After Göbeklitepe in Şanlıurfa, which sheds light on 12,000 years ago in human history and is considered one of the greatest discoveries in the world of archeology, new studies were started in the same region under the name of “Taş Tepeler”.
Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Culture and Tourism and the Türkiye Tourism Promotion and Development Agency (TGA) presented Taş Tepeler, a project that aims to reveal the land where the change in human history took place and a great transformation from the hunter-gatherer way of living to agriculture, with a series of visits, meetings, and events from 21 to 27 September 2021.
TAŞ TEPELER Project involves archaeological excavations and research carried out in seven areas: Göbeklitepe, Karahantepe, Gürcütepe, Sayburç, Çakmaktepe, Sefertepe and the Yeni Mahalle mound.
The Şanlıurfa region is home to the first examples of organized labour and specialization in the history of civilization. Between 2021 and 2024, excavations will be carried out in a total of 12 locations, including Karahantepe, a site with more than 250 T-shaped megalith blocks similar to those found in the UNESCO World Heritage Site, Göbeklitepe. It is believed that the finds from these excavations will make considerable and far-reaching contributions to our knowledge of humanity in prehistoric times, including their daily lives and rituals. It is estimated that there are several sites in Şanlıurfa similar to Göbeklitepe, which reflect the early phases of the Neolithic Age.

Taş Tepeler Project, considered to be the beginning of the transformation of shelters into houses 12,000 years ago, and in which villages emerged, a stratified society formed, and the ability to carry out basic trade developed. It is thought that the monumental megalithic structures in the area were believed to be communal spaces where people gathered.
“Now we have a different view on history,” says Necmi Karul, a professor of prehistory at Istanbul University who is leading the dig at Karahantepe, a site carved into the slope of a hill on a high limestone plateau between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
“Our findings change the perception, still seen in schoolbooks across the world, that settled life resulted from farming and animal husbandry,” he said at a September presentation of the site. “This shows that it begins when humans were still hunter-gatherers and that agriculture is not a cause, but the effect, of settled life.”
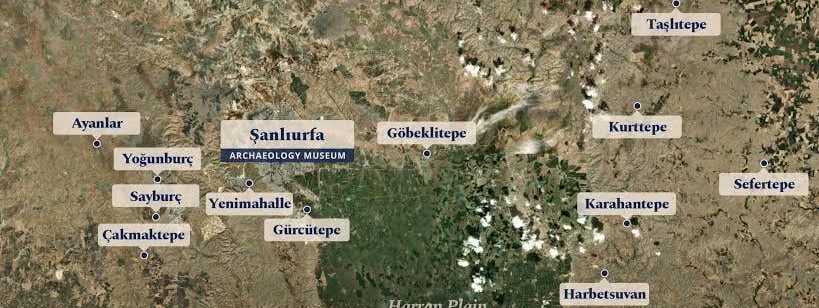
The region of these settlements is named “Taş Tepeler,” literally meaning Stone Hills. Covering an area of 200 kilometers from one end to the other, Taş Tepeler is an Anatolian and Upper Mesopotamian territory that hosted the earliest settled communities.
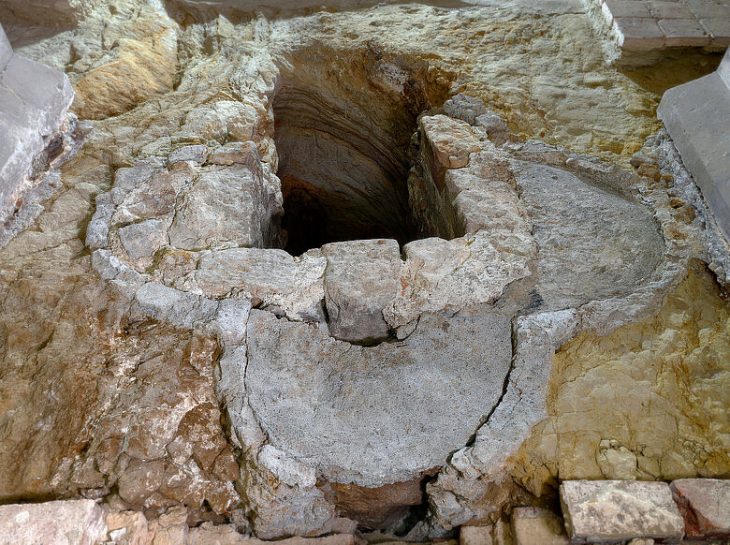
As far as we know, Taş Tepeler is the first example of sedentism and social union on earth. Sacred and secular spaces were built simultaneously at Karahantepe, where humans dwelled year-round for about 1,500 years, and no remnants of farmed vegetation have been found.
