Researchers suggest they may have identified the lost Parthian city of Natounia in the Zagros Mountains of Iraqi Kurdistan.
Although the Parthian Empire was a power in ancient Iran for hundreds of years, not much is known about it due to the lack of primary historical sources.
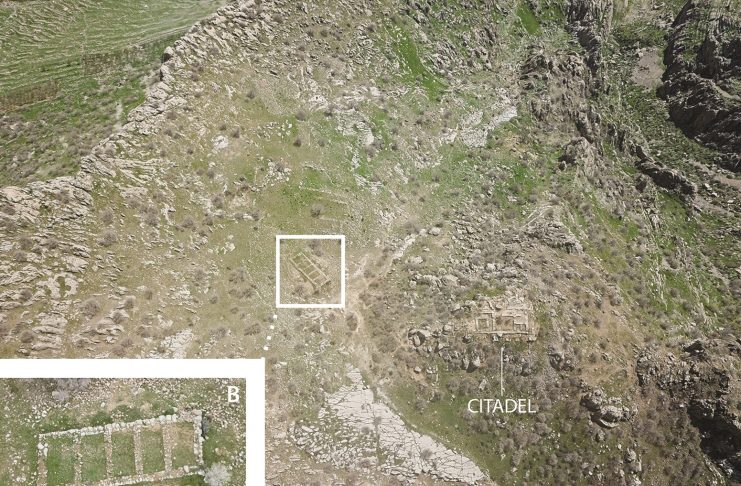
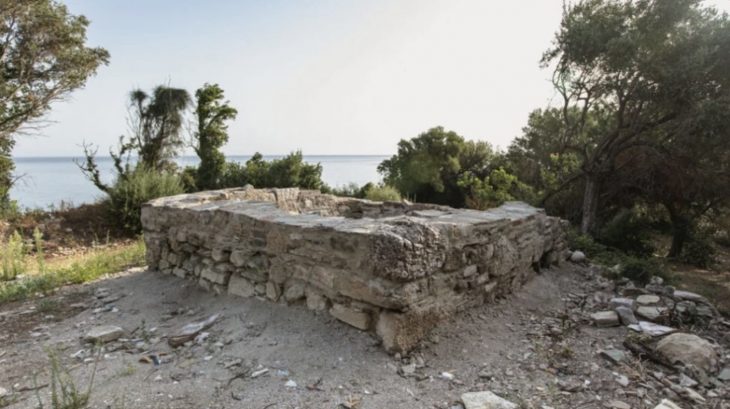
Archaeologists focused on the mountain fortress of Rabana-Merquly, one of the most important regional centers of the Parthian Empire 2000 years ago. The fortress consists of nearly 4km of fortifications, in addition to two smaller settlements, for which Rabana-Merquly is named.
Archaeologists have examined the ruins of a number of rectangular structures that may have acted as barracks as well as a religious complex devoted to the Iranian Zoroastrian deity Anahita over the course of many excavation seasons in 2009, 2019, and 2022.

Evidence shows the fortress was occupied over millennia by different groups, from the time of the Parthians to the Sasanian era, through a period of Islamic occupation, and into the modern era. The new study analyzed the site and came up with some surprising conclusions.
They established that numerous defensive structures built into the mountain are connected as part of the whole site, which sprawls over 100 hectares.
Also, Rabana-Merquly is located on the eastern border of Adiabene, ruled by the kings of a local Parthian dynasty. Among other things, it may have been used to trade, maintain diplomatic relations, or exert military pressure with pastoral tribes in the backcountry.
