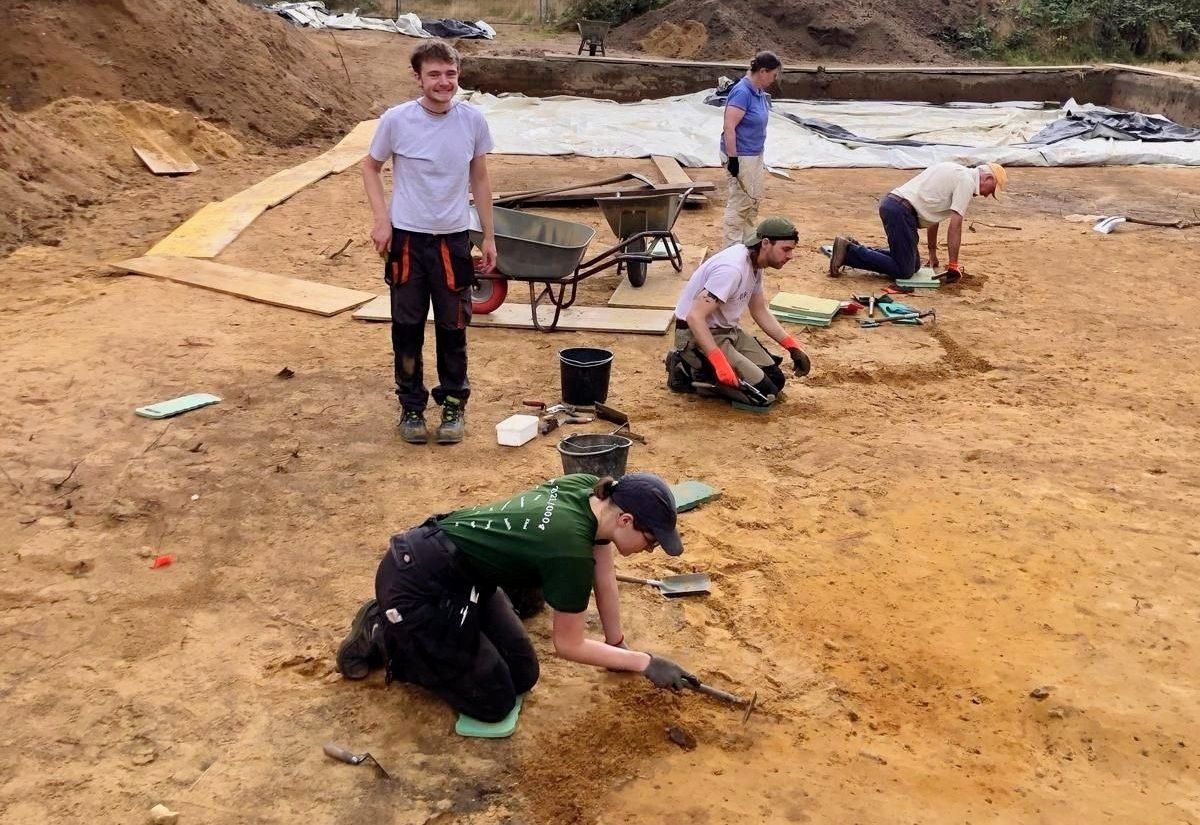
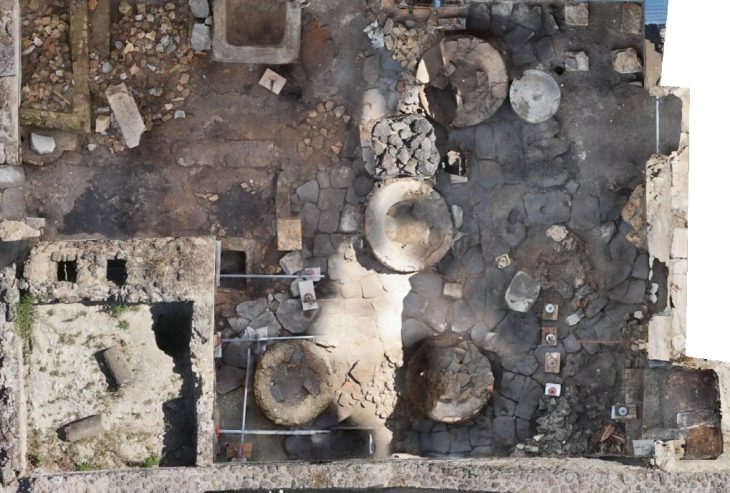
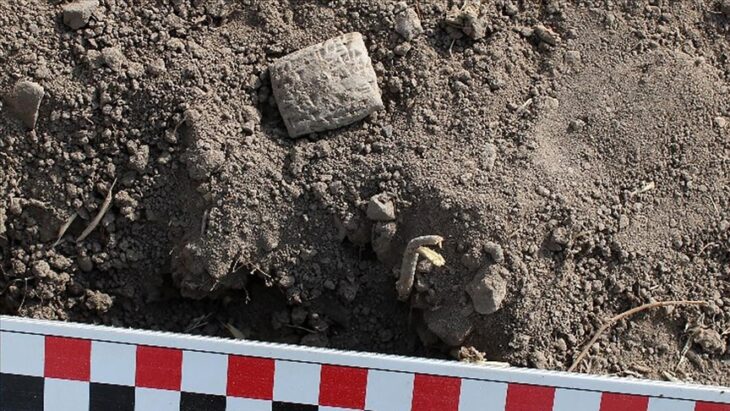
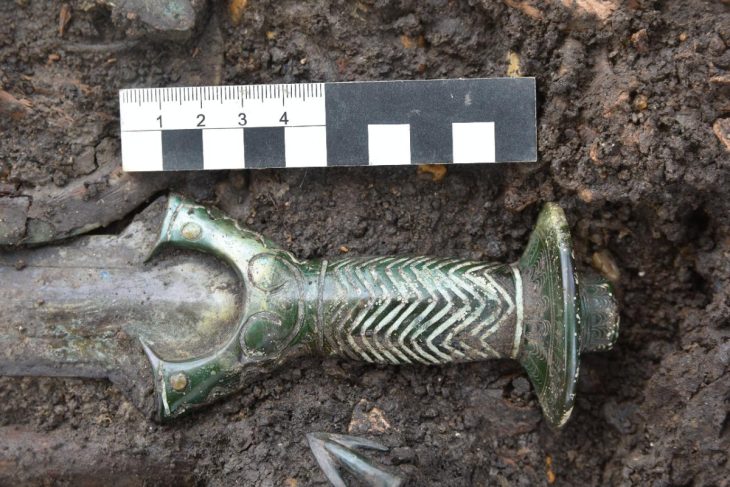
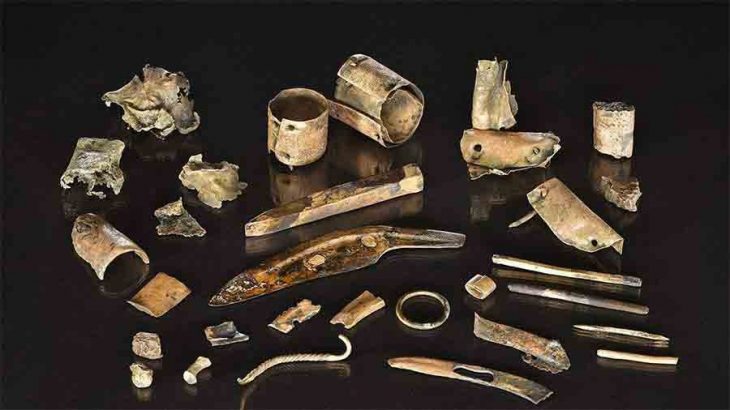
