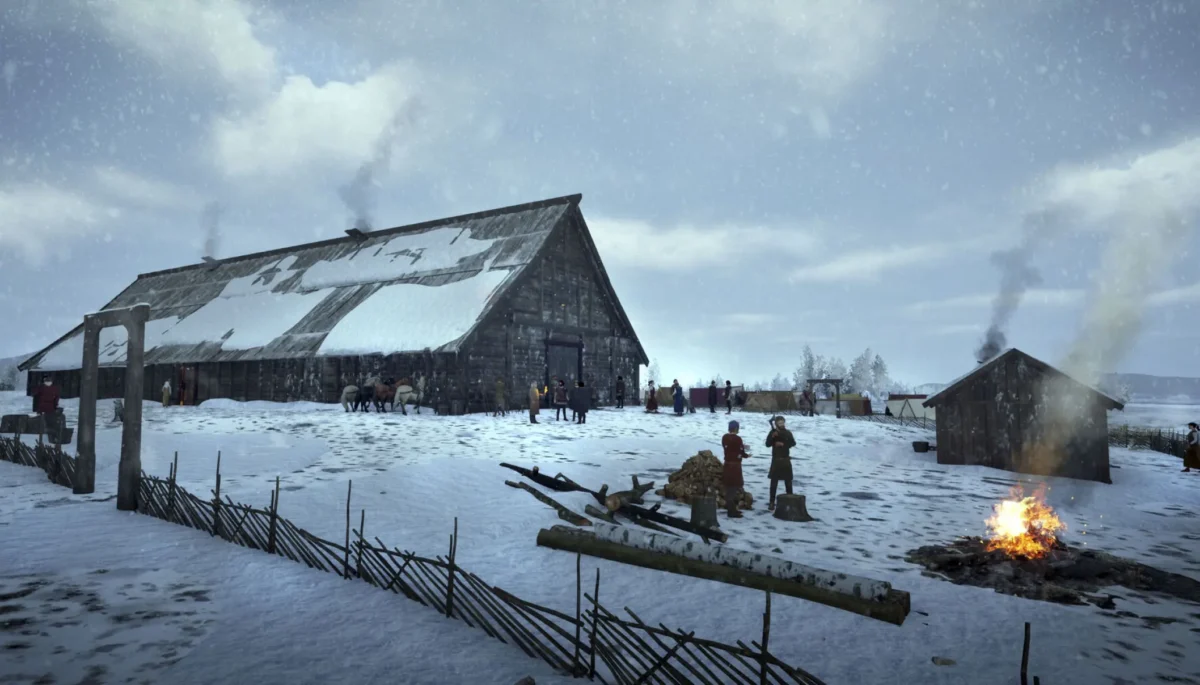
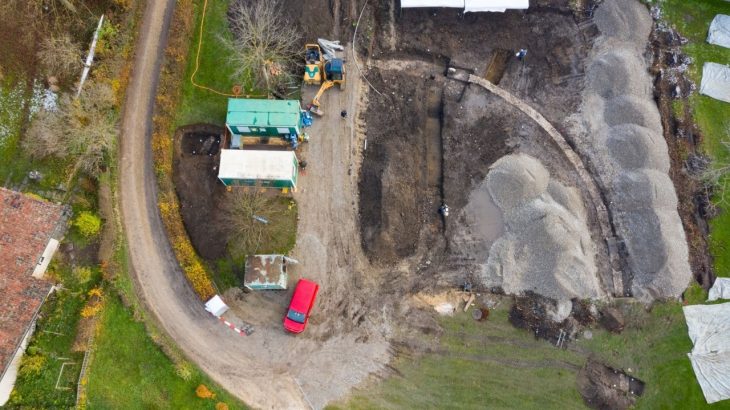
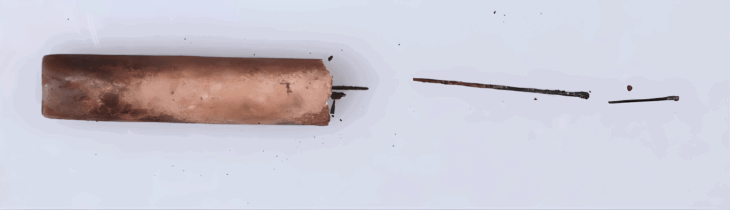
Archaeologists have made a groundbreaking discovery at Øvre Eiker near Oslo, Norway unearthing a longhouse that surpasses any known structures from Denmark or Sweden during the same period, with an astonishing width of 16 meters and a central nave spanning 9 meters between its roof-supporting columns.
The excavations, conducted in the summer of 2023, revealed this remarkable building at Sem, which initially led researchers to believe it dated back to the 1400s due to its unusual proportions. Jes Martens, project leader and associate professor at the University of Oslo’s Museum of Cultural History, expressed his surprise at the find.
However, carbon dating revealed that the longhouse was actually constructed in the 200s, over a millennium earlier than initially thought. Despite initial doubts about the dating results, further testing confirmed the structure’s age.