Göbekli Tepe, which was previously thought to be the only place where nomadic people came to worship, is now considered a part of simultaneous settlements. Recent work has also revealed domestic structures at Göbekli Tepe. “In this region, we encounter monumental structures for the first time in the oldest villages of the world,” Karul says.

Challenging conventional thinking
Scientists have long assumed that the domestication of plants and animals approximately 10,000 years ago pushed people to adopt a sedentary lifestyle and that the increase in food production enabled them to establish complex communities and build the groundwork for civilization. However, emerging evidence that Stone Age people erected permanent buildings for spiritual, rather than technically necessary, activities are challenging the conventional wisdom that they lacked a large-scale civilization with the division of labor and common ceremonial themes.
The Neolithic era, which coincided with the end of the Ice Age, symbolizes humanity’s tremendous transition from foraging to farming.
“It will take time for the scientific community to digest and accept this game-changing research,” says Mehmet Özdoğan, the professor emeritus of archaeology at Istanbul University.

“We must now rethink what we knew—that civilization emerged from a horizontal society that began raising wheat because people were hungry—and assess this period with its multi-faceted society. The foundations for today’s civilization, from family law to inheritance to the state and bureaucracy, were all struck in the Neolithic period,” Özdoğan says.
In Taş Tepeler, which is thought to be the beginning of the process where the shelter turned into a dwelling and real villages emerged 12 thousand years ago, there are finds on humanity’s first use of pottery and the ability to carry out basic trade initiatives. The monumental structures in the region are believed to be communal spaces where people come together.
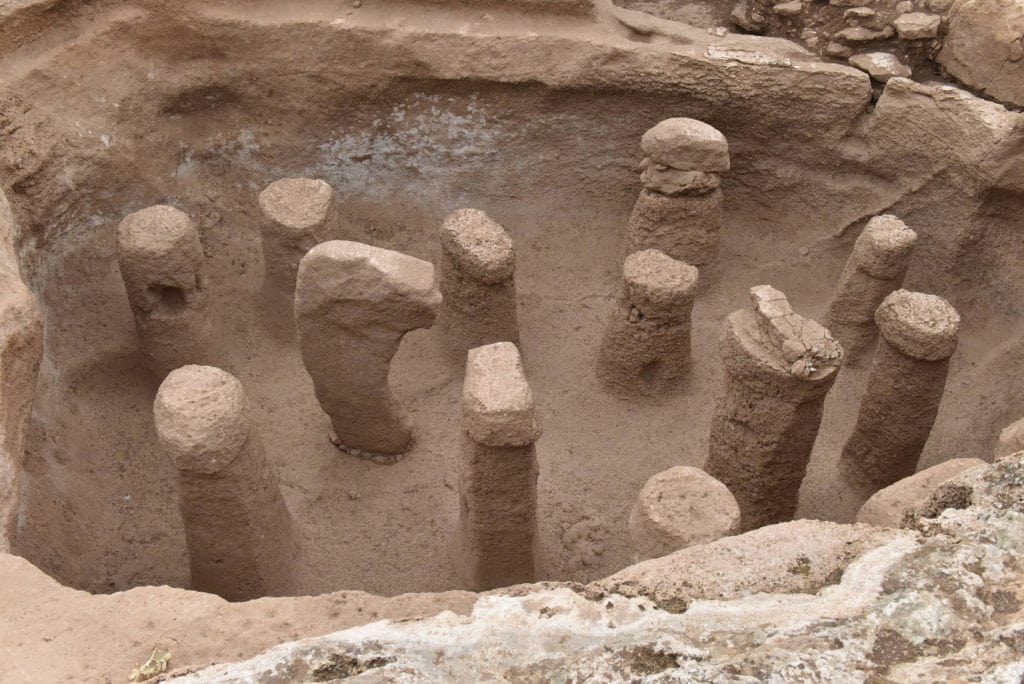
Karahantepe rises within Şanlıurfa’s interesting limestone authentic land structure. These limestone rocks are the main material of the finds.