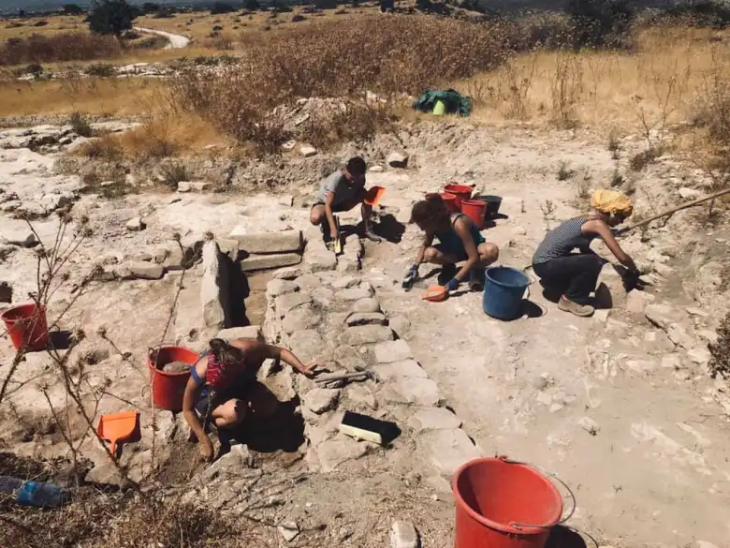
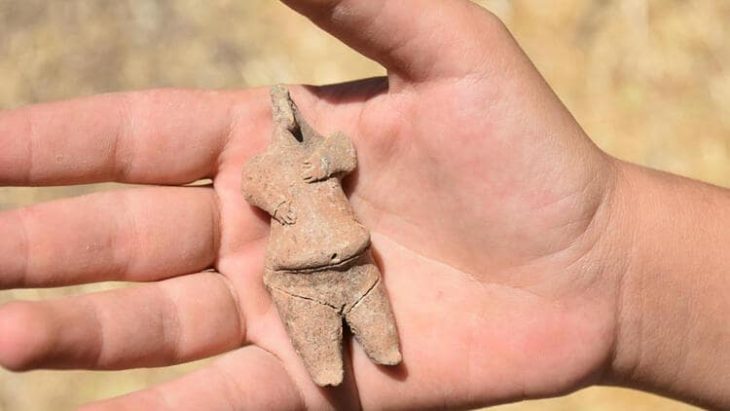
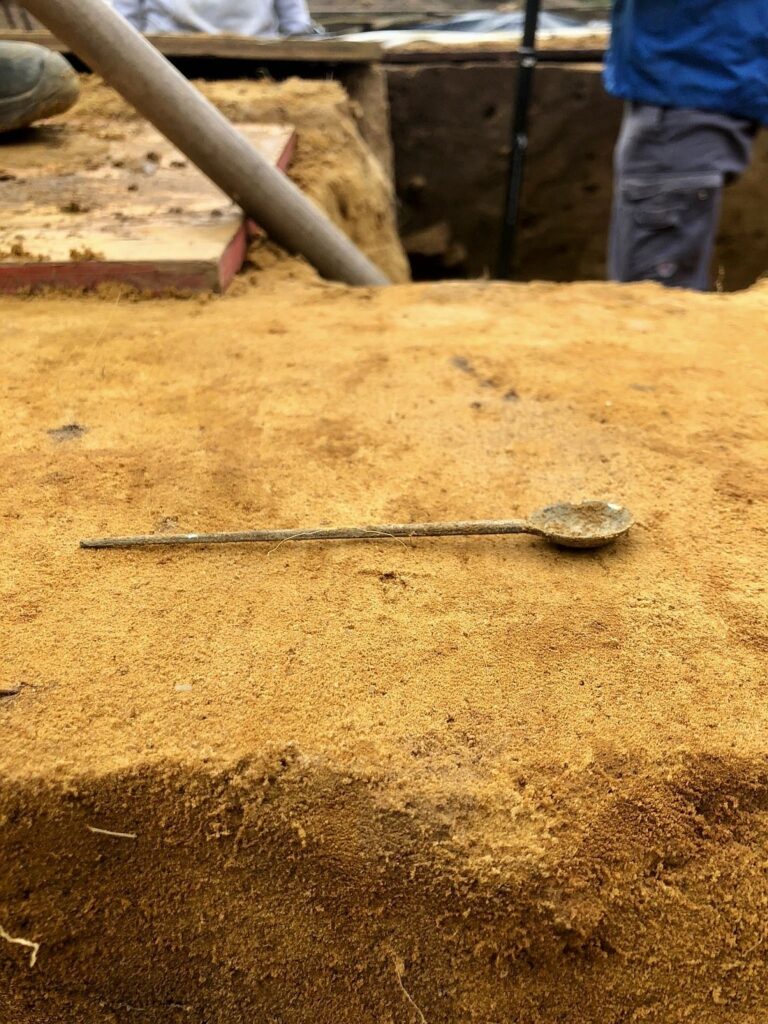
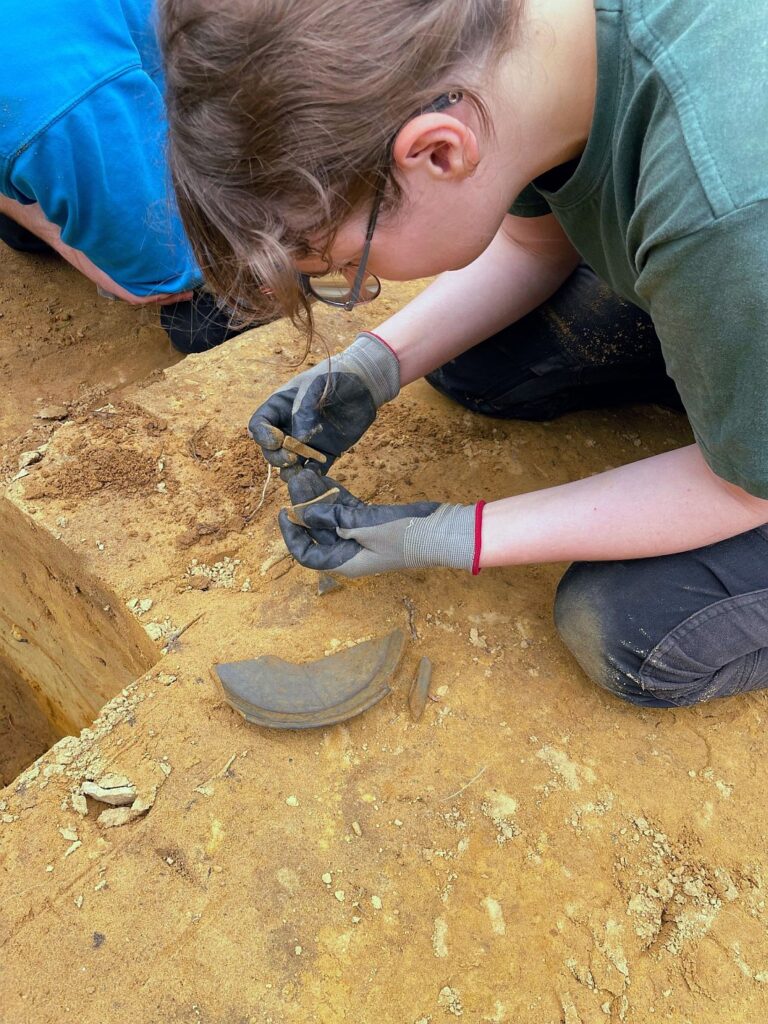
Archaeology students from the University of Cologne have made a remarkable discovery during a four-week excavation at the LWL-Römermuseum in Haltern am See. Among the unearthed finds are the remains of a Roman wine amphora, a bronze spoon, fragments of Terra Sigillata tableware, and evidence of what experts believe to be a 2,000-year-old Roman “refrigerator” (Cooling Pit).
