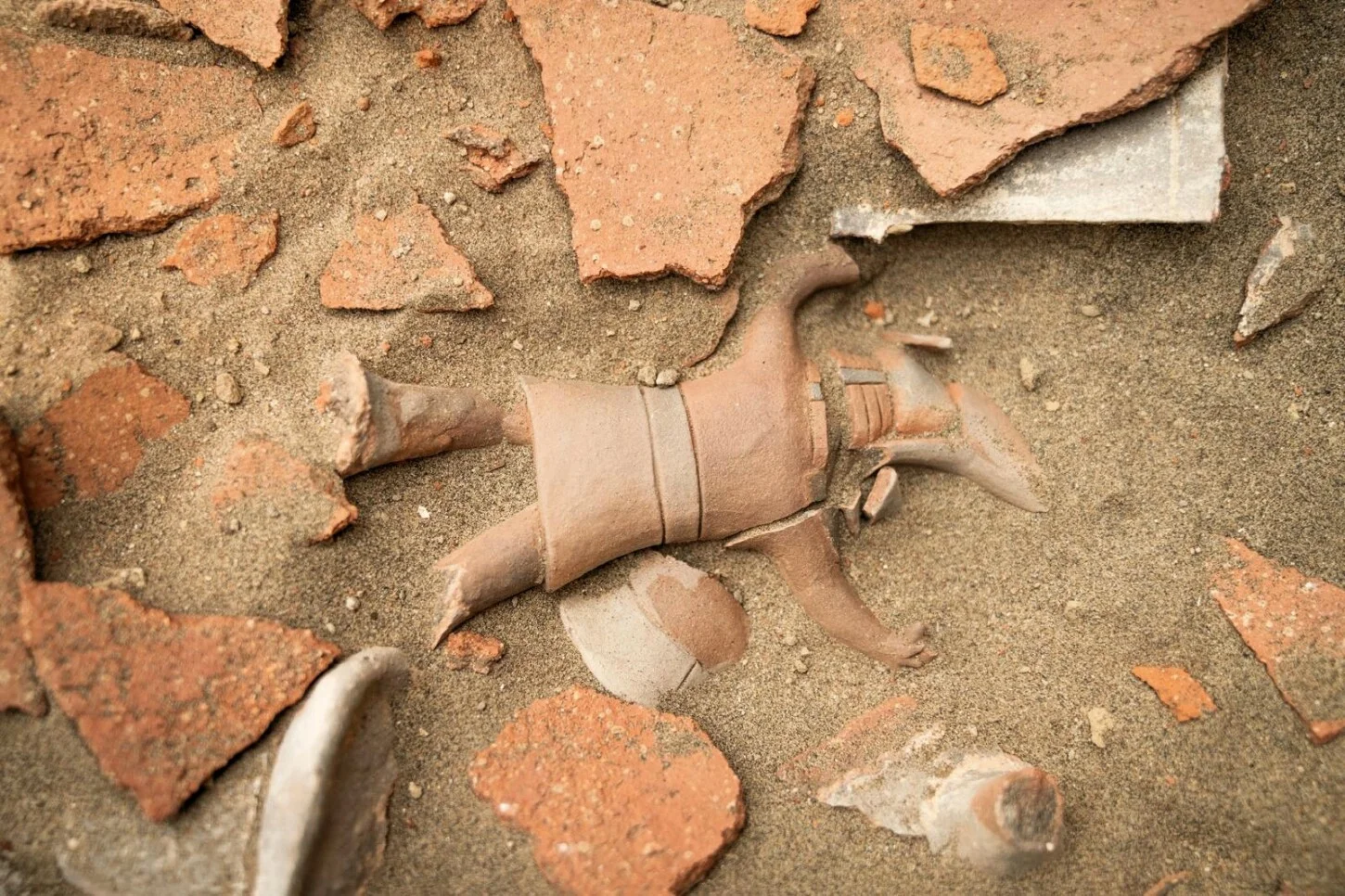
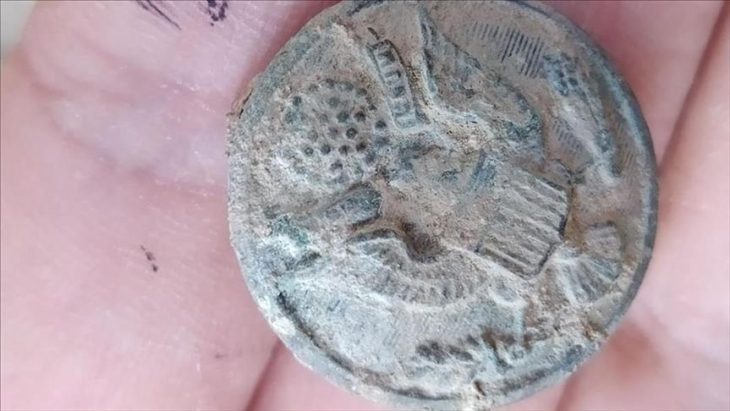
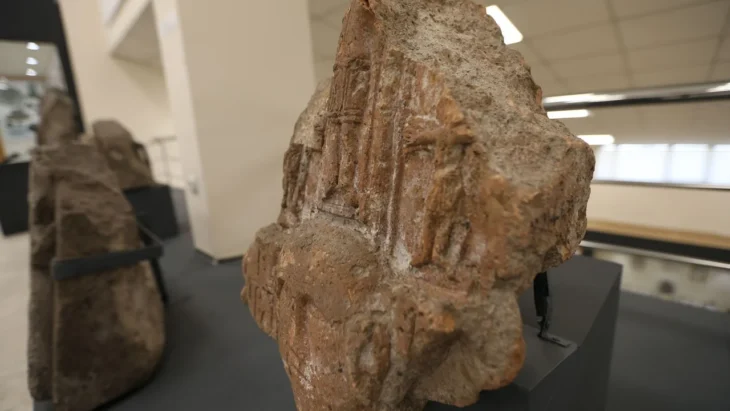
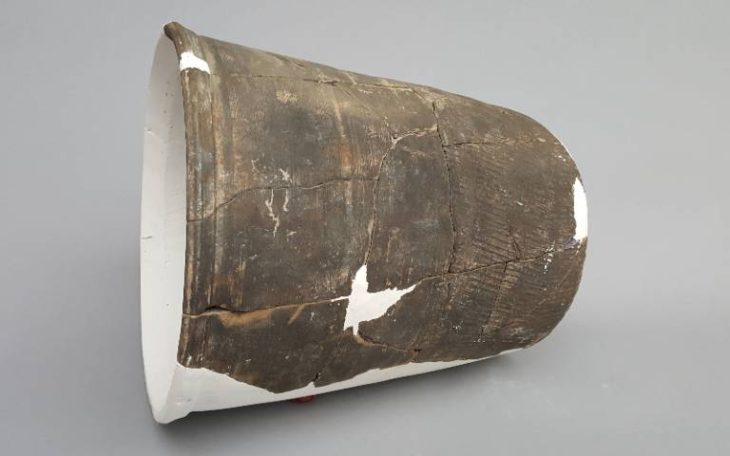
