The Maya civilization was known for its achievements in art, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, and calendar systems. Tikal, the ancient Maya city, was a bustling metropolis that housed tens of thousands of people. The Maya had roads, paved plazas, pyramids, temples, palaces, and homes for its fast-growing population, and agriculture was undoubtedly very important to the yeasts.
According to University of Cincinnati experts, Tikal’s reservoirs – essential supplies of city drinking water — were bordered by trees and wild plants, providing stunning natural splendor in the middle of the busy metropolis.
UC researchers devised a unique method for analyzing ancient plant DNA in the silt of Tikal’s temple and palace reservoirs in order to identify more than 30 species of trees, grasses, vines, and flowering plants that thrived along its banks more than 1,000 years ago.
The study was published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports.
The focus of recent research has been to study the relationship between the Maya and the surrounding neotropical forests using a new form of technical analysis called environmental DNA. An in-depth analysis of Tikal Reservoir found that Tikal Reservoir is an important source of drinking water and available water for the entire population. Among them, trees and wild vegetation are arranged in a planned way in the middle of Tikal, which is likely to provide natural beauty but may also be useful. “Plant Garden”.
The classic Mayan period (250-850 AD) witnessed a huge population explosion, which put additional pressure on existing water sources, especially reservoirs. The study pointed out that, so far, in the context of complex social development, the Central American society and people’s land management practices are poorly understood. “In the absence of concrete evidence, the nature of vegetation around the reservoir has been the subject of scientific hypothesis and artistic rendering for decades.”
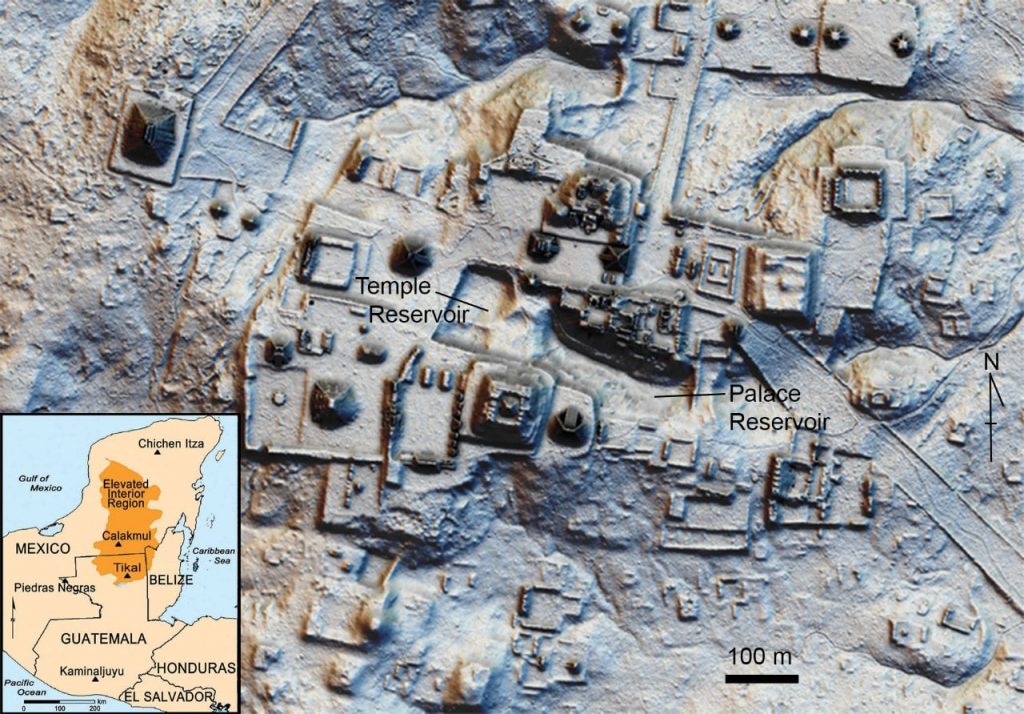
“In order to resolve these hypotheses, we captured the homologous sequences of vascular plant DNA extracted from reservoir sediments by using a targeted enrichment method involving 120 bp gene probes. Our sample covers the pre-Tikal occupation and The time after neutralization (1000 BC to 900 AD). The results show that during the Maya occupation, the banks of the ancient reservoir were mainly native tropical forest vegetation, rather than domesticated species.” Researchers led by ethnobotanist and professor of biology David L. Lentz said and wrote.
Were these wild areas the equivalent of a park?
