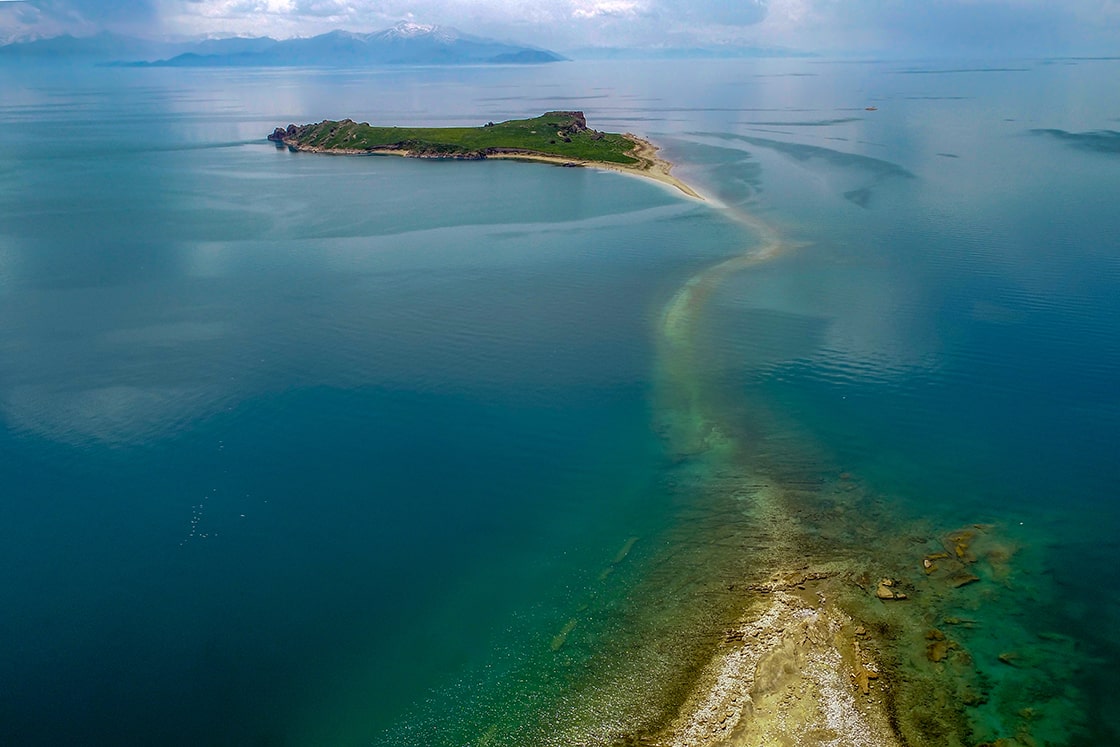
In Lake Van in eastern Turkey, the water level fell due to global warming, and a one-kilometer Urartian road connecting Çarpanak Island to the shore emerged.
The increasing effects of global warming are causing water level changes in the lake during certain periods and with changes in water level, some underwater structures appear.
Çarpanak Island, (Turkish: Çarpanak Adası) or Ktuts or Ktouts (Armenian: Կտուց կղզի Ktuts kghzi), is one of the 4 big islands in Lake Van.
Island is now uninhabited, but formerly contained an Armenian monastery called Ktuts. The ruins of it can still be seen.
Van Yüzüncü Yıl University (YYU) Faculty of Letters, Head of Archeology Department Prof. Dr. Rafet Çavuşoğlu told Anadolu Agency (AA) that Van, formerly Tusba, served as the capital of the Urartians for many years.
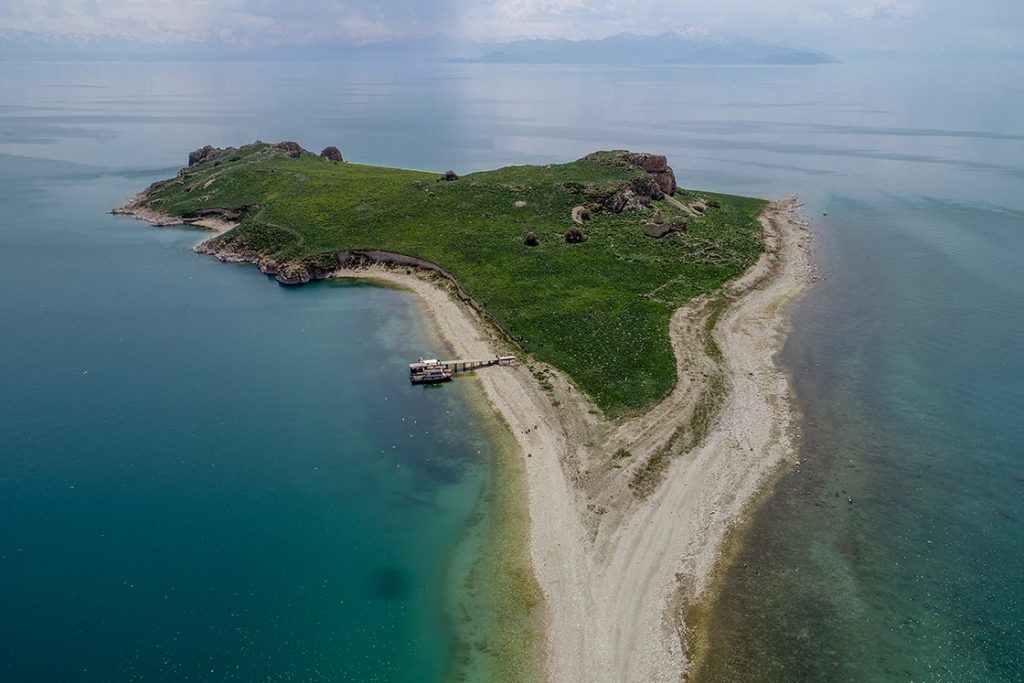

Explaining that the Urartians established transportation networks around Lake Van by both land and sea, Çavuşoğlu said, “One of these roads is the road that starts from Tusba and continues to Kalecik, Topaktaş, and then Çarpanak Island. The ruins on Çarpanak Island, namely the Çarpanak Church, belong to the Middle Ages. While this place was in the form of a peninsula in the Ancient Age, the level of the road was raised and transportation was provided by land. In fact, it is a road that starts from Tusba and continues along the shore of the lake, providing access to the castles. There is an Urartian road that follows the coast from Ayanis and Amik castles to Muradiye.” he said.
Noting that the road to Çarpanak Island was submerged over time, Çavuşoğlu said:
“The most important issue here is the decrease in the water level of Van Lake as a result of the decrease in precipitation after 2021. Therefore, the current path is seen more clearly. From time to time, Lake Van rises and falls. After the last rise in 1994, this road was mostly underwater. This road was built in order to provide access to the Urartian period castles, which were established by the lake, and then to the settlements that continued in the Middle Ages, by road. It is an ancient road that was built as wide as a horse-drawn carriage and was built both to take food and daily necessities to Çarpanak and to transport back and forth from Çarpanak. In the aerial images, it is clearly seen that the road was built by lining up stones, and only the main stones remained as the water eroded the road over time.”
During the Iron Age, the Urartians formed a strong political presence in the Eastern Anatolia region by coming together of several principalities such as Uruatri and Nairi. Architecture and metalworking is a civilization that draws attention, especially in the field of handicrafts.