“It was hard to believe. The longhouses previously found from that period were 5-7 meters wide. Such houses would have fit inside this enormous house at Sem, that’s how large it is,” Martens stated. This discovery not only challenges previous assumptions about the architectural capabilities of the time but also highlights the significance of the site in understanding early Scandinavian history.
Archaeologists believe that the recently discovered longhouse at Øvre Eiker may have served as an early royal hall, reflecting significant power and wealth in the region. Jes Martens, project leader and associate professor at the University of Oslo’s Museum of Cultural History, emphasized the building’s exceptional nature, stating, “A building so exceptional must have represented something very special. It’s a visible sign of power and great wealth.”
The longhouse, dating back to the 200s, is strategically located in a landscape rich in resources from both land and water. During this period, the climate was relatively mild, and water levels were much higher, allowing large ships to sail directly to Sem.
Martens speculated that if a king ruled from this site during the Iron Age—700 years before Harald Fairhair, who is traditionally regarded as Norway’s first king—historical narratives may need to be reconsidered. He noted, “There are some old Scandinavian texts that mention kings dating back to the time of Christ. These stories have been dismissed as myths, but maybe there’s some truth to them.” This discovery could potentially reshape our understanding of early Scandinavian history and the political landscape of the time.
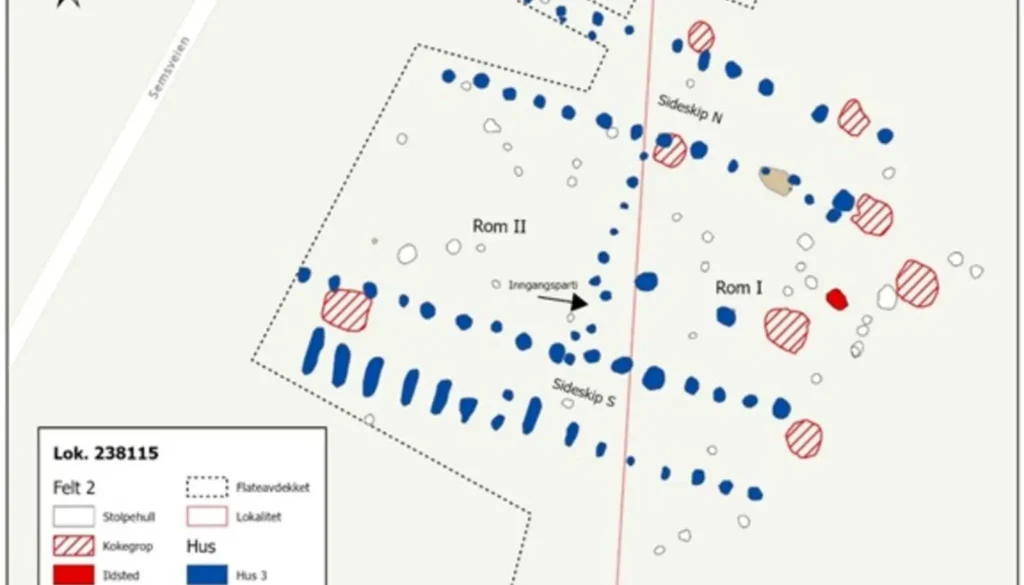
Recent archaeological findings at Sem have bolstered the hypothesis of a Nordic king’s presence in the region during Roman times, suggesting that a royal seat may have sought to unify southern Scandinavia from this strategic power center. Jes Martens, project leader and associate professor at the University of Oslo’s Museum of Cultural History, emphasized the significance of these discoveries.
Martens pointed to the thousands of weapons and war equipment unearthed in Jutland and Funen, Denmark, which date back to this period and are believed to have originated from Norway and Sweden. “These weapons must have been transported there by an army trying to conquer western Denmark. This army must have been organized from a specific place, and the one who organized them must have had great power and access to vast resources,” he explained.
