Two fortress settlements and two new open-air temples were discovered during a survey in Tunceli province in the Eastern Anatolia Region of Türkiye.
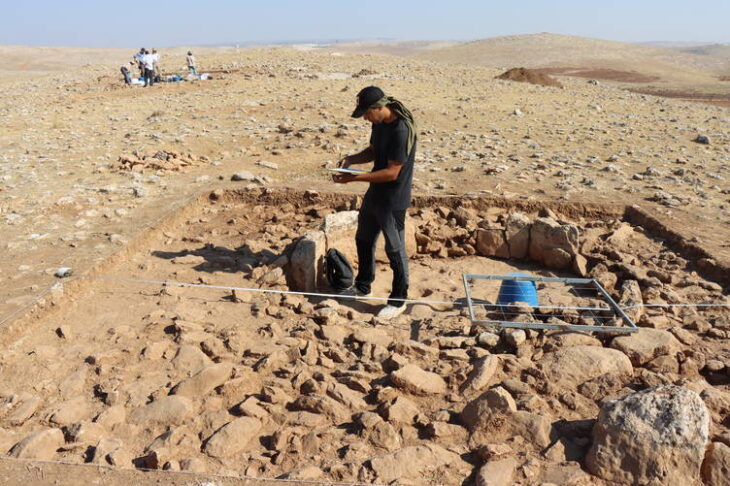
The discovery was made within the scope of the “Iron Age and Hellenistic Age Tunceli Survey” project, which has been carried out within the borders of Tunceli province since 2016.
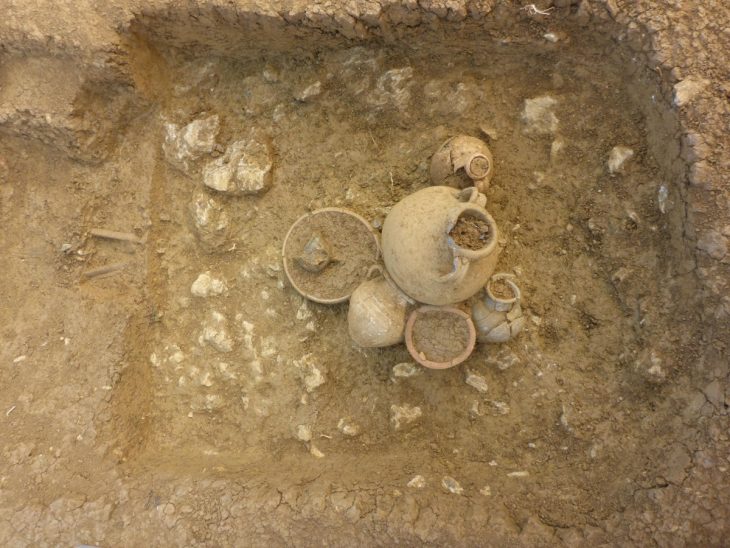
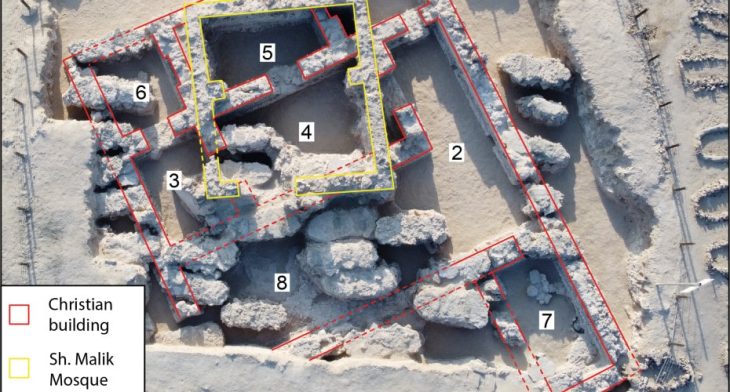
Two fortress settlements and two new open-air temples discovered during the survey were published in the 61st issue of the Pamukkale University Social Sciences Institute Journal.
Associate Professor Serkan Erdoğan noted that one of the newly discovered castle settlements is located in the easternmost part of today’s Tunceli provincial borders and the other is almost in the westernmost part of these borders. “The two fortress settlements named Lower Harik (Doluca) in the southeastern Anatolian region host a new type of temple that we have not known before,” he said.