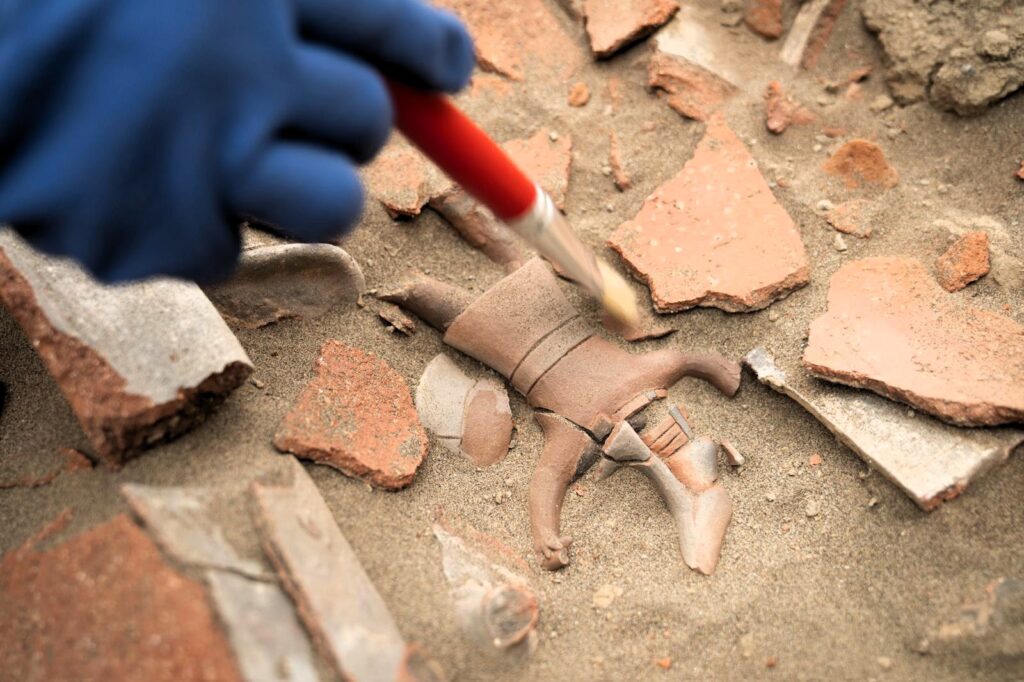
Archaeologists have uncovered a fragmented vessel depicting a warrior at Chankillo, the oldest solar observatory in the Americas, located in Peru’s Casma Valley.
