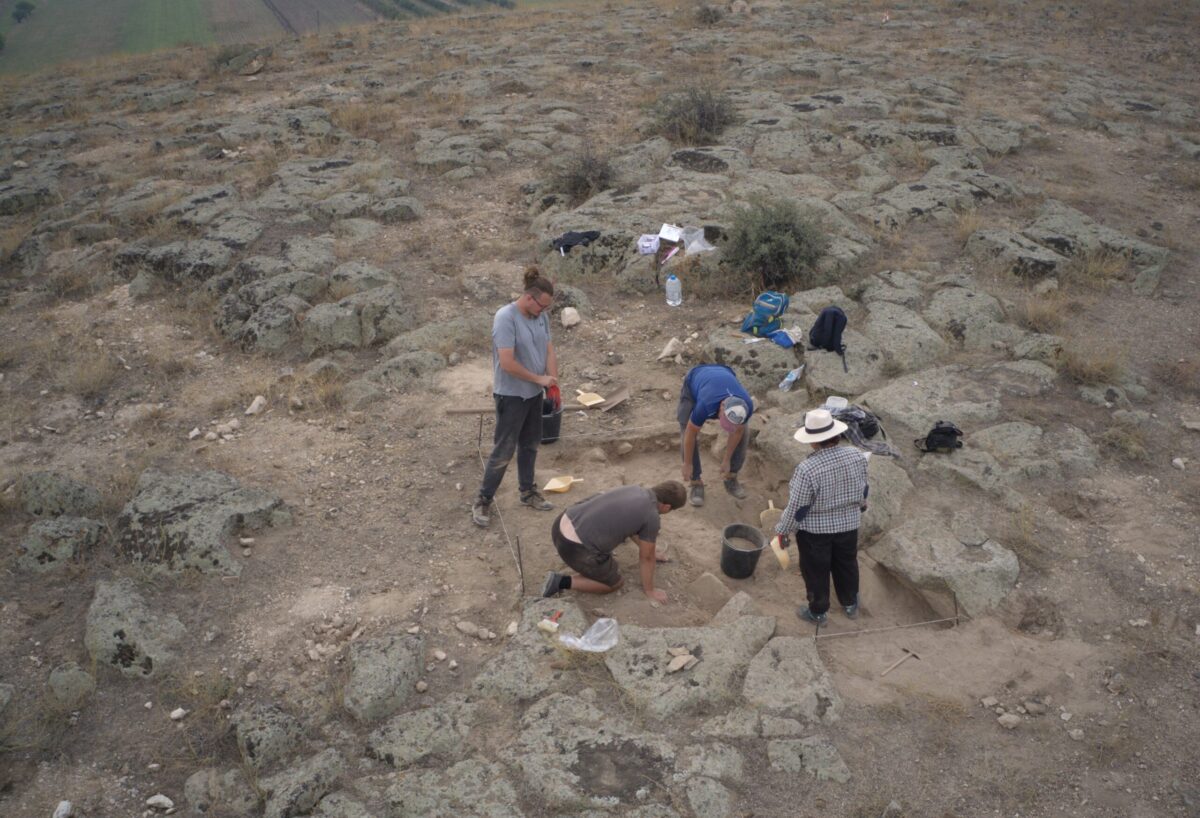
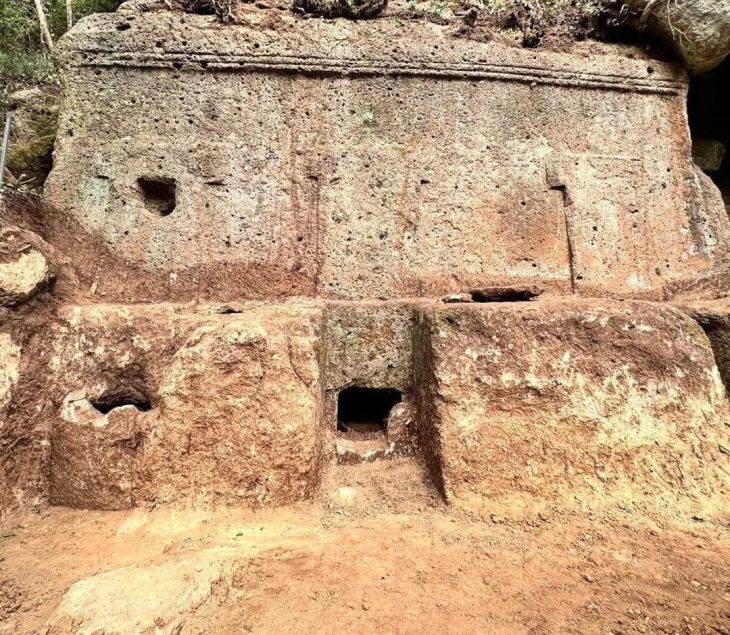
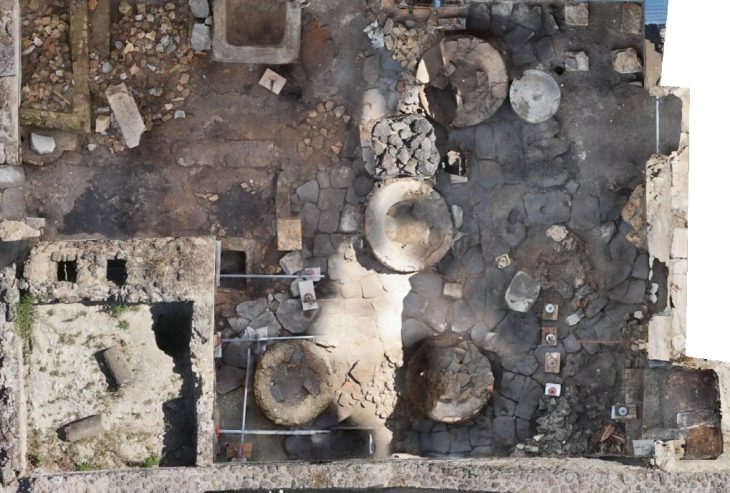
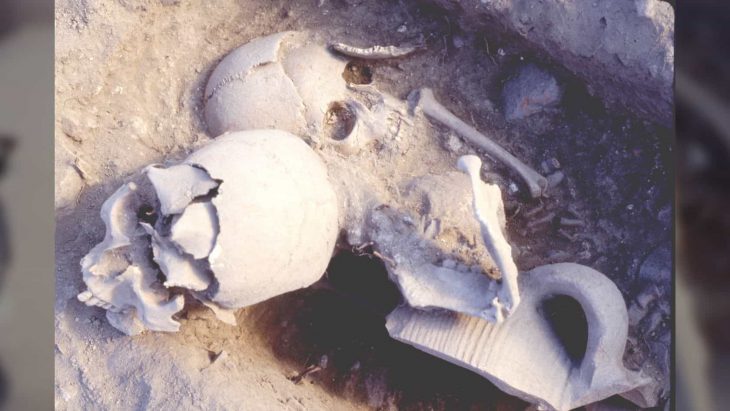
An Armenian-Polish archaeological team has uncovered remnants of 6th-century BC houses, a cremation cemetery, and signs of a significant earthquake at the ancient site of Davti Blur in Armenia.
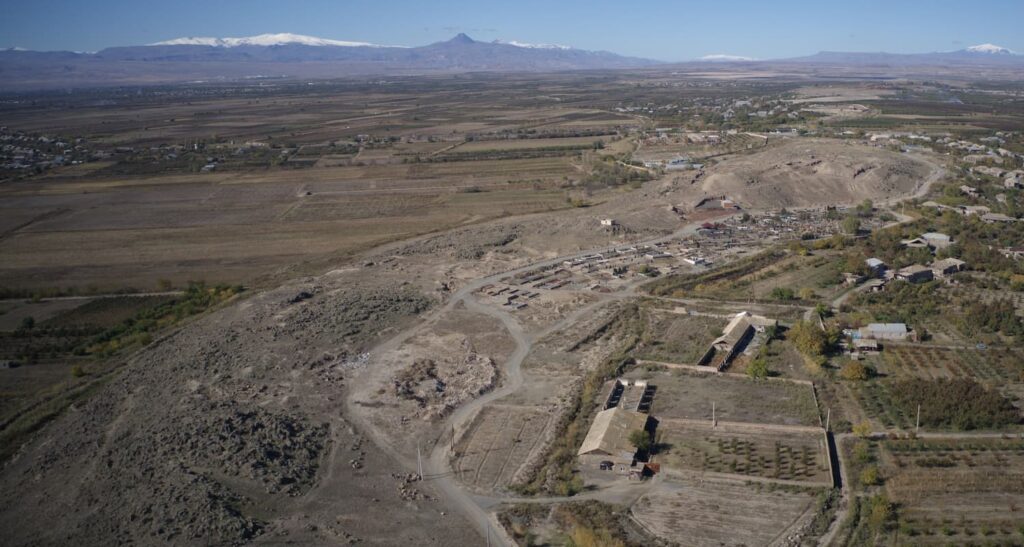
Excavations at Davti Blur, located in Nor Armavir, resumed in October 2024 after a long hiatus as part of a new Armenian-Polish research project. The initiative is led by Dr. Mateusz Iskra from the Mediterranean Archaeology Center at the University of Warsaw and Hasmik Simonyan from the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnography of the National Academy of Sciences of Armenia, along with the Cultural Heritage Protection and Museum Reserves Service.