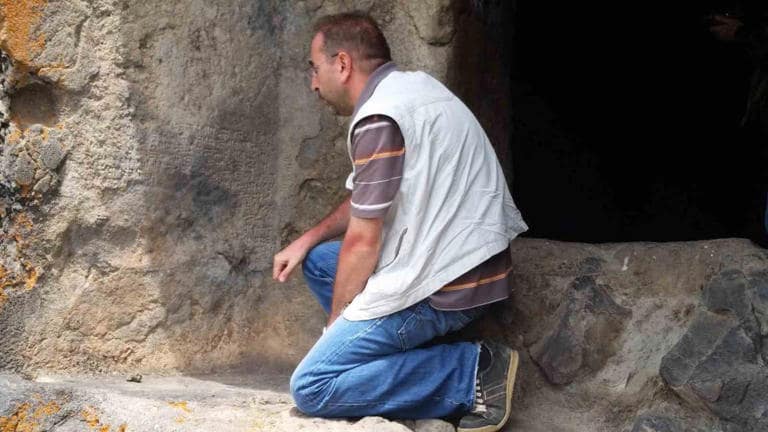

Associate Professor Serkan Erdoğan noted that one of the newly discovered castle settlements is located in the easternmost part of today’s Tunceli provincial borders and the other is almost in the westernmost part of these borders.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“The two fortress settlements, one named Masumu-Pak fortress located in the Hozat-Çemişgezek -Ovacık triangle and the other named Aşağı Harik (Doluca), located on the banks of the Peri Çayı (Peri stream) east of Nazımiye in the southeastern Anatolian region host a new type of temple that we have not known before,” he stated.
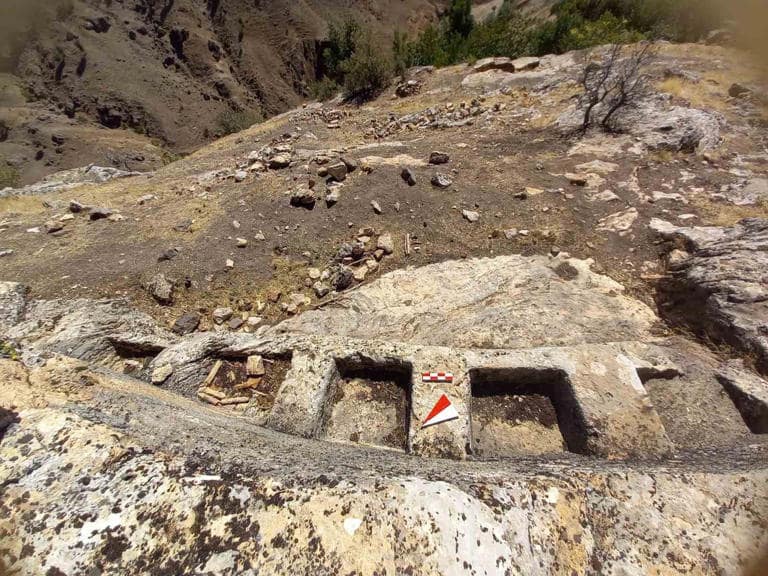

Researchers noted that While the Iron Age traces are intense in Aşağı Doluca Fortress (Lower Doluca Fortress), the Iron Age and Medieval structures are evident in the Masumu-Pak Fortress.
It has been established that the buildings regarded as open-air temples in the settlements of Aşağı Doluca Fortress and Masumu-Pak Fortress share similar form and construction characteristics.
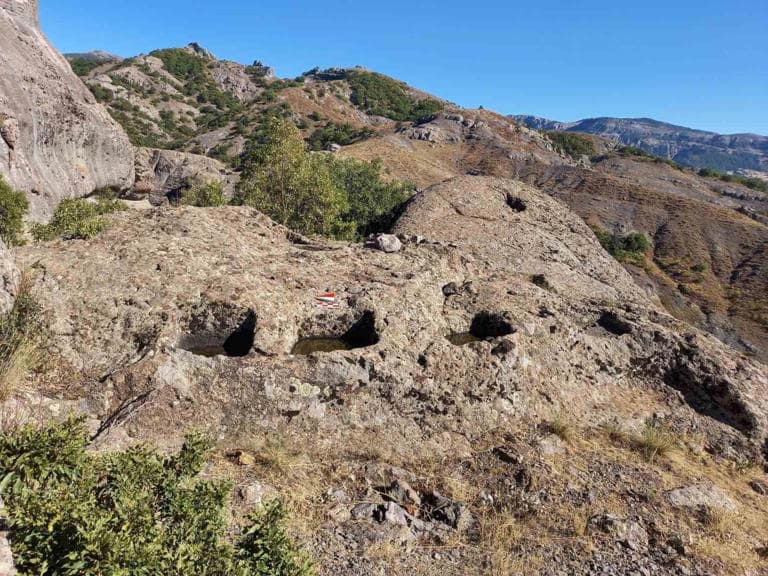
The primary similarity between the outdoor prayer spaces in the two communities is the architectural feature that resembles an altar etched into the rocks, with a platform in front of it.
