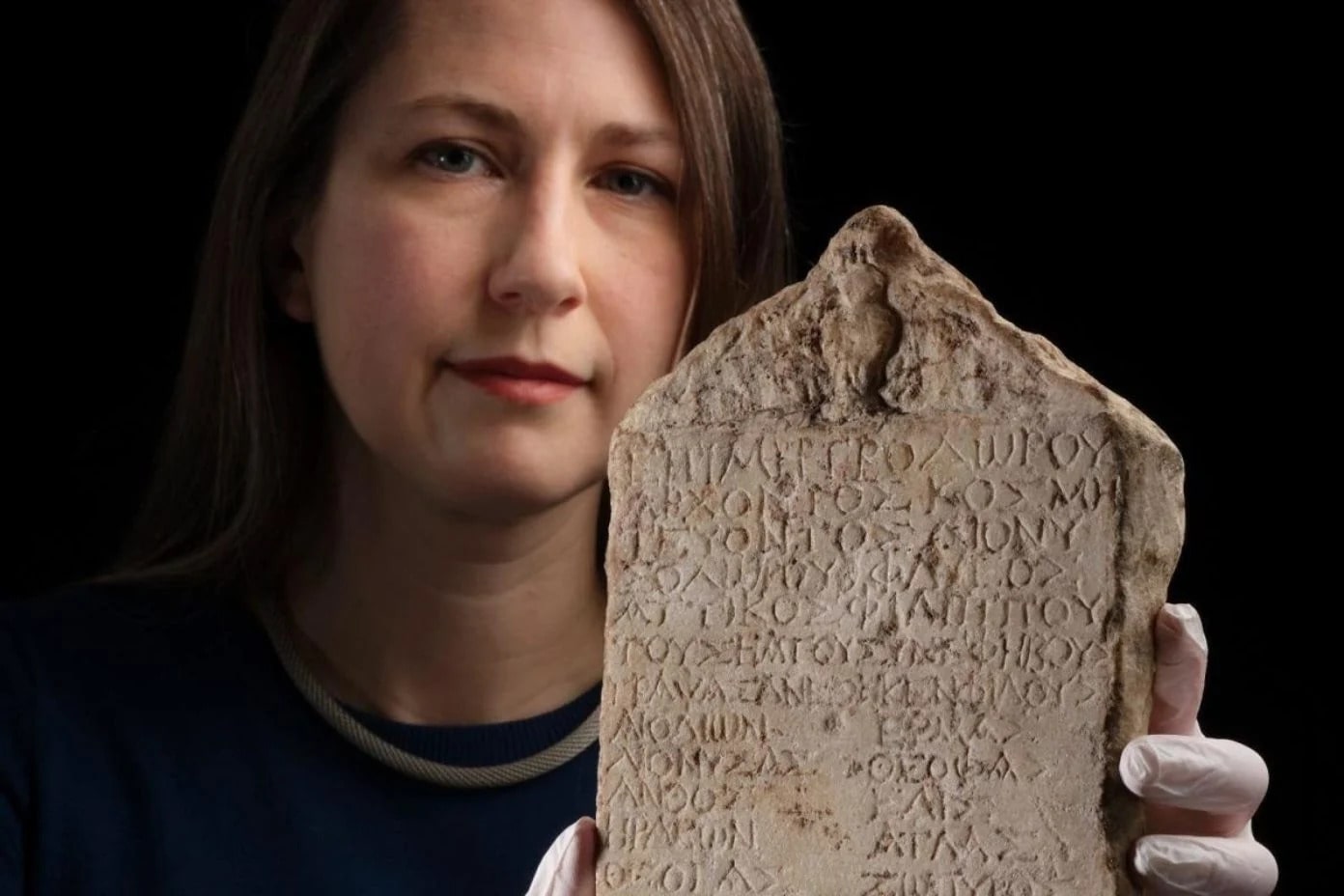
Historians have discovered that an ancient Greek inscription on a marble slab in the collection of the National Museums of Scotland is a rare, previously unknown “graduate school yearbook” type list of names.
The carved letters on this marble are a list of ephebic friends, and close friends, who passed through the ephebate in Athens, a year of rigorous military and civil training during the reign of Emperor Claudius (AD 41-54).
An ephebus was a youth in ancient Greece who had reached the age of puberty. Ephebi (the plural of “ephebus”) aged 18 or 19 were at one time required to undergo two years of stringent military training, but the requirement became less compulsory and the training less rigorous and militaristic over time. The youthfulness of the ephebi inspired the adjective “ephebic”.
Ephebic training became a requirement for all young males eligible for admission as Attic citizens in the 4th century B.C. If they were 18 years old of Attic parentage on both sides, the youths would be de jure citizens, but to actually exercise those rights (vote, be a party to a lawsuit, attend the assembly), first, they had to sign up for two years of military studies. The requirement was ultimately dropped, and by the 2nd century B.C., ephebic training was open to foreigners and the study of literature and philosophy was added to the curriculum. From roughly 39 A.D., everyone who had completed an ephebic training was considered an Attic citizen.

