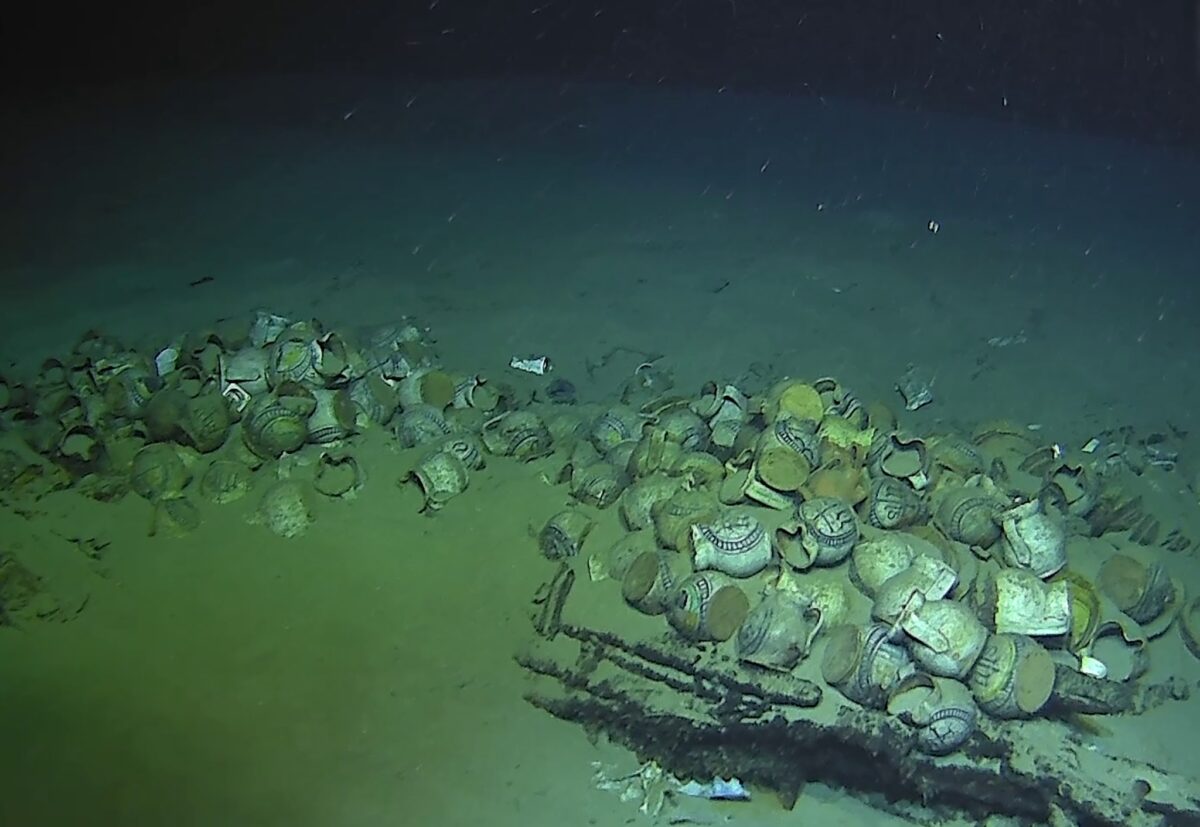
The deepest shipwreck ever documented in French territorial waters has been found over 2,500 meters below the surface.
In a remarkable discovery, the French Navy’s CEPHISMER team identified an uncharted shipwreck on March 4, 2025, during a deep-sea exploration mission off the coast of Ramatuelle (Var, Provence). The operation was part of France’s national strategy for seabed mastery, blending military and scientific objectives to enhance underwater awareness.
