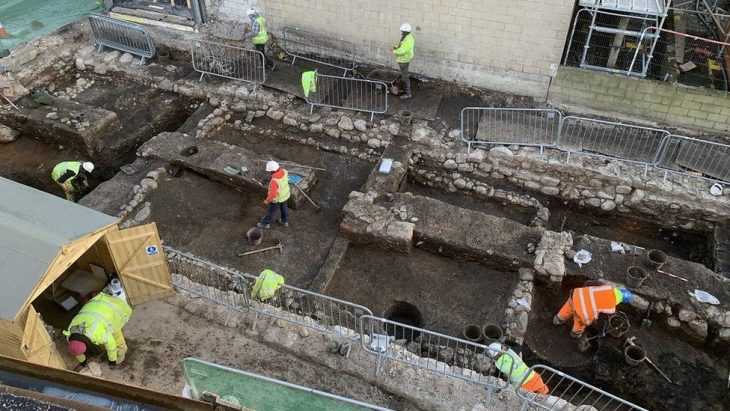
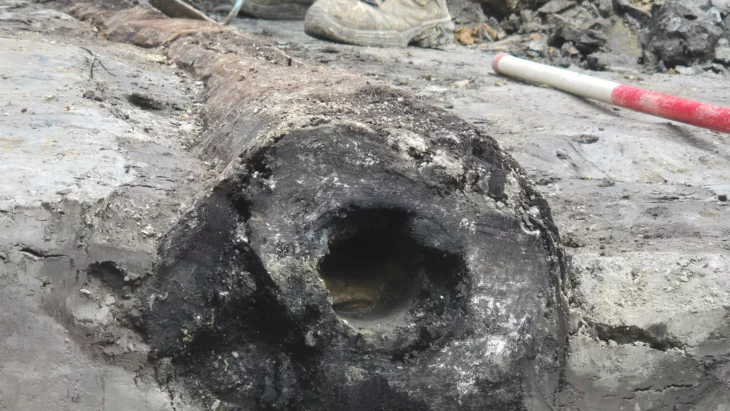
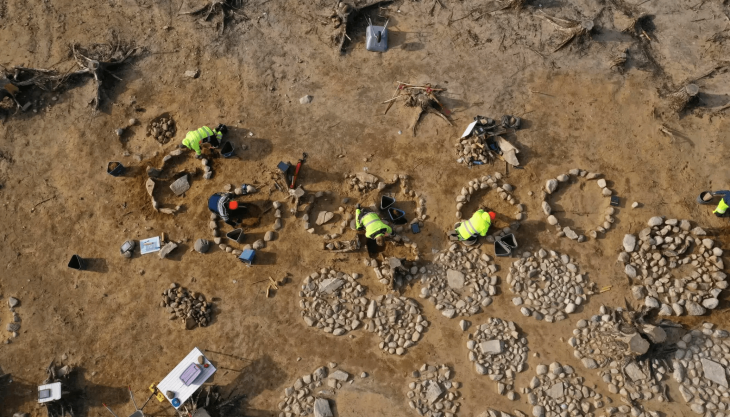
While building a road in the village of Vinjeøra in central Norway, three ancient mortuary houses dating back to the Iron and Viking Ages were discovered. What’s more, not a single person was buried in them!
Mortuary houses date between 500 and 950 CE and these discoveries, described in their recent work published in Medieval Archaeology, reveal a fascinating glimpse into the mysterious funerary rituals of the past.
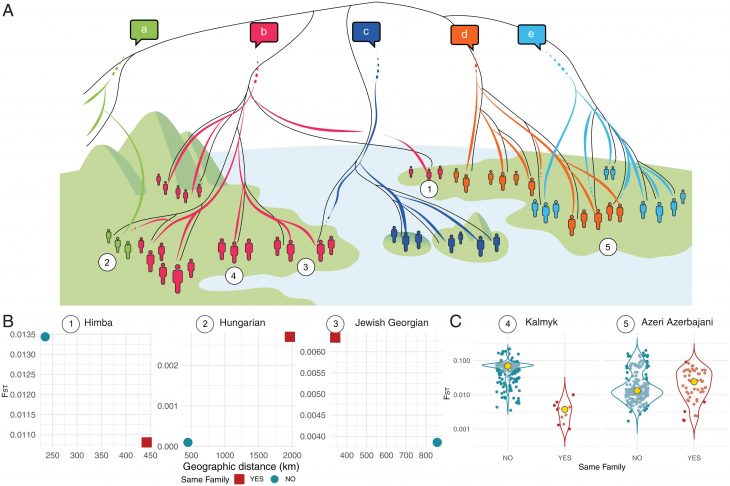
The analysis of the 3 Vinjeøra mortuary houses is published in the journal Medieval Archaeology. Recent work published by Dr. Raymond Sauvage and Dr. Richard Macphail describes the excavation and interpretation of three Iron- and Viking-Age mortuary houses in central Norway, Skeiet, in the village of Vinjeøra.