Translated as “David’s Hill,” this site is a testament to the historical grandeur of the Kingdom of Urartu and offers invaluable insights into the cultural and architectural legacy of a civilization that flourished in the South Caucasus millennia ago.
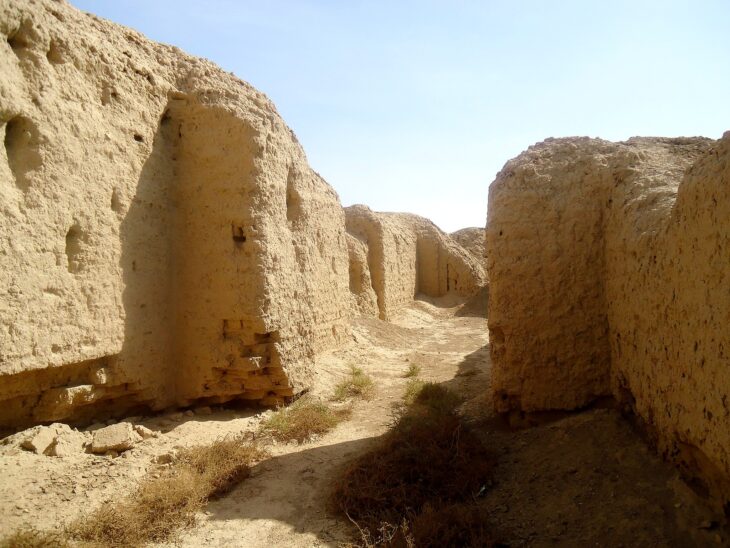
Davti Blur is part of the ancient settlement of Argisztihinili, established in 774 BC. During the 8th and 7th centuries BC, this site served as a vital administrative and economic hub of the Kingdom of Urartu. Among its remarkable structures are a well-preserved citadel and a residential district, which, according to earlier studies, housed substantial dwellings belonging to the local elite.

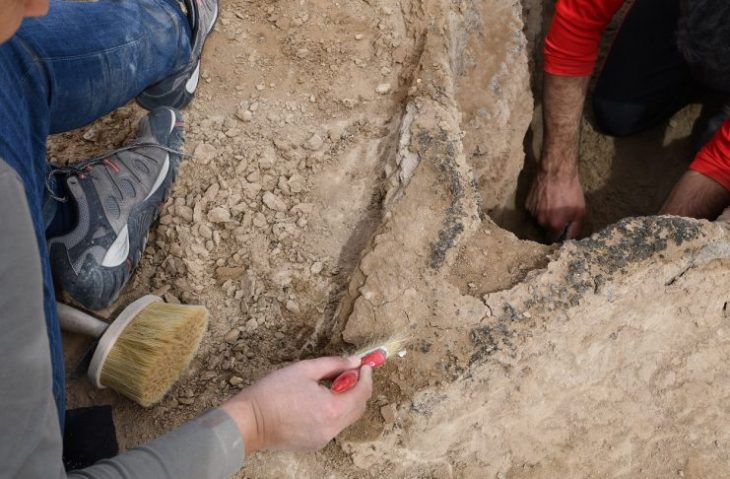
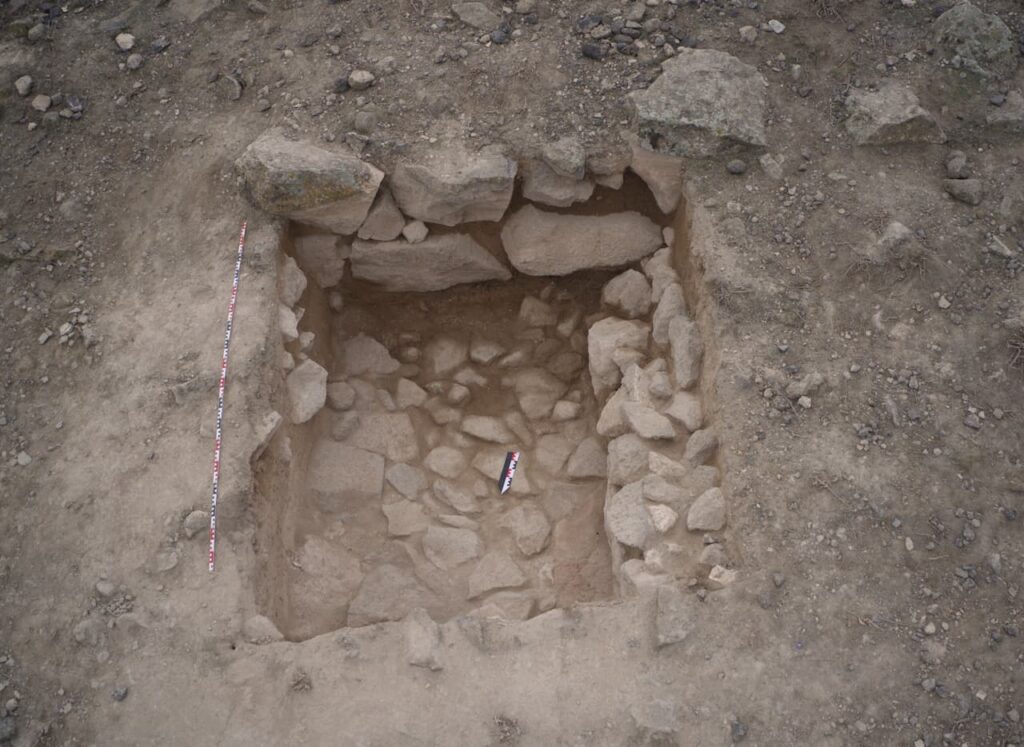
Recent excavations have unveiled remnants of houses dating back to the 6th century BC, a period marking the decline of the Kingdom of Urartu. The walls of these structures, impressively thick at nearly 1.5 meters, have been remarkably preserved. Moreover, excavations revealed fragments of floors belonging to two rooms, whose exact purposes remain undetermined.