This rare find links ancient solar ceremonies to the military and political power of elite groups over 2,300 years ago, offering new insights into the ceremonial and societal practices of the Casma culture.
Discovery of the Patazca-Style Warrior Vessel
The vessel, crafted in the Patazca style, was deliberately broken, likely as part of a ritual offering or during a conflict-related event. Patazca ceramics, produced in the northern coastal Andes around 500 BCE–200 CE, are characterized by highly detailed figurative designs, often depicting humans, animals, and scenes of combat or ritual.
These vessels frequently show expressive figures in dynamic poses, reflecting both daily life and ceremonial practices. The style is associated with the Casma culture, known for its complex society, monumental architecture, and sophisticated ceremonial traditions.
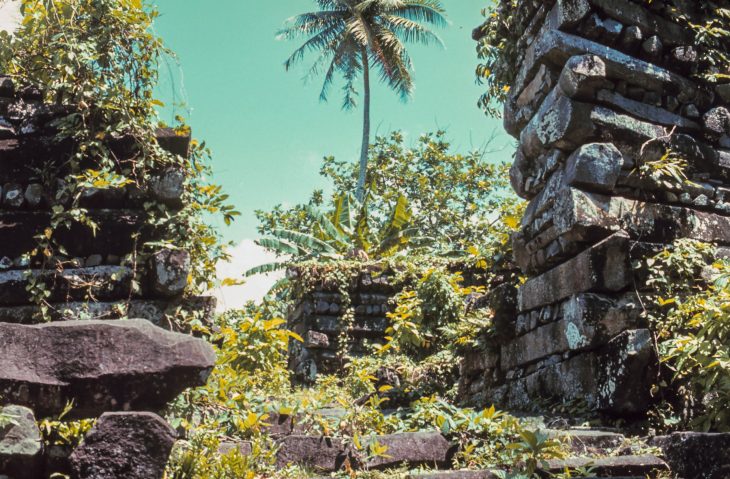
Located near the entrance to the Chankillo Solar Observatory, the vessel emphasizes the ceremonial role of such objects in religious practices tied to solar observation. Researchers link the warrior imagery to the Fortified Temple, a central hub for political, military, and ritual activities of the elite.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Ritual Significance and Elite Power
The Peruvian Ministry of Culture explains that the discovery confirms ritual objects were not purely decorative; they communicated identity, authority, and social status. The intentional smashing of the vessel likely played a role in ceremonies that reinforced elite dominance.
“This vessel shows how ancient elites combined ritual and imagery to assert control and maintain societal order,” ministry officials stated.
