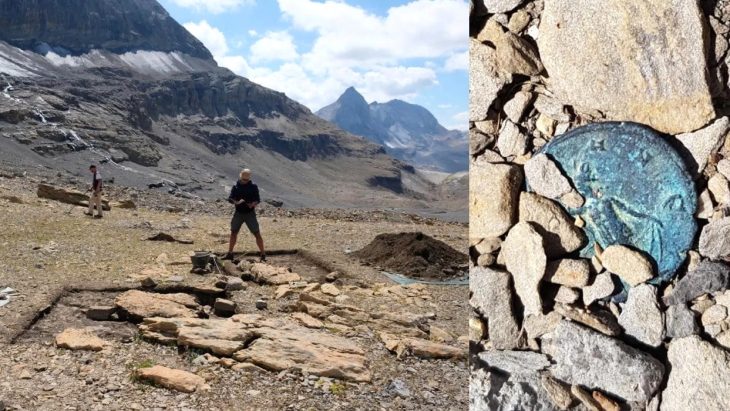
One of Europe’s most important Roman archeological sites is the Fort of Vindolanda, one of the earliest Roman garrisons built by the Roman army in England. It was a Roman auxiliary near Hadrian’s Wall that guarded a major highway called the Stanegate.
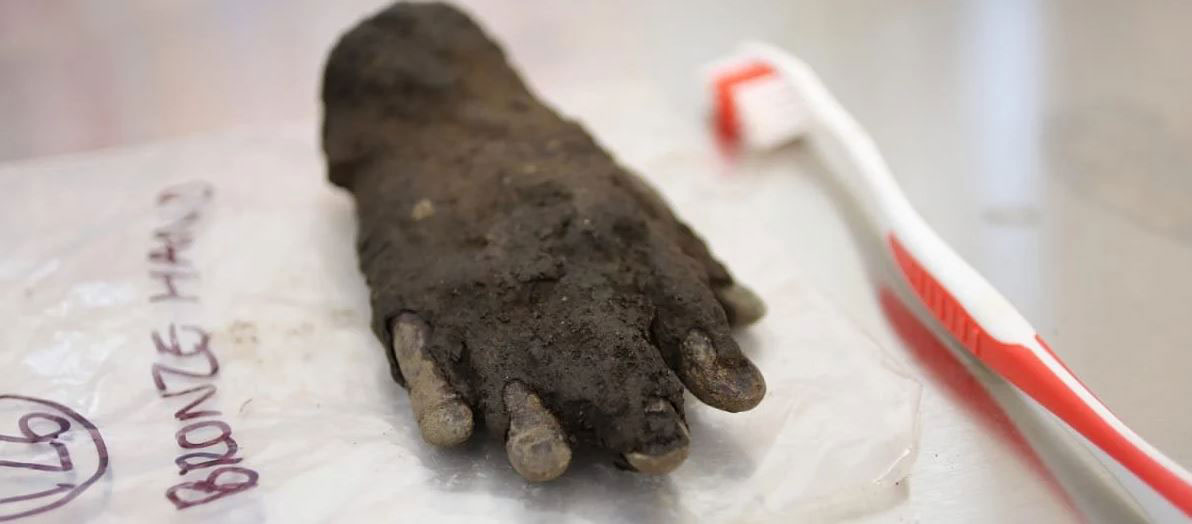
Only a few weeks had passed since the start of the excavation season at Vindolanda when a remarkable artifact was discovered 1.5 meters below present-day ground level in the uppermost layers of the northern Severan ditch fill.
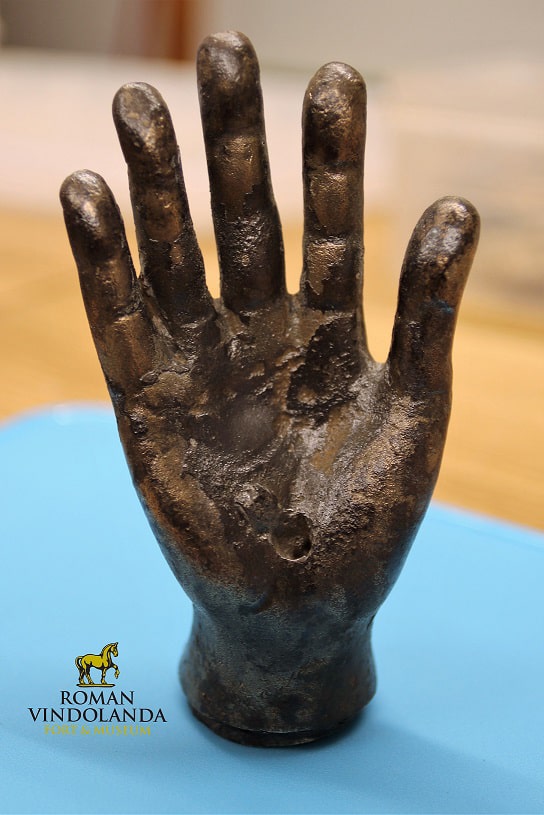
A small, child-sized, and eerily life-like bronze hand had been discarded in the ditch. Close inspection of the artifact after conservation at Vindolanda revealed that the 10cm hand originally had an attachment, now missing, inserted into the palm.
The hand is very well crafted, especially on the palm-facing side, indicating that its purpose was to profile the object that it once held. The base of the hand is socketed and would have been originally fixed to a pole.
The hand was uncovered some metres beyond a temple dedicated to Jupiter Dolichenus, tucked into the northern wall of the third-century fort at Vindolanda which was excavated in 2009.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The newly discovered hand most likely served a cult function and was possibly associated with Jupiter Dolichenus, a god and mystery cult that was popular in the Roman Empire from the early second to mid-third centuries AD.

Similar votive hand specimens have been discovered in or near other Jupiter Dolichenus temples, though most are slightly larger than the Vindolanda specimen and some are fortunate enough to still have inscriptions mentioning the god.
Jupiter Dolichenus is depicted holding a thunderbolt in his hand with an upraised arm signifying his destructive power, the open votive hand symbolizes the protection and well-being that he could also bring.
The hand is now on public display in the same gallery as the altars dedicated to Jupiter Dolichenus at the Vindolanda Museum.
Between AD 85 and 370, nine timber or stone forts were built at Vindolanda, resulting in one of the most complex archaeological sites in Britain and a unique cultural legacy of frontier life.
Today, Vindolanda is an ongoing active archaeological site, with previous excavations uncovering thousands of perfectly preserved shoes, textiles, wooden objects, and the Vindolanda tablets (the oldest surviving documents in Britain that date from the 1st and 2nd century AD).
Cover Photo: Vindolanda Charitable Trust