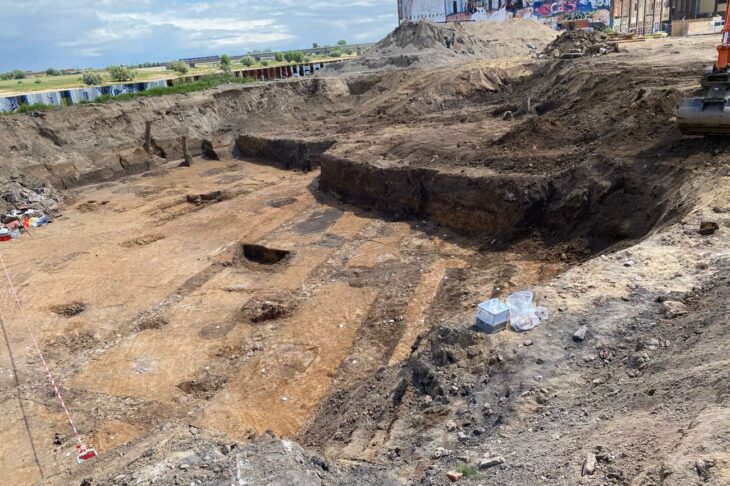
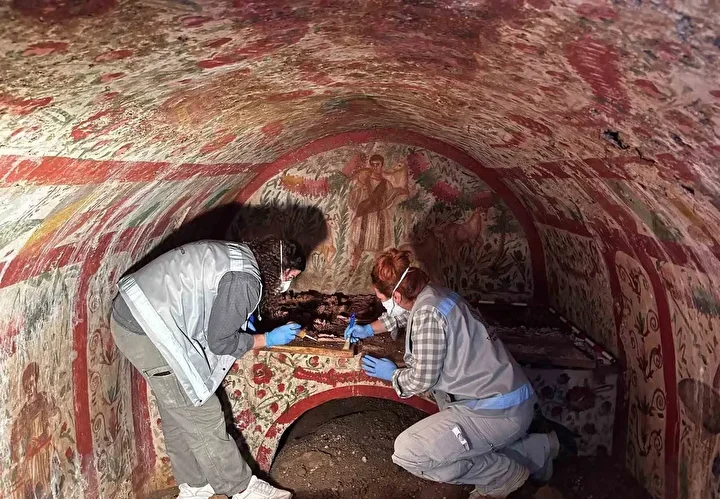
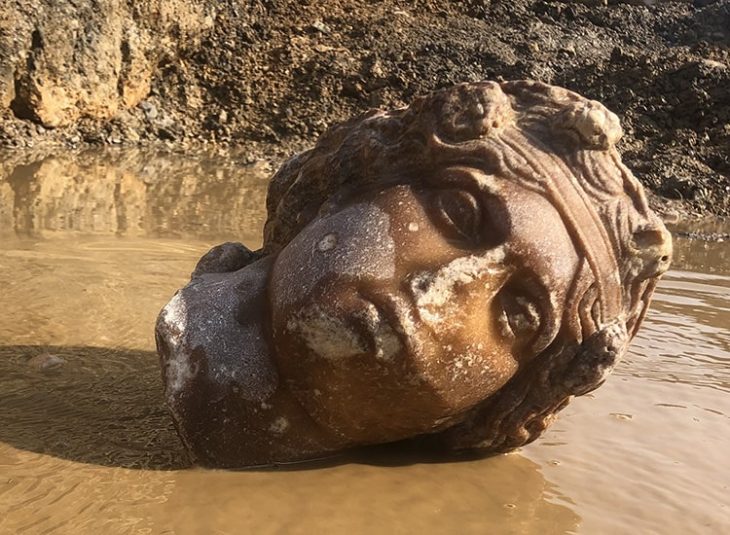
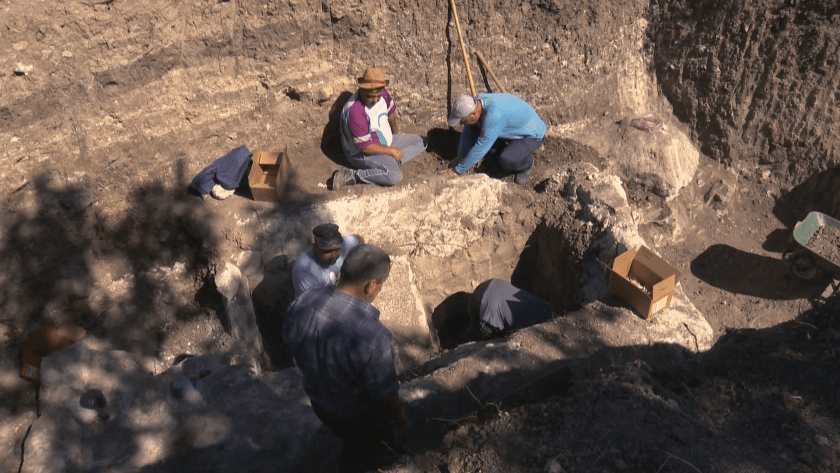
Archaeologists from the Haskovo Regional Museum of History discovered a third Thracian tomb with murals the likes of those in Kazanlak and Alexandrovo, Bulgarian National Television (BNT) reported. The tomb dates from the late 4th and early 3rd century BC.