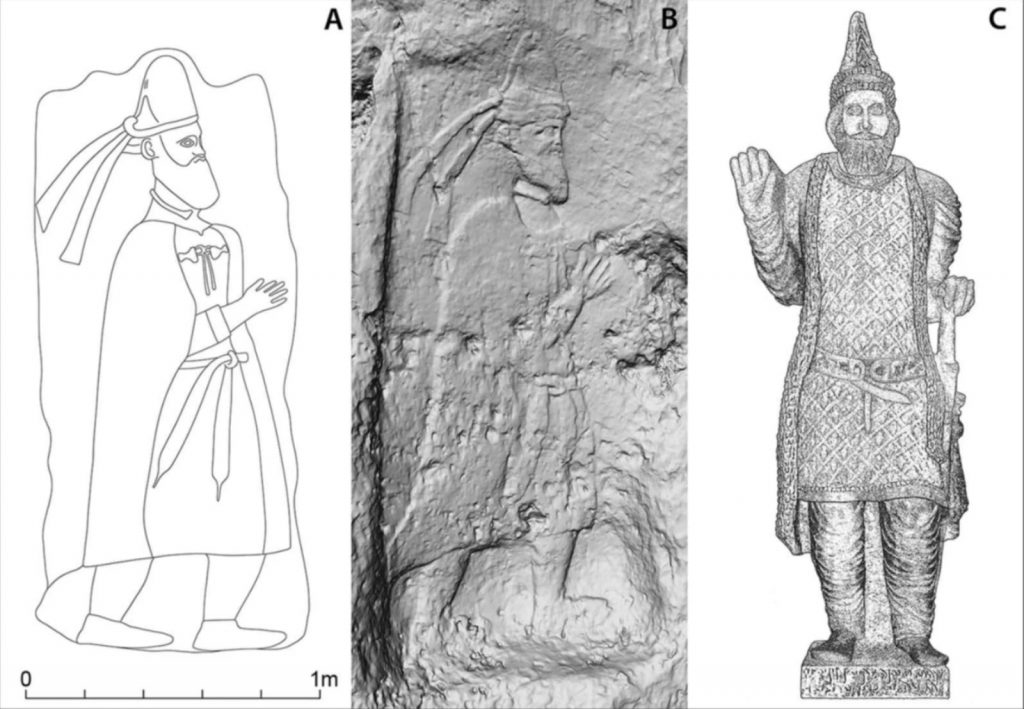
The main reason they came to this conclusion is based on the rock reliefs of an unnamed king they believe was a member of the ruling Parthian dynasty of the ancient Adiabene kingdom, and the site’s location in the Lower Zab.

The striking resemblance between the figures’ clothing and the statue of King Adiabene found at Hatra suggests that the relief may represent the founder, either Natounissar or a direct descendant, suggesting that the site was actually Natounia.
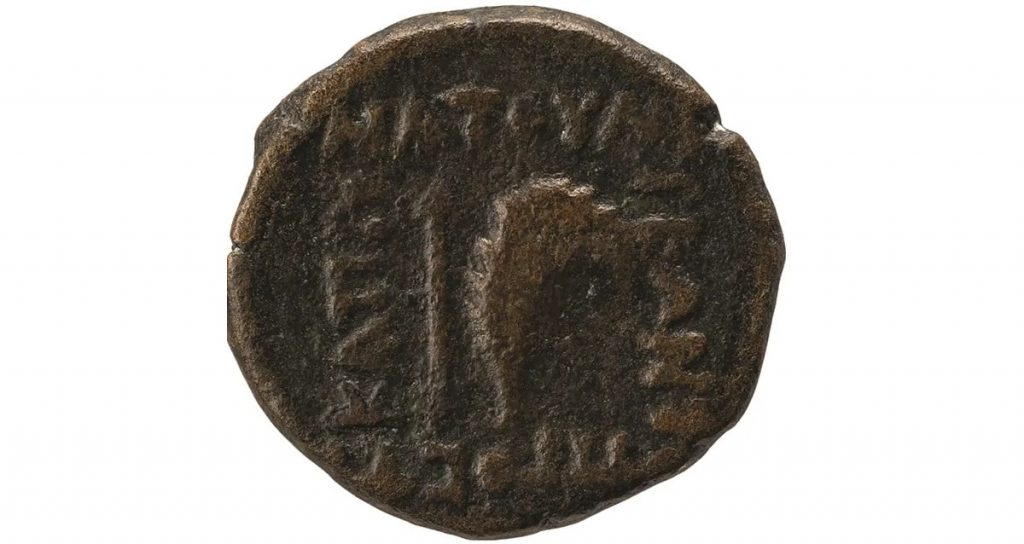
Until recently, the only information on this city was contained on a few coins from the first century BCE that were discovered in the present-day Turkish province of Nusaybin. The inscriptions on the coins indicate that they were made around the first half of the first century BCE, which is roughly when the remnants of this settlement were discovered.
The study authors also argue that the place name Natounissarokerta, as well as being composed of the royal name Natounissar, contains the Parthian word for moat or fortification.
The research was published in Antiquity by researchers in Germany and Iraq on Tuesday.
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2022.74
Cover Photo: Antiquity