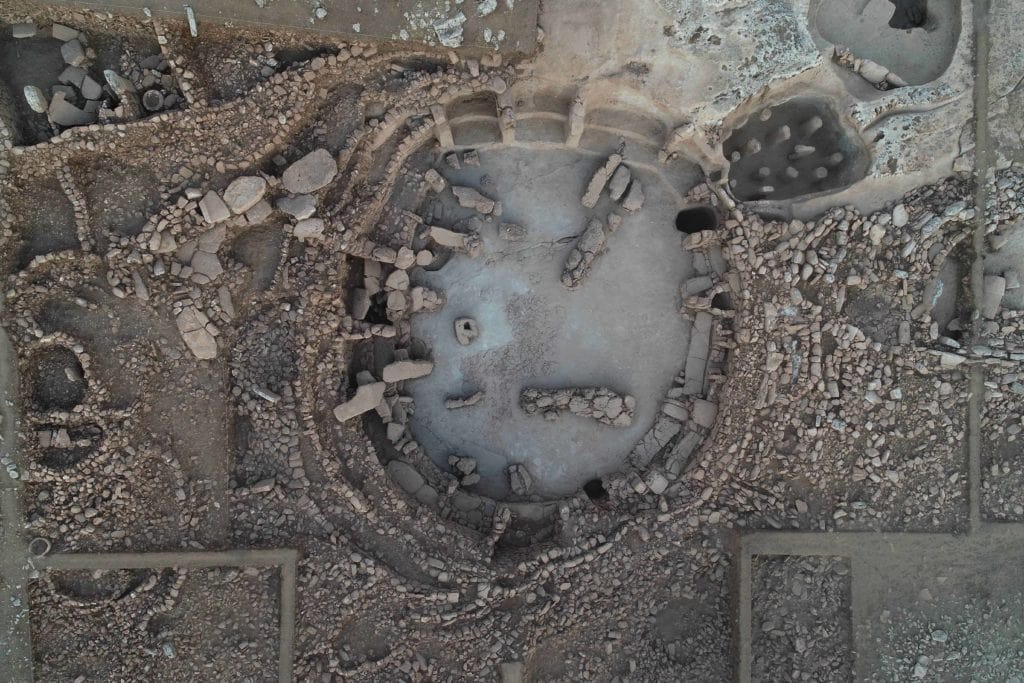
Karahantepe’s circular rooms were planned out in advance, and “the very skillful processing of bedrock reveals an impressive prehistoric architectural engineering”, Karul says. “Building multiple structures with different purposes is the reflection of a complicated belief system. It’s not possible to talk about religion in its true sense, but we see a set of distinct, limited rituals that are radically set forth.”
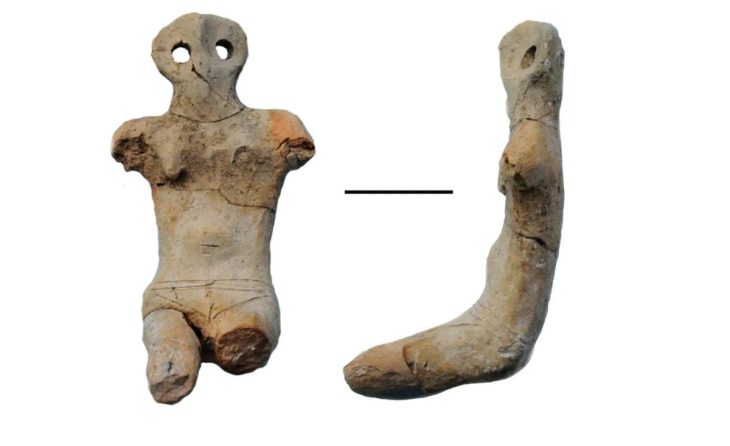
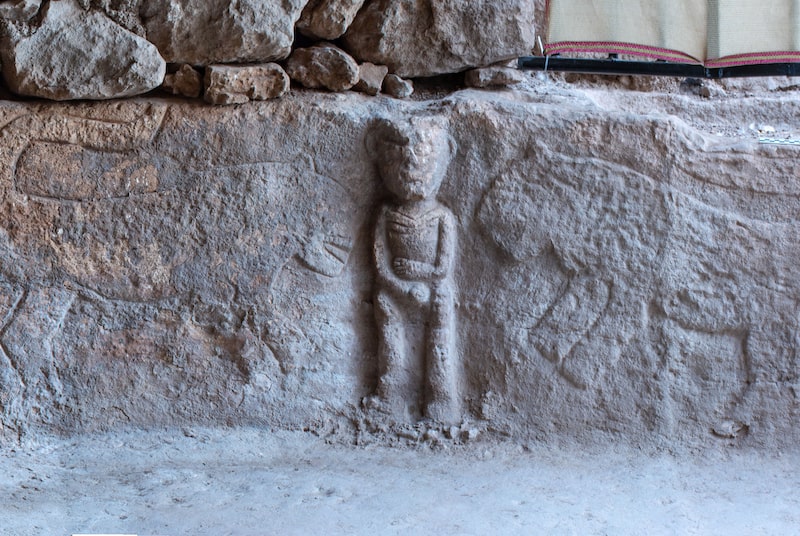
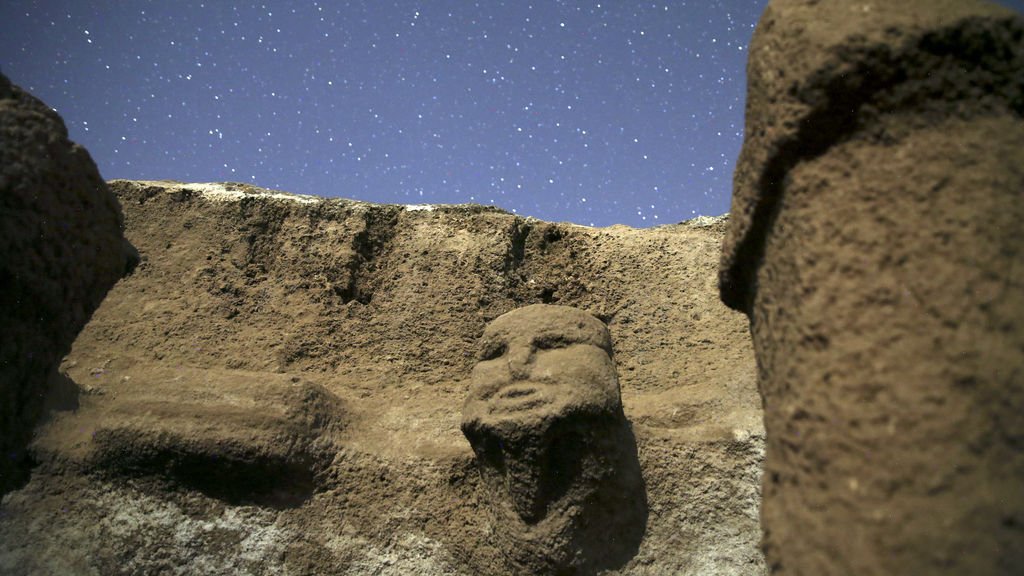
Attacking beasts grabbing men’s heads are shown in stone reliefs, which range from insects to mammals. There are more images of people than at Göbekli Tepe, which is around 200 years earlier, showing that humans had begun to regard themselves as separate from the animal world, according to Karul. At Karahantepe, dozens of T-shaped stelae—abstract renderings of the human form—have been discovered.