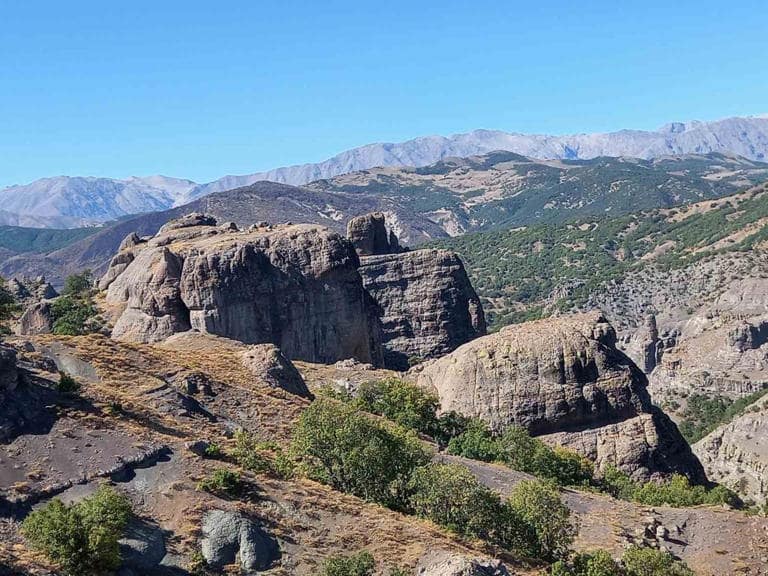

Researchers said that the temples showed that they were built in a period of 7 centuries BC (9-8 centuries BC) when Urartian dominated the region.
The question of whether these temples, which have local characteristics, were built for local gods/cults or the worship of the known great gods of a certain period, remains unclear.
Assoc. Dr. Serkan Erdoğan said, “The Lower Harik Castle and Temple, located in today’s castle hamlet settlement, is also known as a sacred place called Moro Sur (Red Snake). “Today, those who still want to find healing continue to call out by saying “Ya Moro Sur, Tu esta (You exist, Moro Sur),” he said.
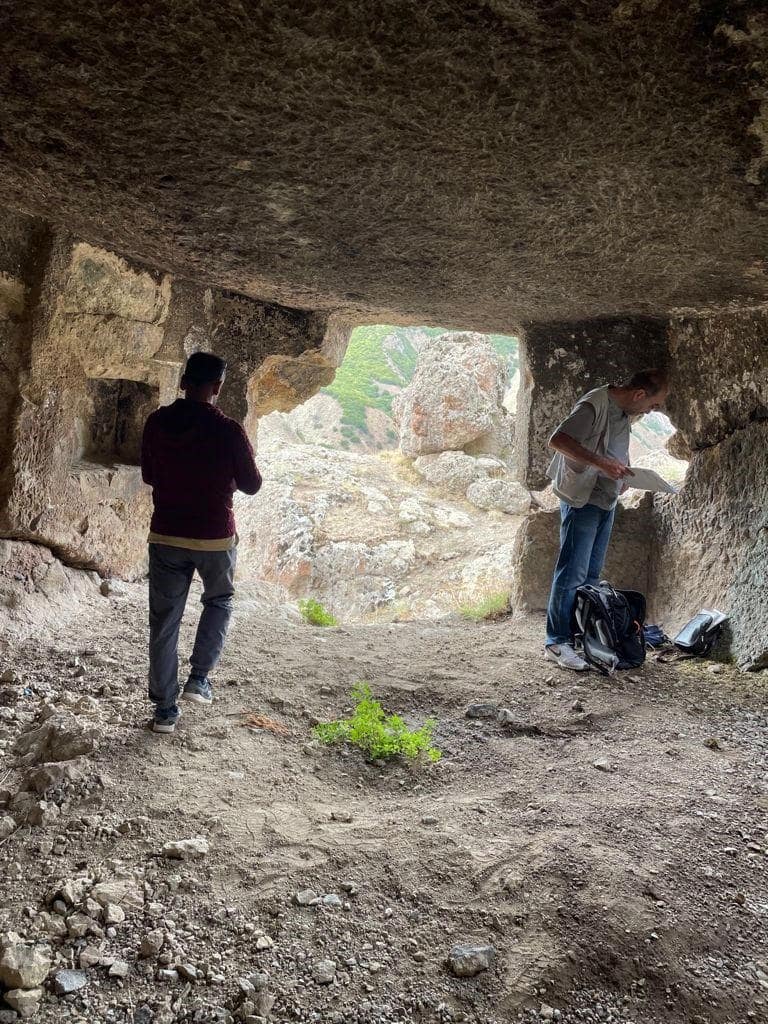

Emphasizing that the snake motif is affirmed in geography, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Erdoğan stated that the Moresur myth has an original and authentic structure and that the history of this area as a sacred place dates back to ancient times.