The excavation, conducted during the students’ semester break, focused on the site of the ancient Roman military base Aliso, one of the most important Roman strongholds north of the Alps. According to Dr. Bettina Tremmel, a Roman specialist at the Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe (LWL), the newly uncovered structures could be crucial in expanding the museum’s “Römerbaustelle Aliso” open-air reconstruction project. “It is not yet clear whether the building remains belong to a soldiers’ barrack or an atrium-style house,” Tremmel explained. “However, one of the pits discovered may have served as a kind of refrigerator — an ancient storage space used by the Romans to keep food and drinks cool.”
Unearthing Daily Life in a Roman Fortress
The site of Haltern am See has long been recognized as a window into the everyday lives of Roman soldiers and settlers in Germania. The excavation revealed not only structural remains but also everyday objects that shed light on domestic routines inside the camp. The bronze spoon and wine amphora fragments indicate the consumption of imported goods — especially Mediterranean wines — which were transported in large amphorae to the frontier provinces of the Roman Empire.
The discovery of Terra Sigillata, a fine red-glazed tableware known as “stamped earth” due to its potters’ marks, adds further evidence of the Romans’ sophisticated dining culture. These items were luxury goods in their time, often used by officers or wealthy merchants.
Students also uncovered gaming pieces and Roman coins, providing insight into the leisure activities and economic life of the legionaries stationed in the camp.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The Mystery of the “Roman Refrigerator”
One of the most fascinating aspects of the excavation is the identification of a possible Roman Cooling Pit, or Kühlgrube. Such features were used throughout the Roman Empire to preserve perishable foodstuffs — from cheese and meat to wine and fruits. These pits were typically dug into the ground and sometimes lined with clay or stone to maintain a stable, cool temperature.
In warmer regions, Romans also built cellars or hypocaust-cooled storage rooms under their villas. In frontier provinces like Germania, where the climate was cooler, simple underground pits often sufficed. The pit discovered in Haltern likely functioned in this way, perhaps covered with wooden planks and filled with straw or sand for insulation.
“Romans were surprisingly innovative when it came to food storage,” says Professor Eckhard Deschler-Erb, who led the excavation on behalf of the University of Cologne’s Department of Roman Provincial Archaeology. “Discoveries like this show that even in the northernmost military outposts, they adapted their technology and daily habits to local conditions.”
Evidence of the Camp’s Dramatic End
Another key observation made by the excavation team concerns the unusually thick post trenches discovered at several points around the site. Dr. Tremmel explains that these might be linked to the “hot demolition” carried out by the Romans when they abandoned the camp. “The trenches became wider when the posts were pulled out — they had burned the wooden posts first, then removed the remains,” she said. This destruction layer may date back to the turbulent years following the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (9 CE), when Roman forces withdrew from Germania after suffering heavy losses.
Haltern’s Long Archaeological Tradition
Haltern am See is one of the most studied Roman sites in Germany. Archaeological research began here as early as 1899, and the town has since become a training ground for generations of archaeologists. The excavation continues this legacy: “We are proud to revive this long-standing tradition,” says Deschler-Erb. “Our students are now analyzing their findings and preparing a contribution for the next issue of Archaeology in Westphalia-Lippe.”
Over the past 125 years, methods of excavation and documentation have evolved significantly, yet Haltern remains central to understanding the Roman occupation in northern Europe. The LWL-Römermuseum’s interactive exhibits and ongoing digs make it a living laboratory for both scholars and visitors interested in ancient Roman history.

A Glimpse into Roman Innovation
The discovery of a Roman “refrigerator” in Haltern highlights the ingenuity of ancient engineering. From sophisticated aqueducts to underfloor heating systems and food preservation methods, Roman innovation was not confined to Rome itself but extended deep into its provinces. The Haltern find offers rare, tangible evidence of how Roman soldiers lived — not only how they fought and built but how they ate, drank, and adapted to life at the edge of the empire.
As research continues, Haltern am See once again proves itself a key site for understanding how the Romans brought Mediterranean culture — and perhaps a taste for chilled wine — to the forests of ancient Germania.
Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe (LWL)
Cover Image Credit: University of Cologne, Archaeology of the Roman Provinces / R. Eckardt