chronicles, such as the 16th-century Relaciones Geográficas, which offer only partial glimpses into the area’s past. Reyes Álvarez emphasized that although the Costa Chica has been visited by researchers since the 1960s, no comprehensive record of its archaeological wealth exists. “This reconnaissance is the first step toward research, protection, and conservation,” he noted.
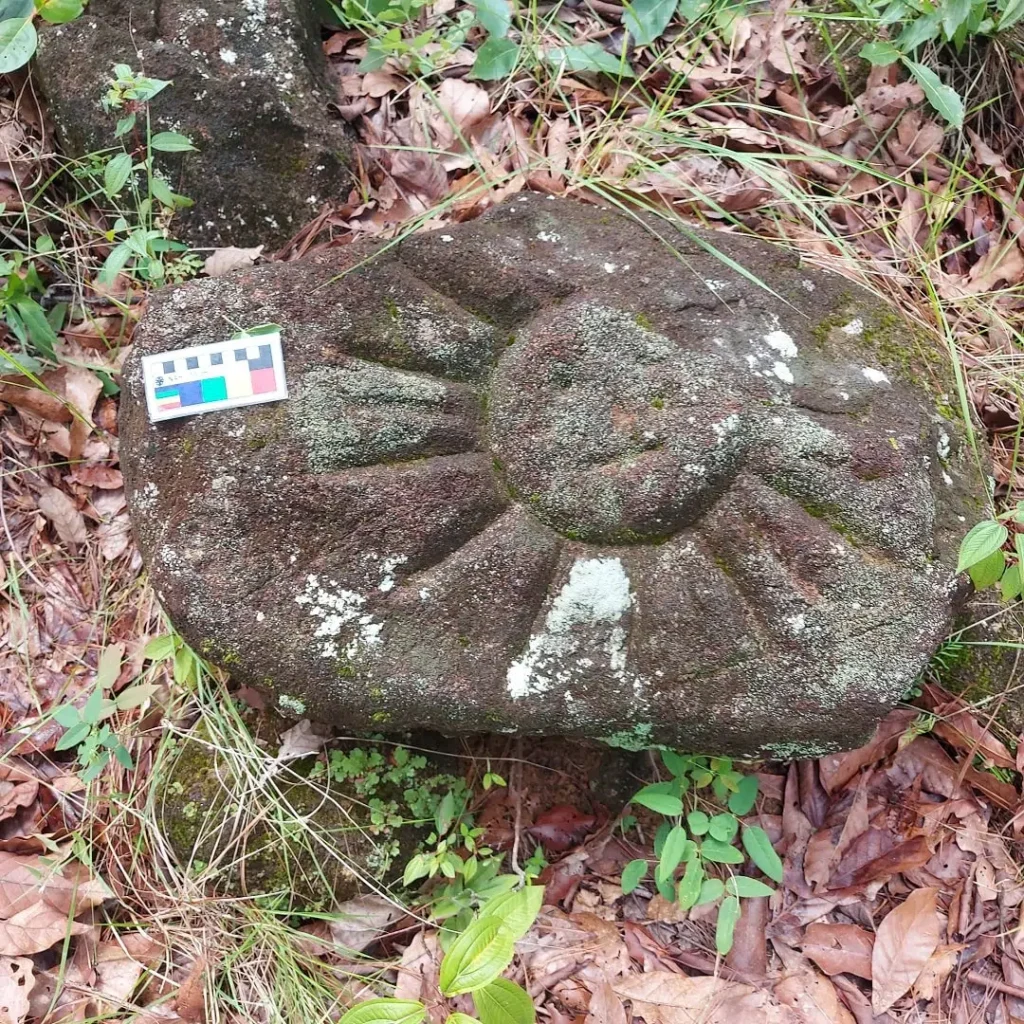

Toward an Amuzgo Archaeology
INAH specialists plan to compile the petroglyphs and carved motifs into an iconographic catalog that will help enrich the cultural identity of Tlacoachistlahuaca. For Pérez Negrete, the effort is not only about preservation but also about clarifying the origins of the Amuzgo people, whose identity has been shaped by narratives often contradictory between oral traditions. “We need hard archaeological data to contribute to this history,” he said.
While no immediate excavation campaigns or public exhibitions were announced, researchers stressed the importance of protecting the hilltop sanctuary and associated sites. The documentation underscores the Costa Chica’s archaeological significance, pointing to centuries of ritual life where communities honored the sun, asked for rain, and tied their agricultural cycles to cosmic order long before European contact.
The Piedra Letra discovery highlights the enduring cultural depth of Guerrero’s landscape, reaffirming the region as a vital but still underexplored chapter in Mexico’s ancient history.
Cover Image Credit: Archaeologists from Mexico’s INAH uncovered an ancient ceremonial complex in Guerrero featuring mysterious indigenous carvings, dating back to AD 650–1150. INAH