The Odrysian Kingdom was established around 460 BC by the Thracian tribe the Odrysians and lasted until the Roman conquest in 46 AD. The Odrysian Kingdom included the territories of the entire modern-day Bulgaria, Northern Greece, the European part of Turkey, and a small part of Southeastern Romania.
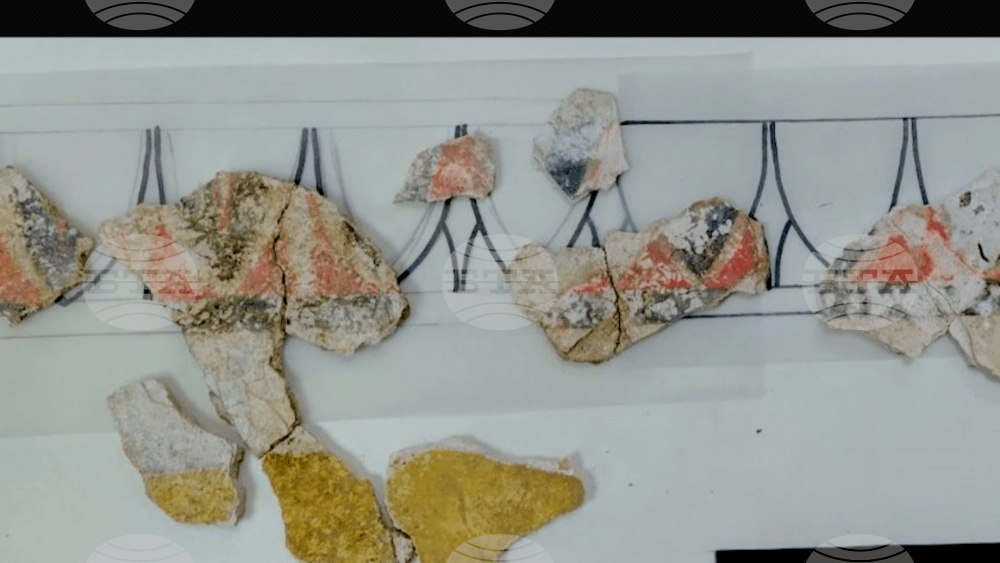
Unfortunately, at this point, the Thracian murals in the tomb itself have been damaged; all that was discovered were the indicative pieces of the murals in a treasure hunter’s pit by Teketo village.
Archaeologists from the Haskovo Regional Museum of History uncovered wall paintings destroyed by treasure hunters. Despite the damages, the condition of the tomb surprised the archaeologists.