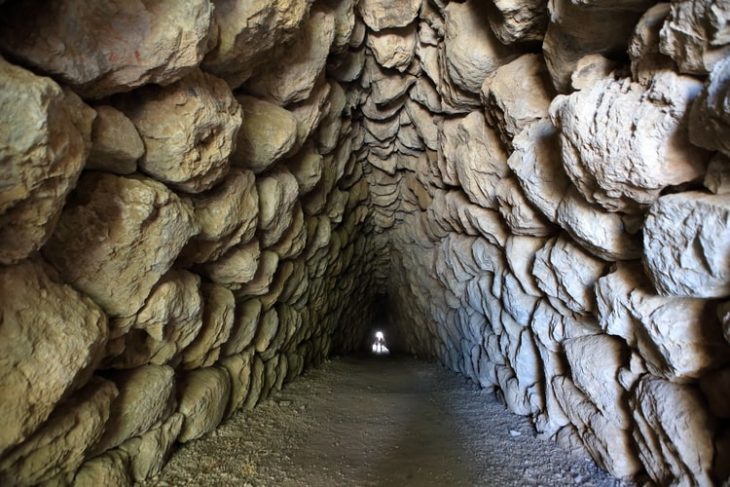
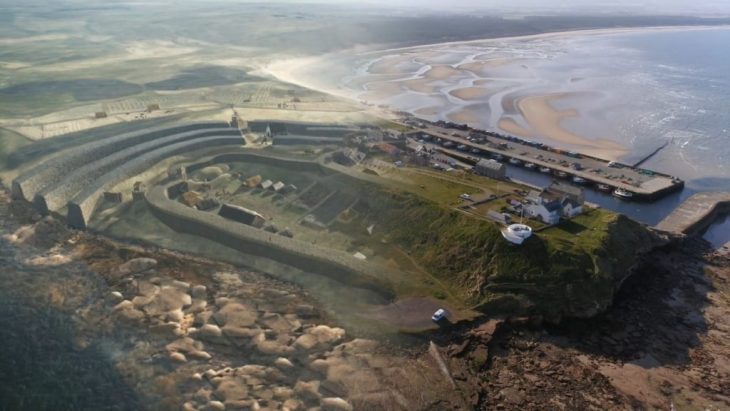
Chankillo: The Oldest Solar Observatory in the Americas
Chankillo, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2021, is celebrated for its Thirteen Towers, recognized as the oldest solar observatory in the Americas. Constructed over 2,300 years ago by the Casma culture, the towers are precisely aligned to mark the positions of the sunrise and sunset throughout the year, creating a full horizon calendar. This advanced astronomical knowledge allowed ancient inhabitants to accurately predict seasonal changes, optimize agricultural cycles, and schedule ceremonial events, reflecting a sophisticated understanding of the solar calendar.
The observatory’s design also demonstrates the interplay between science, religion, and political authority. By controlling knowledge of solar cycles, the elites of Chankillo could organize ritual events that reinforced their social and political dominance, linking celestial observation directly to power and ceremonial authority. The site’s combination of monumental architecture, ritual spaces, and astronomical precision makes Chankillo a unique testament to the ingenuity and organizational complexity of early Andean civilizations.
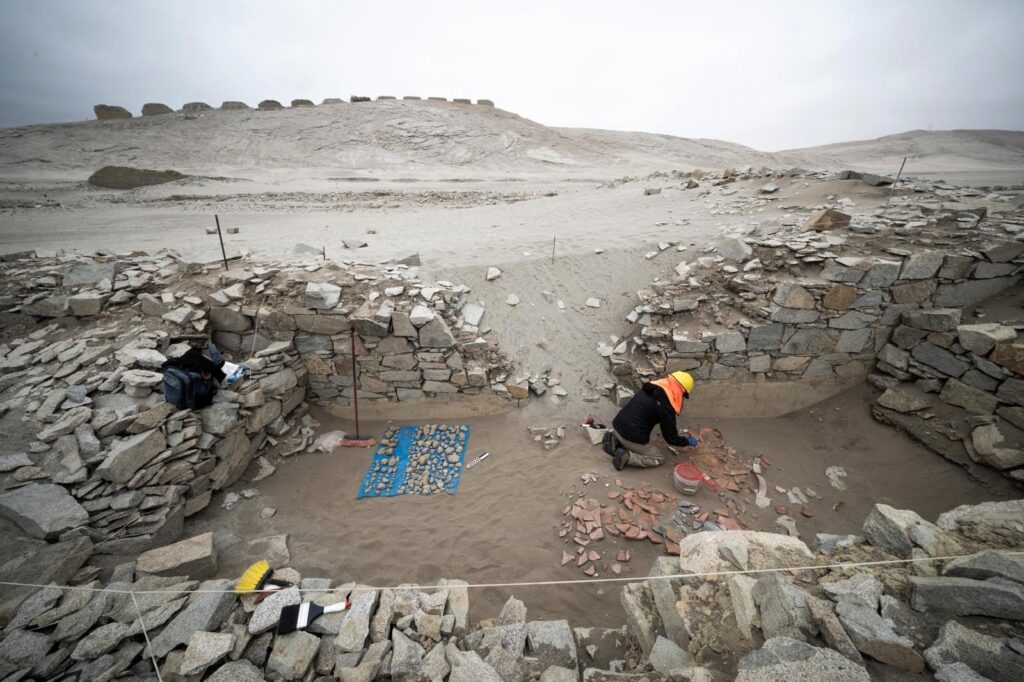

Linking Military Authority to Ceremonial Practices
The warrior vessel strengthens the interpretation that Chankillo was more than a solar observatory. It served as a ceremonial and military stage where elites asserted power through ritual, astronomy, and force.
