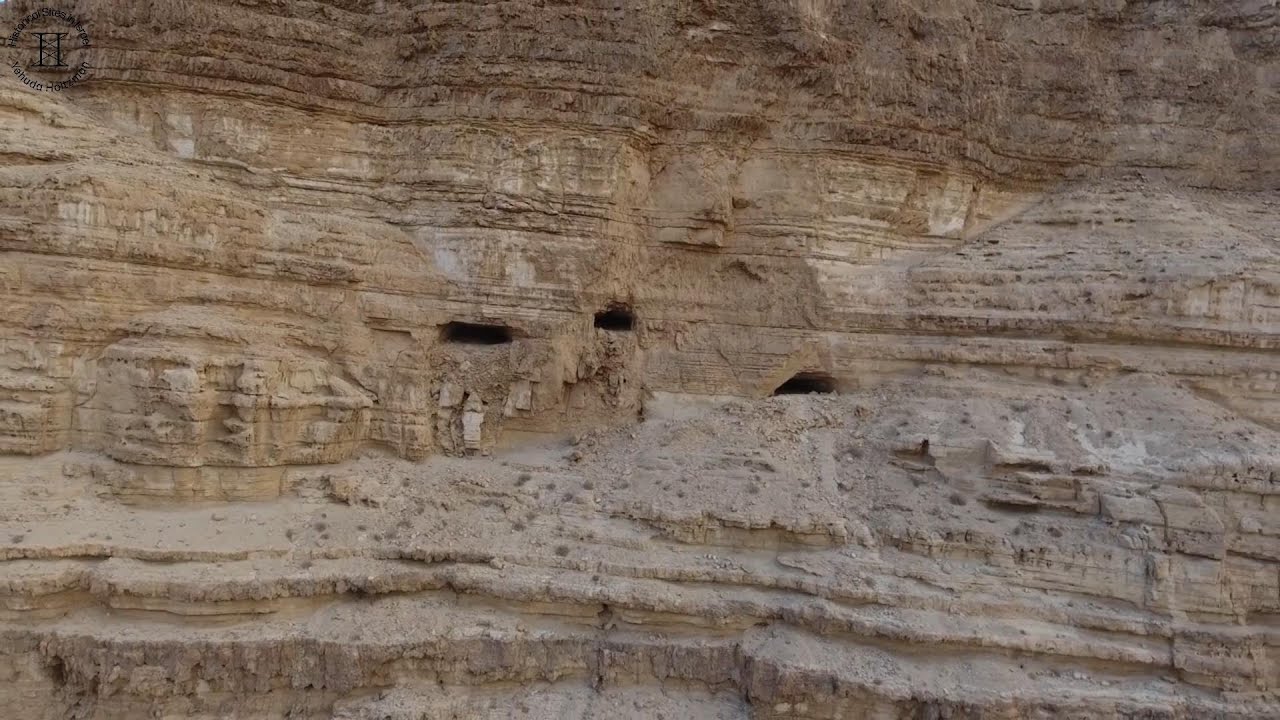
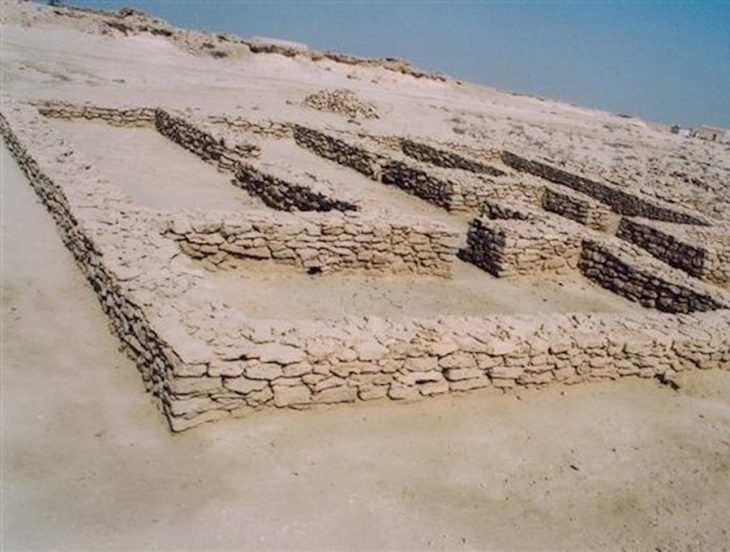
The Cave of Letters in Israel is one such site that has yielded a large number of papyrus letters and documents. It was discovered in the early 1960s CE and was excavated by the famed Israeli archaeologist Yigael Yadin from 1960-1961.
