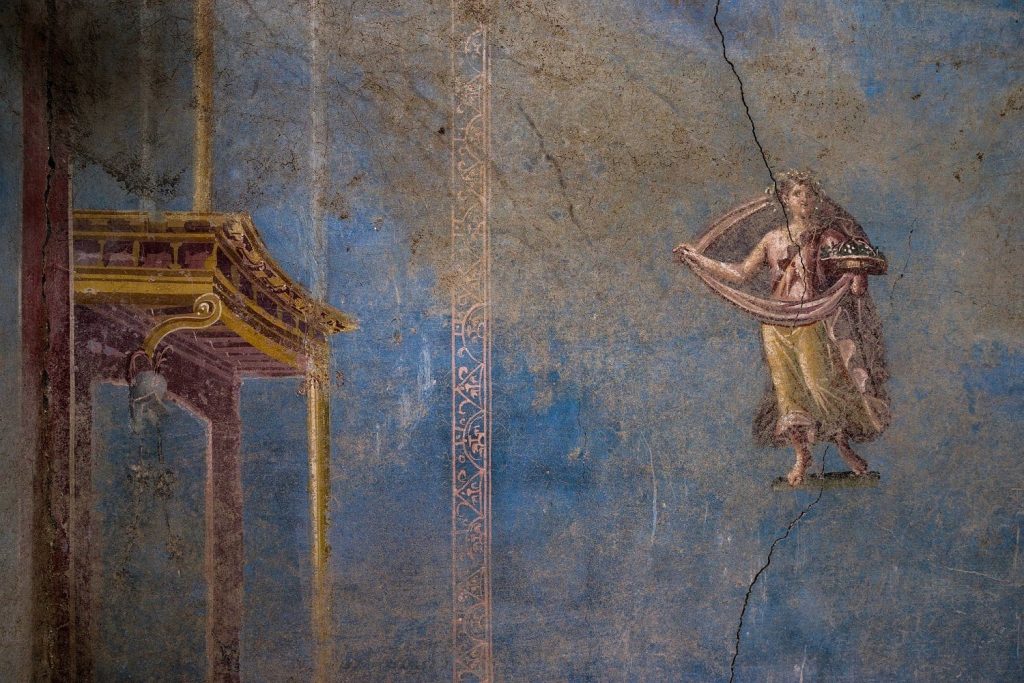
Archaeologists digging away at ash covering the ancient city of Pompeii have uncovered a room with walls frescoed in an unusual and sublime sky blue.
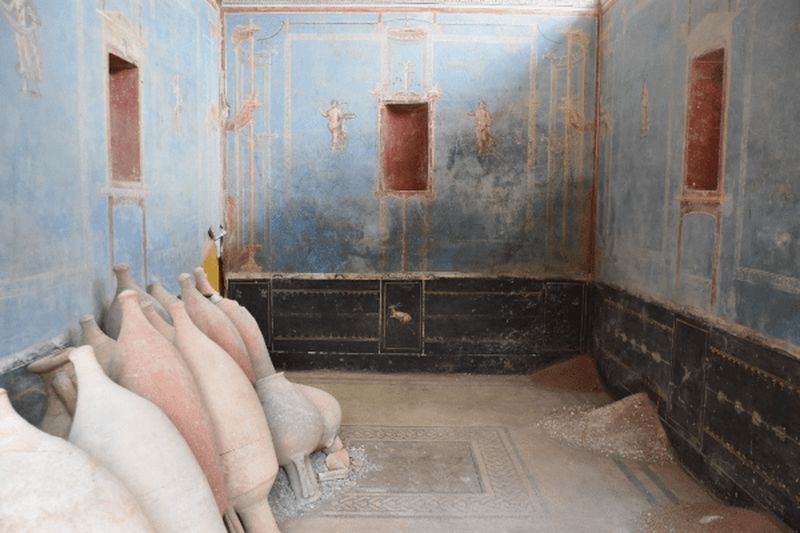
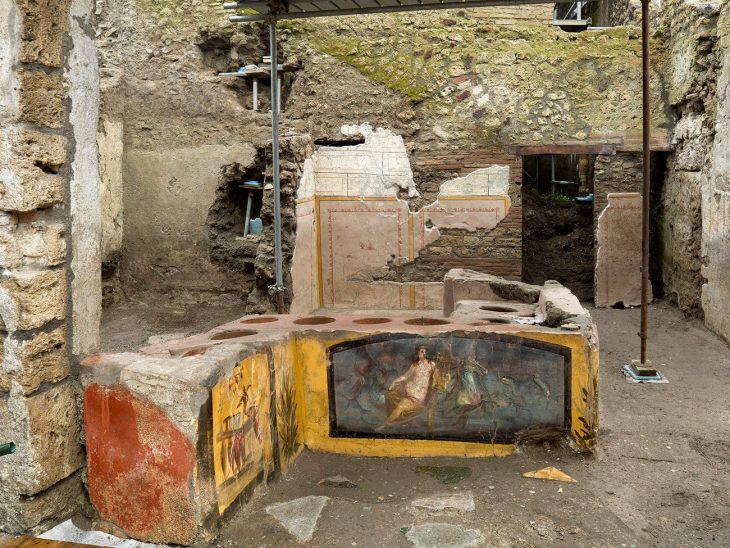
In Pompeii’s Regio IX neighborhood, the area known as Insula 10 is still being excavated by archaeologists. Archaeologists are still excavating this area, and a recent discovery includes a gorgeous sky-blue sacrarium, a place for ritual and the preservation of holy artifacts—brilliant red lines the niches, where statues and other devotional iconography likely stood.
The 8-square-meter room is decorated in the Fourth Style (c. 60–79 C.E.), an intricate aesthetic that was less ornamental than its predecessor but took a more narrative and architectural approach. Against the azure background, female figures pose gracefully, their garments blowing in the breeze. Four of the women represent the seasons. Two are allegories of agriculture and pastoralism, the former indicated by a plow, the latter by the pedum, a short staff used by shepherds.

When Mount Vesuvius erupted, researchers think the room was being used for storage as part of a larger renovation. In addition to building supplies and a stack of empty oyster shells that were probably intended to be ground and added to plaster, the team discovered 15 amphorae, two jugs, and two lamps in the area.
Pompeiians typically reserved blue for the most sacred of spaces, and neither the color nor the accompanying frescoes appear in a discovery nearby. Therefore, the team suggested that the room was used for pagan rituals and storing sacred objects as the blue color has only been found in places of great importance.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
As noted by the History Blog, archaeologists also excavated the servants’ quarters of the villa of Civita Giuliana, a stark contrast to the sacrarium. In the servants’ quarters of the villa of Civita Giuliana, another exceptional discovery of work tools and supplies shows how the other half lived.
There are no glorious frescoes in this small space. The room contained a bed, work tools, a basket, rope, and wooden planks, the shapes of which were preserved by volcanic matter, and researchers were able to recreate their forms in plaster.
Archaeologists explain: “As the ash solidified, forming a very solid layer known as “cinerite,” organic material such as human bodies, animals, or wooden objects decayed, leaving a void in the ground. These voids can be filled with plaster during excavation, to regain the original shape from the “negative” impression. A technique that led to extraordinary results in the villa of Civita Giuliana, from the casts of two victims and a horse to those of the modest beds in the servile quarter.”
Cover Photo: Archaeological Park of Pompeii