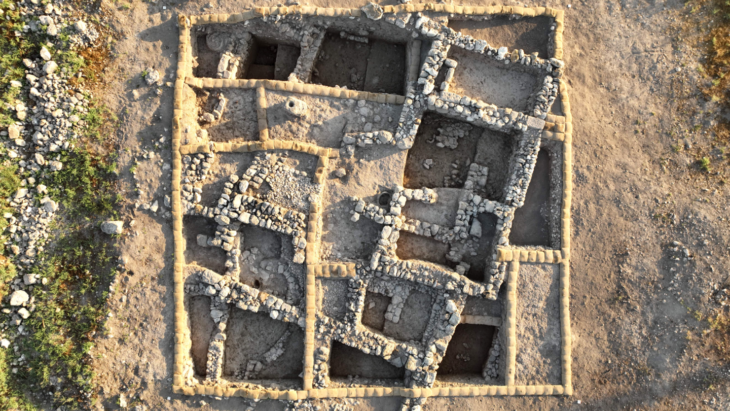
Discovered in a test pit excavated in 1996, the pre-Christian cemetery was verified by excavation. However, three mortuary houses were unexpectedly discovered by excavators more recently, next to the leveled burial mounds.
Mortuary houses are small, house-like structures, often found within ancient cemeteries. They might contain graves, tombs, or perhaps even the cremated remains of the deceased. These houses weren’t just for the dead; they were places where the living could visit, leave offerings, and perhaps even worship their ancestors.
Excavations revealed the mortuary houses are unique among the 12 others in Norway and 1 in Sweden which have previously been identified.
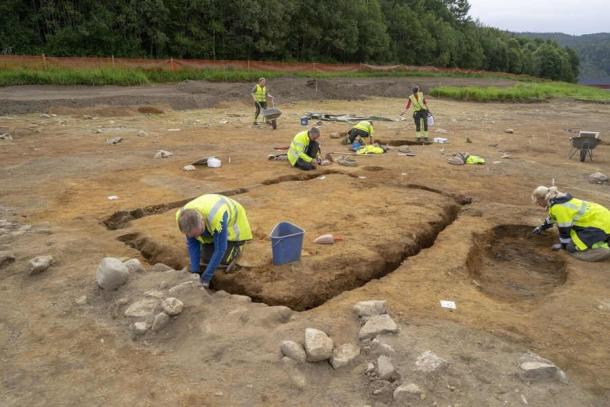

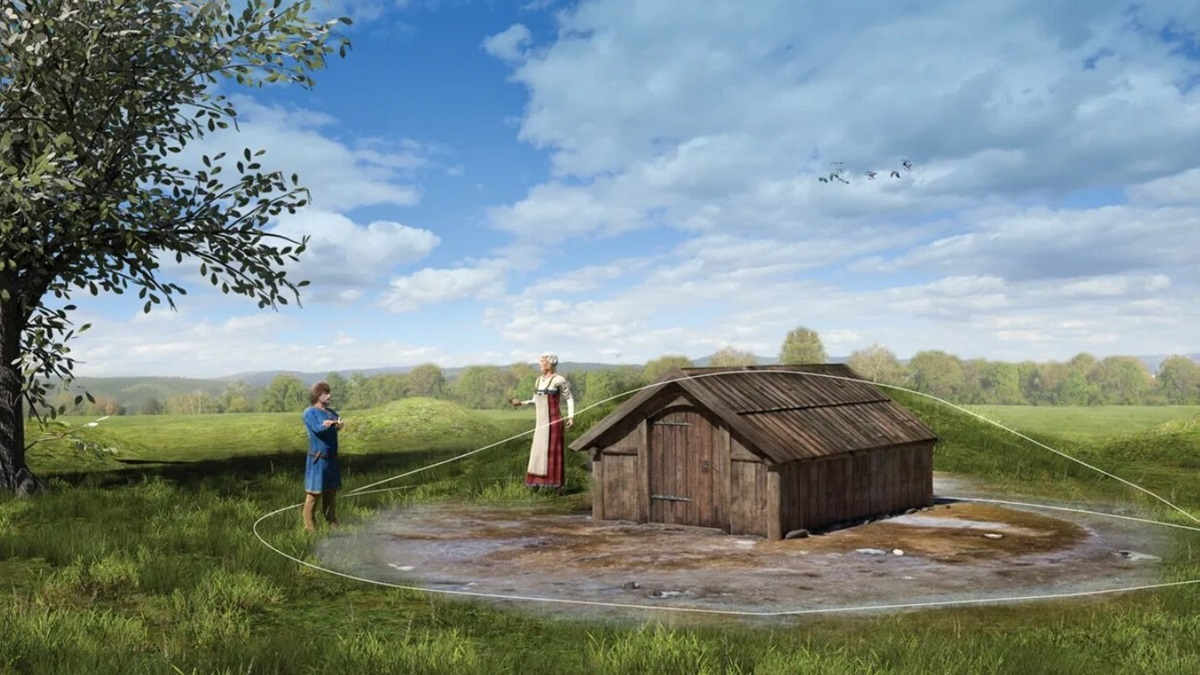
These mortuary houses had no permanent occupants, meaning that no evidence of a buried person was discovered within, despite being constructed for the dead. These homes had doors and entrances as if beckoning the living to enter. Visitors had to crouch to enter due to the low entrances, which made entering these cramped, dim areas feel intimate and almost reverent.
“I think that the most surprising thing was that we did not find any evidence of a permanent tomb or a buried person inside the houses,” says author Raymond Sauvage, an archaeologist from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. “Also, the fact that they had doors and entrances that may have led into the mortuary house and burial mound was something I had not thought of prior to the analysis.”
The presence of entrances suggests that the mortuary houses were always open for living people to revisit. Trampled soil at the entrances confirms this.
