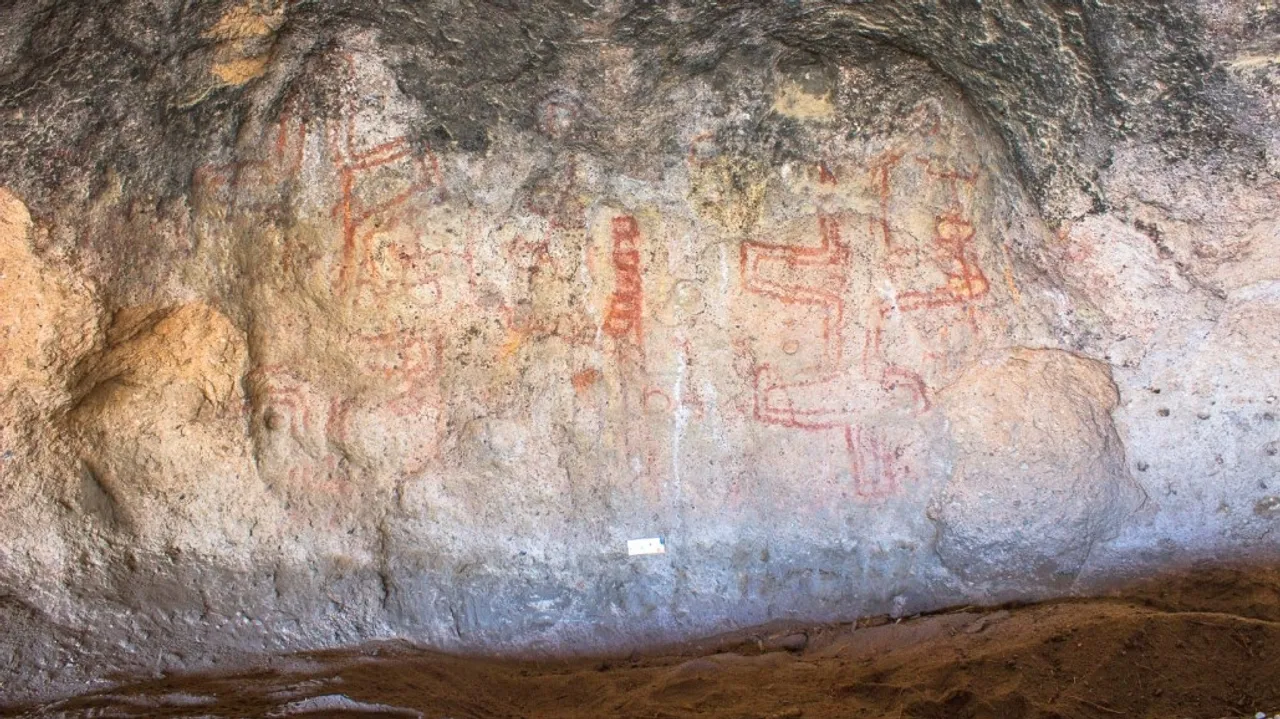
An astounding collection of almost 900 rock paintings, dating back approximately 8,200 years, has been discovered in northwestern Argentina.
The Huenul Cave 1, a 630-square-meter rock shelter located in northern Patagonia, the interior is adorned with approximately 900 unique ancient paintings featuring an array of geometric patterns, human figures, and animal depictions. However, cave art was previously thought to have been made within the last few thousand years.
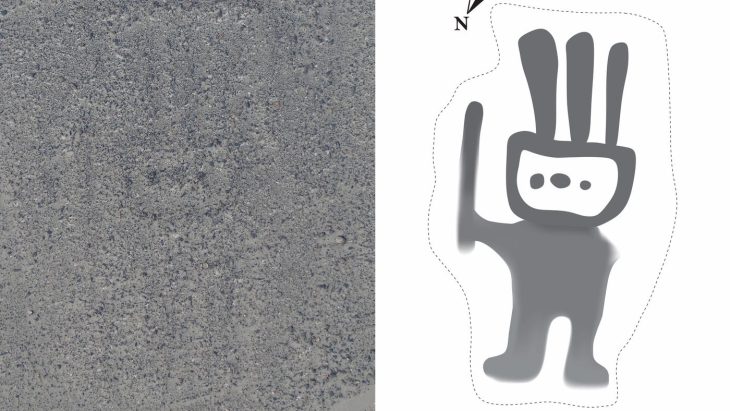
A study recently published in Science Advances found that one mysterious comblike pattern was made roughly 8,200 years ago.
Cave artists recreated the same design in black pigment for thousands of years thereafter. According to the New York Times, this design may have been used to communicate during shifts in climate change.
The enormous artwork, which features images of people, animals, and other designs, was dated by archaeologists by removing small fragments of black pigment from the drawings. Because the pigment was derived from plant matter, scientists were able to date the cave paintings using radiocarbon dating.
Archaeologists also discovered that the black painting was made from charred wood sourced from burned bushes or cacti.

“[The cave] is not the oldest occupation in South America, but it is the oldest directly radiocarbon-dated pigment-based rock art in South America,” study co-author Ramiro Barberena, an archeologist at Temuco Catholic University in Chile and CONICET, told Live Science.
During the late Holocene, this region of Patagonia was known for being very dry and hot, according to the study. Therefore, researchers point out the importance of information exchange.
“These [drawings] span more or less across 3,000 years within a single motif,” Ramiro Barberena said. “We propose that there was a transmission of information across multiple human generations, which inhabited the same region and the same site.”
Over 3,000 years, the comb motif might have helped to preserve the people’s oral traditions and collective memories. Although it currently acts as a documentation of how individuals have addressed the prior climate change challenges, the motif’s meaning, and intent are still unknown.
Patagonia, a region at South America’s southern tip, was first inhabited around 12,000 years ago. Around 10,000 years ago, Patagonia became increasingly arid, making it more difficult to live there. The archaeological record in the cave suggests that the site was abandoned around this time.