“I think they were. I don’t know how public they would have been,” Lentz said. “This was a sacred area of the city surrounded by temples and palaces. I don’t know if the commoners would have been that welcome.”
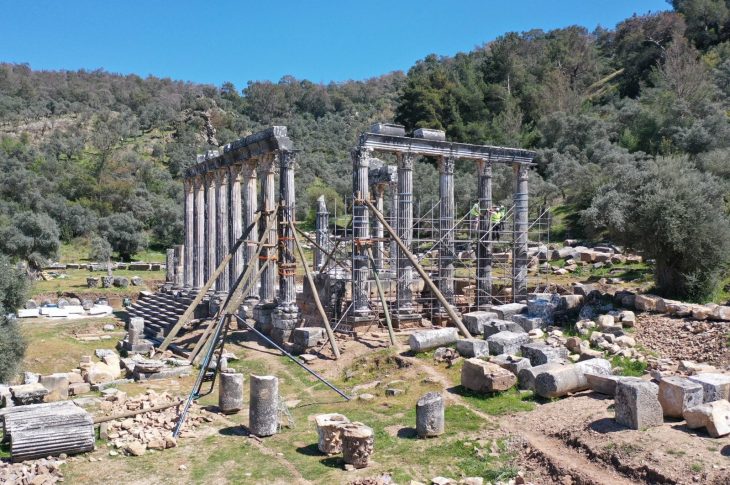
Tikal was a thriving center of Mesoamerican power, religion, and trade in what is now northern Guatemala, reaching its zenith more than 1,200 years ago. The archaeological and cultural site is now a beautiful national park surrounded by primary rainforest.
However, the region would have looked very different over 1,000 years ago. Instead of rainforest, the city center would have been encircled by residences and farm plots of maize, beans, and squash, enough to feed 60,000 or more people. Tikal had a larger population than Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Atlantic City, New Jersey, or Pensacola, Florida at its peak.
Given the known and widespread deforestation that happened around Tikal throughout its rise and collapse, the existence of an undamaged forest in the city would have been notable, according to Nicholas Dunning, a UC geography professor, and research co-author.
“It would not have been much of a park — maybe 50 meters by 50 meters,” Dunning said. “But it would have been in vivid contrast to the surrounding area of the city’s central precinct, which was essentially entirely paved with plaster with many of the buildings colored red.”
The reservoirs would have held significance beyond their value as an important source of water, he said.
“Given that the Maya were a forest culture whose cosmology included many forest elements (for example, certain sacred trees that held up the sky) having a sacred grove adjacent to the sacred spring and pool at the heart of the city was an extremely potent symbol — kind of like parts of the cosmos in miniature,” Dunning said. “On the other hand, ancient Maya cities as a whole were very green.”

Tikal put today’s urban gardens to shame.
“Away from the central precinct of Tikal, most of the land was either managed trees or crops,” Dunning said. “Just about every household complex had significant gardens. A great deal of the food consumed by the residents of Maya cities was probably grown within the city itself or its immediate hinterland. Nothing much like a modern Western city.”
Researchers previously knew about the crops and wild plants that flourished in ancient Tikal by examining old pollen or charcoal, according to Lentz. UC used next-generation DNA sequencing for their research, which can identify plants and animals using even tiny strands of DNA.
With the help of Rapid Genomics in Florida, scientists from the University of California developed a novel probe to select plant DNA in sediment samples. They managed to amplify small strands of DNA from chloroplasts, plant structures where photosynthesis takes place. Then, scientists could match ancient Tikal samples with the DNA of known plant species in a similar way that they amplify ribosomal DNA to identify bacterial species.
Microbiologists Alison Weiss, a professor in UC’s College of Medicine, and Trinity Hamilton, now with the University of Minnesota, took up the task of analyzing ancient microbial DNA from the reservoir’s sediment samples. “The DNA is ancient so it tends to be degraded with short little sequences. The analysis was quite challenging because we were the first to do this. Bacterial ribosomal DNA has a database. There was no database for this. We had to take sequences one by one and search the general database to find the best match,” said the researchers.
A significant portion of the project was a shot in the dark, so as to speak. To get a picture of the vegetation surrounding Tikal’s reservoirs was a huge step forward, and this model of environmental DNA analysis is extremely promising. In fact, moving forward, they hope to be able to apply this science to other Maya city sites in the future.
Source: CINCINNATI UNIVERSITY
