The earliest of the three dates back to around 450–600 AD, during the Iron Age. The most common method of interring the dead at this time was cremation. Built between 600 and 800, the second structure would have come around the time that burials were becoming more common. The third mortuary house was erected 800–950 CE when the local people had shifted completely from cremation to burying their dead.
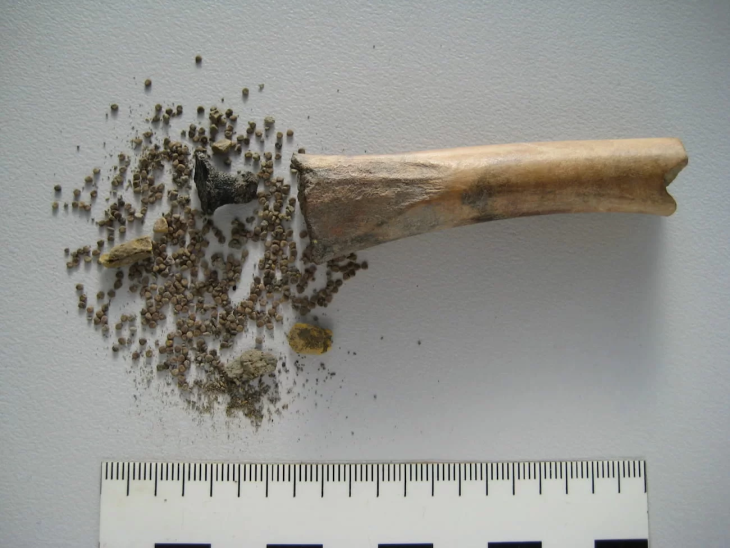
For almost 100–200 years each, these mortuary houses remained an essential component of the funerary rites despite changes in the manner in which the deceased were interred. Even though no graves were discovered within, the archaeologists did find some interesting artifacts, including nails, arrowheads, and pieces of bone.
The mortuary houses, built to resemble contemporary dwellings, might reflect the belief that the dead continued to “live” in their burial mounds.
The fact that no actual burials have taken place in these houses, however, suggests another possibility: maybe they functioned as the dead’s temporary resting places while their bodies were being prepared for a more permanent burial, akin to the Norse burial ritual that the traveler Ibn Fadlan described in the tenth century.
The mortuary houses of Norway are still very enigmatic and more research will be needed to truly understand their function.
https://doi.org/10.1080/00766097.2024.2347753
Cover Image: Artist’s interpretation of one of the Skeiet mortuary houses. The burial mound is indicated by the conjectured lines. Credit: Sauvage and Macphail 2024; illustration by Arkikon, NTNU University Museum