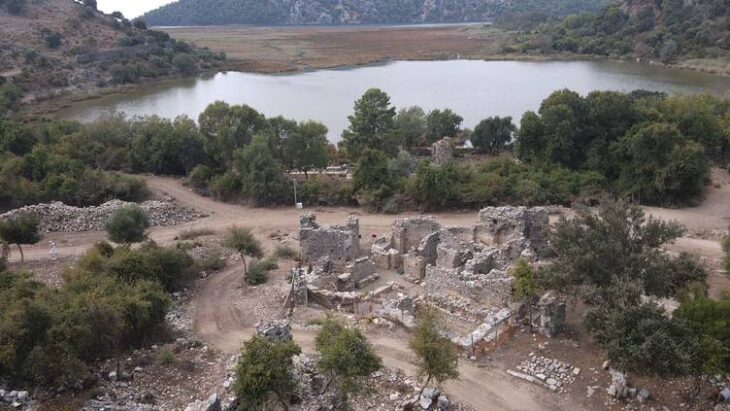
Near the southern city of Haskovo, there are hundreds of mounds, and the majority of them probably cover tombs. The race with treasure hunters there is inequal, by far not in favour of archaeologist.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

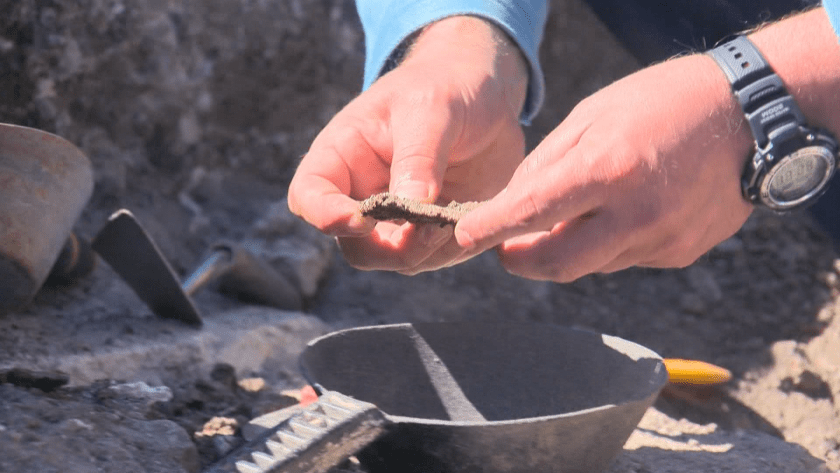
“Here we have only the top layer, the finest, the stucco. It is made of very fine mortar plaster with marble dust usually to make it so fine and the coloured decoration is applied over it. This is with a deep red orange. We have something like green here, a stripe,” archaeologist Assoc. Prof. Dr. Georgi Nehrizov told BNT, demonstrating the top of the piece.
Some of the coloured pieces perfectly match the decorative frieze around the murals at the Alexandrovo tomb.
“This band which ends the figurative hunting scene of the tomb. This is the so-called kymation. Lesbo kymation, a series of kyne (waves) which are a purely decorative ornament. The same can be seen in Kazanlak. This kymation is present only on those in which there are figural scenes. The same applies to other Hellenistic tombs found not in Thrace, but in Greece and Italy,” added Nehrizov.

However, it will provide valuable information for science and open a new chapter in the history of the Odrysians.
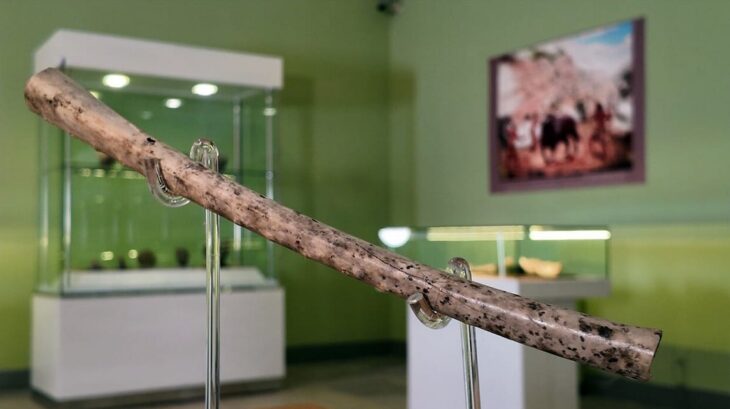
“It is curious to show you a situation that puzzles us too. Here we see fragments of protective clothing, under this block. This is a chasuble that is constructed of small plates that are sewn to a leather or cloth garment. We see 7-8 of them here,” said Assoc. Prof. Georgi Nehrizov, head of the archaeological excavations.
It is still unclear what these protective clothing are doing between two stones, and archaeologists are trying to find out.
The discovery of the tomb was announced by the team of archaeologists of Associate Professor Georgi Nehrizov from the National Archaeological Institute with Museum at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences on April 25 this year. The collection of donations to support the discovery, research and future display of the tomb continues, and the amount collected so far is nearly BGN 26,000.
BG64RZBB91553120056106 – Regional History Museum – Haskovo
Cover Photo: The mural pieces discovered by the archaeologists (BNT Photo)