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“These were not fortification walls but rather the walls of two residential houses, which turned out to be very well preserved,” Dr. Mateusz Iskra described.
Surprisingly, the archaeologists also discovered evidence of a cremation cemetery. “The deceased were cremated, and their fragmented bones, along with parts of the funeral pyre and ornaments, were placed in urns. These urns were typically covered with a shallow dish and placed in rock niches, covered with a thin layer of soil,” Dr. Iskra detailed.
As a result, such artifacts are relatively easy to uncover, even for amateur treasure hunters. The team found evidence of illegal activity, including scattered and broken urns and smaller artifacts at the former cemetery site.

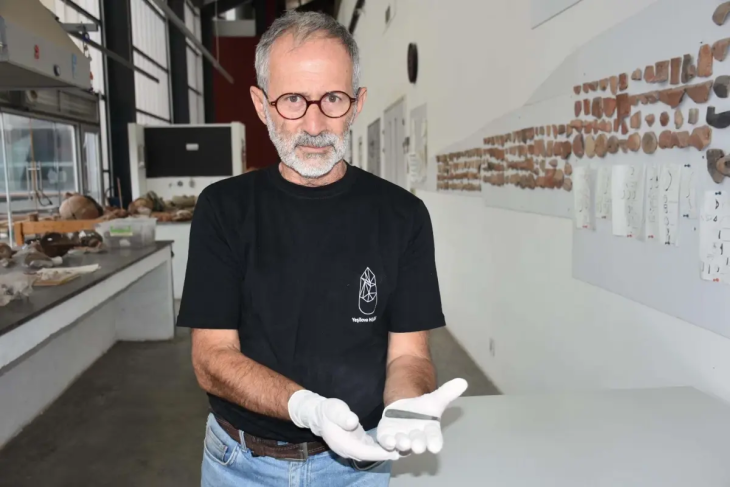
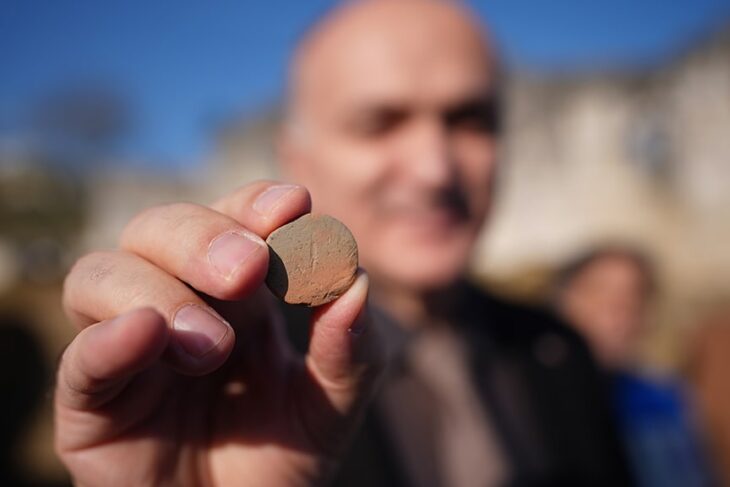
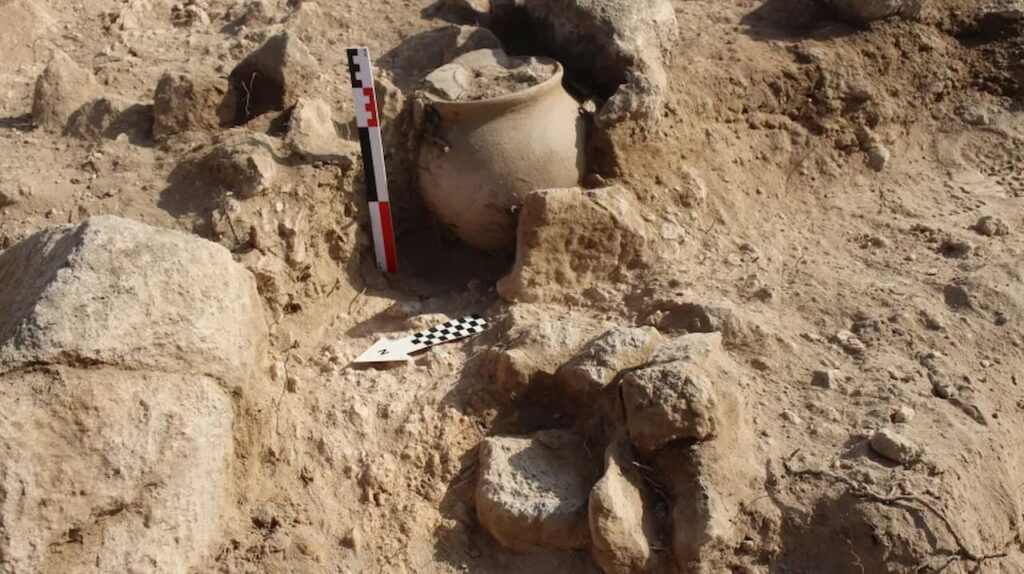
Despite the damage inflicted by looters and metal detectors, researchers successfully recovered several intact artifacts, including an urn adorned with a decorative plate, which has been preliminarily dated to the first half of the 7th century BC. Additionally, a variety of metal items associated with the clothing of the deceased were also uncovered.