The Fortified Temple, stretching over 300 meters, highlights Chankillo’s dual function as a sacred and strategic location. Warrior depictions on the vessel provide evidence of militaristic aspects of elite identity, linking rituals to the assertion of authority.
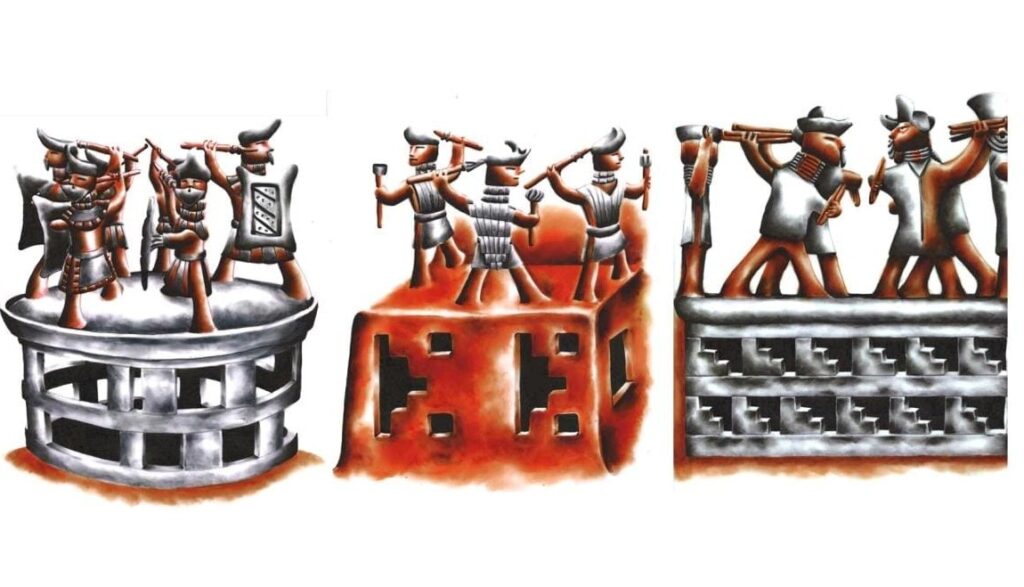

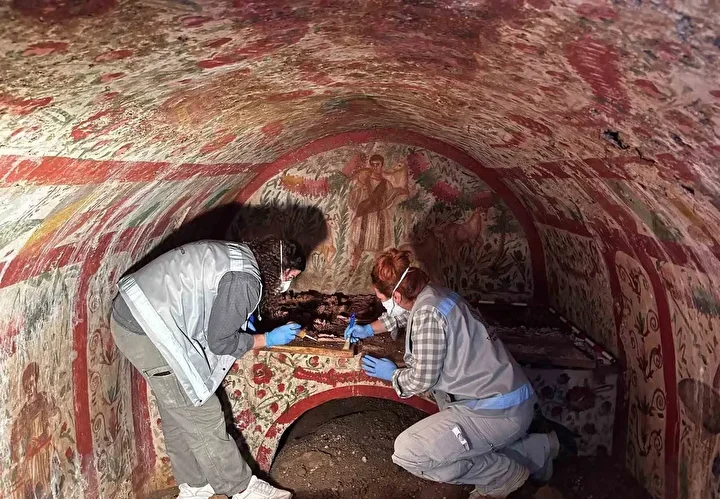
Continuing Research and Cultural Insights
The Ministry of Culture continues excavations to uncover more about Chankillo’s social, political, and religious structures. The discovery of the warrior vessel illustrates the sophistication of Andean societies centuries before the Inca Empire.
Chankillo remains unique for combining astronomical, ritual, and defensive features. The Thirteen Towers form one of the most precise ancient horizon calendars, while the Fortified Temple and ceremonial spaces reveal the Casma culture’s complex hierarchy. Artifacts like this warrior vessel offer a window into how elites communicated power, identity, and connection to the cosmos.
Ongoing research at Chankillo will likely reveal more evidence of how early Andean civilizations used astronomy, ritual, and military organization to maintain control. This discovery adds a compelling layer to the story of Chankillo, highlighting the central role of strength and authority in elite rituals.
Cover Image Credit: Ministry of Culture of Peru