It lists a group of 31 friends who went through the Athenian ephebate together during the reign of the Roman Emperor Claudius (AD 41-54) and was intended to commemorate the close relationships they had formed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
When they read heard about it, experts assumed it was a replica of a similar list in the collection of the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford, but when they examined it, they realized that was not the case.
Because inscriptions from this time period are uncommon, scholars say it’s even more remarkable that the newly discovered ephebic list dates from the same year and cohort as the Ashmolean’s inscription.
Dr. Peter Liddel, professor of Greek history and epigraphy at the University of Manchester, who led the discovery, said: “Because of lockdown we were not able to travel to the museum until July 2021, and on seeing it we realized that this was not a copy of an already known inscription but it was a completely unique new discovery which had been in the storerooms of the NMS for a very long time, since the 1880s, and it listed a group of young men who called themselves co-ephebes or co-cadets and friends.
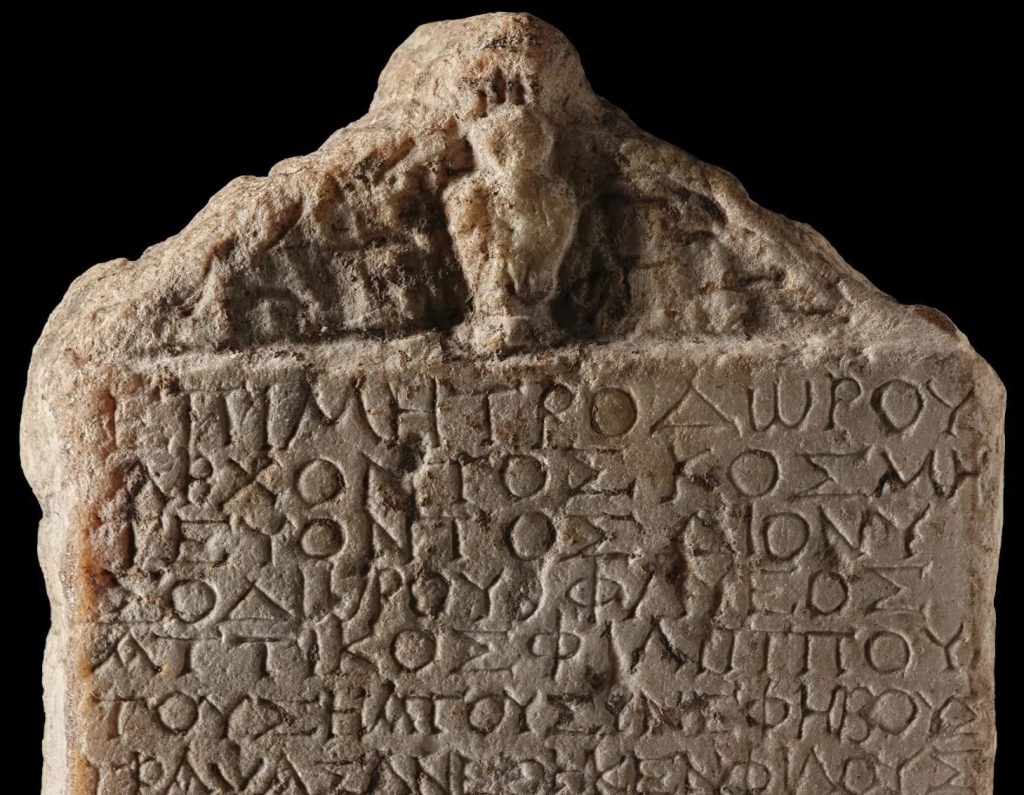

“It turned out to be a list of the cadets for one particular year during the period 41-54 AD, the reign of Claudius, and it gives us new names, names we’d never come across before in ancient Greek, and it also gives us among the earliest evidence for non-citizens taking part in the ephebate in this period.
The top of the plaque is peaked and a worn relief believed to depict a small oil amphora of the type ephebes would have used in the school gymnasium. It is not known where the list was displayed but it is thought it could have been put up somewhere such as the gymnasium where the young men trained.
In the archonship of Metrodoros, when the superintendent was Dionysodoros (son of Dionysodoros) of Phlya, Attikos son of Philippos, having inscribed his own fellow ephebes (and) friends, dedicated (this).
The 31 names are inscribed in two columns under the dedication. Attikos’ select bros in the ephebate were Aiolion, Dionysas, Anthos, Herakon, Theogas, Charopeinos, Tryphon, Dorion, Phidias, Symmachos, Athenion, Antipas, Euodos, Metrobios, Hypsigonos, Apollonides, Hermas, Theophas, (H?)elis, Atlas, Zopyros, Euthiktos, Mousais, Aneiketos, Sekoundos, Zosimos, Primos, Dionys, Eisigenes, Sotas and Androneikos.
The inscription is published this week.
Cover Photo: National Museums Scotland