All of the animals are portrayed as aggressive and they are all masculine animals. Stating that the presence of several motifs on the stones indicates the existence of some partnerships, Karul said, “It shows that societies have common memories. It makes sense when we think of Karahantepe together with Göbeklitepe. We are trying to make the process of approximately 1500 years understandable.”

Karahantepe, which was registered as a first-degree archaeological site in 2007, is located in the Tek Tek Mountains National Park.
During the visit to Karahantepe, Republic of Türkiye Minister of Culture and Tourism, Mehmet Nuri Ersoy, noted that the sites and their excavations reveal the important contribution of Anatolia to human history.
While excavations continue, Turkey could open Karahantepe to tourists next year, according to the culture minister Mehmet Nuri Ersoy.
Karahantepe, which is a 46-kilometer drive from the city center in Şanlıurfa, was discovered in 1997. The first excavations were launched on the site in 2019. Karahantepe houses more than 250 T-shaped megaliths featuring animal depictions.
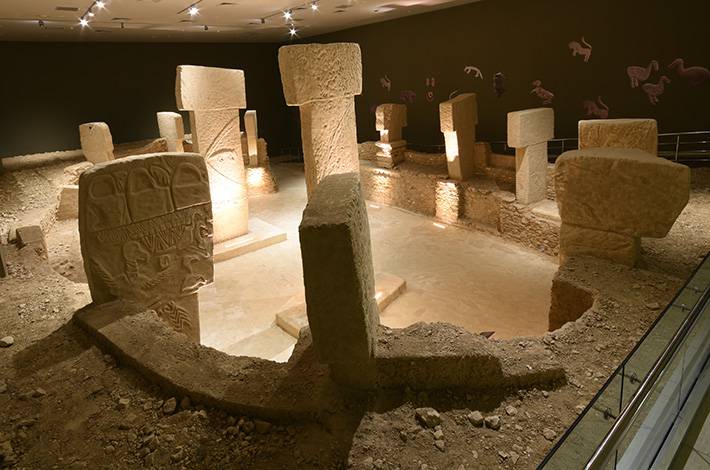
An exhibition featuring these stelae and sculptures has been opened at the Şanlıurfa Archaeological Museum.
Cover Photo: Karahantepe. TGA
