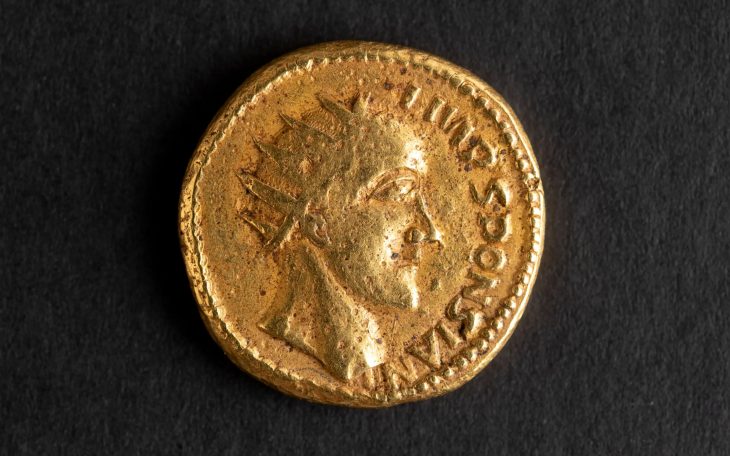
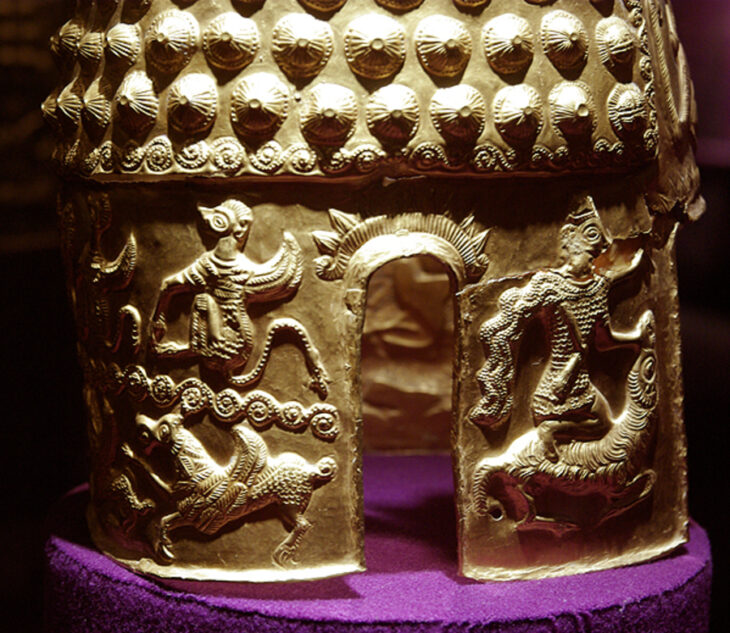
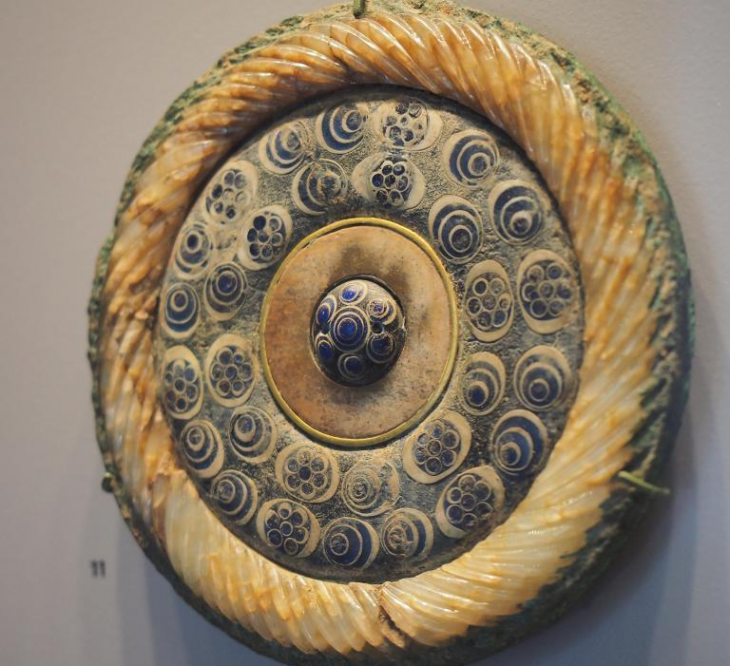
Additionally, a remarkable find in a bog near the longhouse—the Solberg vase—adds further weight to the theory. This exceptionally elaborate Roman cameo glass vase is the only one of its kind discovered outside the Roman Empire, suggesting it was owned by powerful individuals and possibly gifted to a king in the north.
“For a long time, people wondered what the Solberg Vase was doing in Norway. Now we might be closer to an answer,” Martens stated. “It’s always exciting to find sensational discoveries that confirm history, but it’s even more exciting when they give us a new perspective on history.” These findings not only enhance our understanding of the region’s past but also challenge existing narratives about the political dynamics of early Scandinavia.
The 2023 excavation was made possible through funding from the Norwegian Directorate for Cultural Heritage and was the result of a collaborative effort involving the Museum of Cultural History, the county municipality, and dedicated members of local metal detector clubs.
Jes Martens, addressing the importance of further research, stated, “We have only examined half of the house and have many questions. The purpose of the various rooms and side aisles remains unclear. We believe that answers lie in the other part of the building, which could provide valuable insights into the activities that took place here.”
Archaeologists are now seeking additional funding to continue their work at the site, as only 21 meters of the building’s length have been uncovered thus far. Longhouses from this era generally measured two to three times their width, indicating that the structure likely continues beyond the current excavation area. Regrettably, the remaining portion of the building is situated beneath a roadway and a field on the opposite side, thereby underscoring the pressing necessity for financial resources to facilitate further investigation of this significant archaeological site.
Cover Image Credit: This is how the experts envision the stately building at Sem might have appeared. Image Credit: Arkikon / Museum of Cultural History / Norwegian News Agency