Letters and papyri fragments from the Roman Empire era were discovered when the cave was examined. Some are connected to the Bar Kokhba revolt.
The Cave of Letters was found above a canyon called Nahal Hever. The cave is located in the Judean desert near the Dead Sea and can only be reached by climbing 50 feet (15.24 meters) to the cave’s entrance.
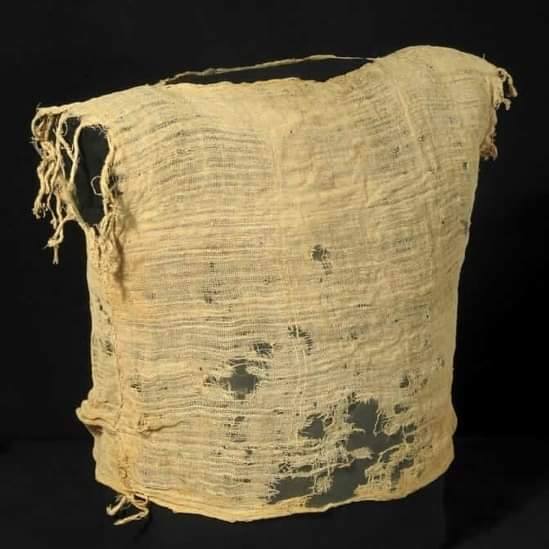
Archaeologists discovered a 1900-year-old child’s nightgown in the Cave of Letters, and the clothing tells a heartfelt story.
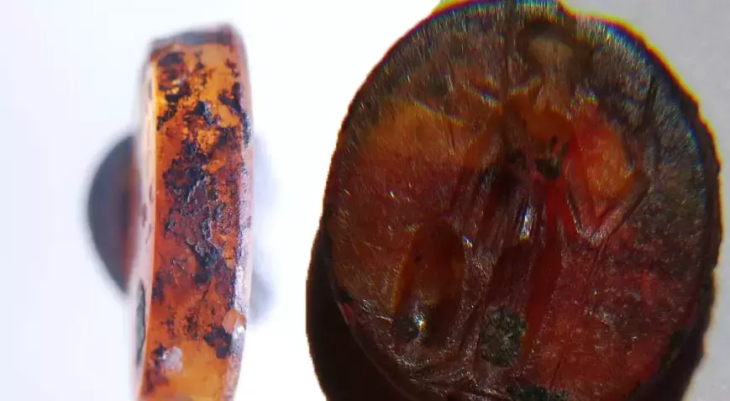
Over the years, thousands of scraps of textiles dating from the Roman period have been found at different sites in Israel, but textiles with intriguing “knots” have only been uncovered in the Cave of the Letters in the Judean Desert.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“The knots are like small pendants at the bottom of the garment, created by tying part of the fabric around substances known for their protective qualities: resin, salt, iron sulfate, asphalt, henna, seeds, and other unidentified materials. The binding was done by winding a flax thread around the material several times,” says Dr. Orit Shamir, Israel Antiquities Authority textile specialist.
The gown had knots at the hem, and by size, belonged to a child. It was most likely used as an undergarment underneath a colorful wool upper garment for decoration. The gown is made up of two equal-sized panels sewn together along their upper edges, with an opening in the middle for the neck.
The gown is adorned with flax threads hanging down from both sides of the neck. “If we examine the fabric from which the tunic was made,” says Dr. Shamir, “We’ll find that the thickness and density of the threads are not uniform. The weaving was simple, manufactured according to a simple twining technique, and occasionally mistakes were made. The sewing up of the garment is also not meticulous, and the garment has several holes, some of which resulted from wear and tear.”
Since there is no doubt that the nightgown is meant for a child, it may be speculated that the knots were hung on it to protect the child from illness and harm. “You can really imagine a mother hiding salt for protection and tying up a piece of the flax garment while reciting prayers and hopes for her son or daughter,” says Dr. Shamir.