“We managed to find an intact urn covered with a stamped dish. Thanks to the distinctive pottery mark, we can already date this burial to the first half of the 7th century BC,” Dr. Iskra stated.
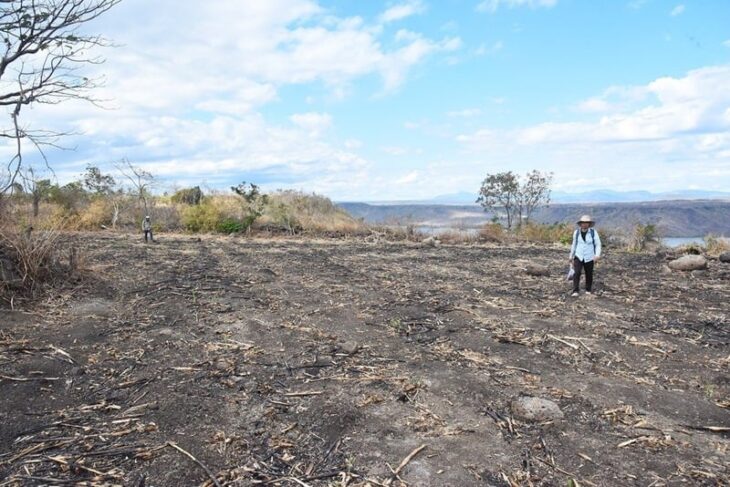
A team from the University of Warsaw’s Department of Geology, led by Professor Barbara Woronko, also worked on-site. Preliminary investigations revealed fault lines characteristic of an earthquake. Initial data suggest that this was a highly destructive and powerful event, but it is too early to determine its exact timing.

The second season of excavations is planned for May and June 2025. Hasmik Simonyan announced that the researchers aim to continue mapping the site.
Simonyan highlighted the ambitious vision of transforming Davti Blur into a vibrant archaeological reserve that welcomes tourists, complemented by educational programs designed to foster a deeper appreciation among the Armenian population for the significance of preserving their rich cultural heritage.
Cover Image Credit: Dr. Mateusz Iskra. Research at the Davti Blur site.