A 16th-Century Merchant Vessel, Exceptionally Preserved
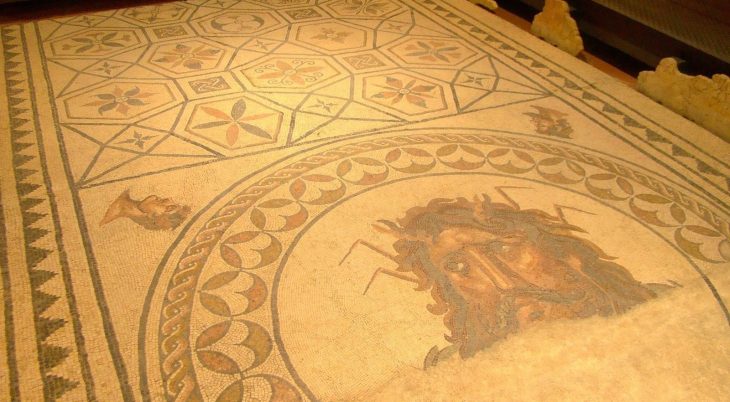
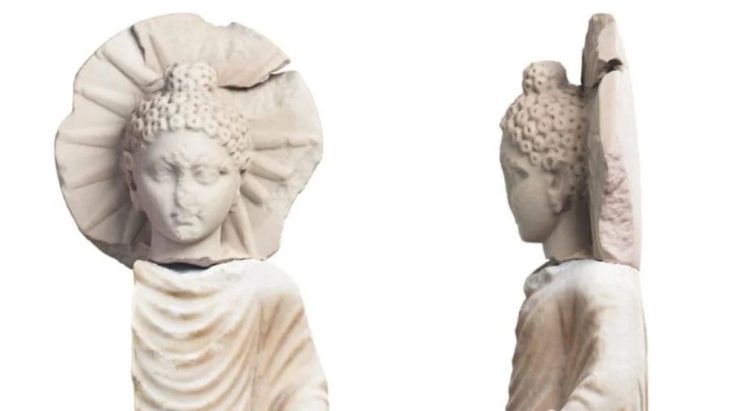
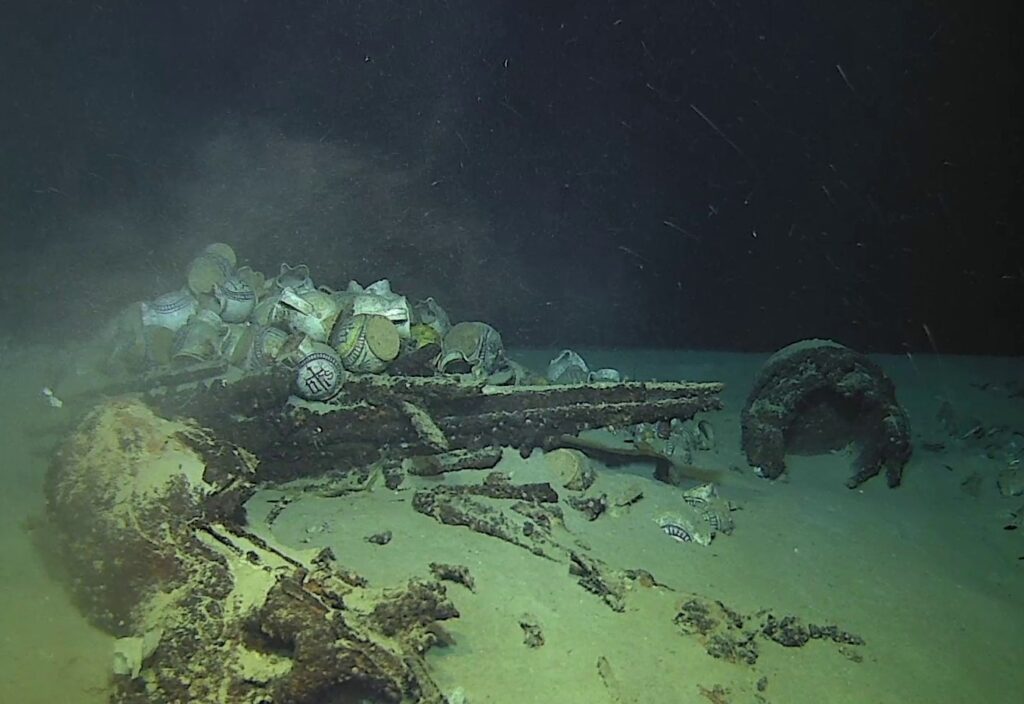
Measuring 30 meters long and 7 meters wide, the wreck is believed to be a large 16th-century merchant ship. Its remarkably preserved cargo includes around 200 multicolored faience jugs, many still embedded in sediment. These globular jugs, featuring pinched spouts and ribbon handles, are adorned with Ligurian-style motifs—ranging from the Christogram “IHS” to decorative geometric and floral patterns. The vessel also carried around 100 plates, likely of the same Ligurian origin.
Additional artifacts such as anchors, cannons, and cooking cauldrons were identified, offering a rare glimpse into the daily operations of a Renaissance-era trading vessel. Many other remains are still partially buried beneath the sand, awaiting detailed archaeological investigation.

A Unique Underwater Cultural Heritage Discovery
According to France’s Mediterranean Maritime Prefecture and the Ministry of Culture’s Department of Underwater Archaeology (Drassm), this is the deepest underwater cultural heritage (UCH) site ever recorded in French jurisdiction. The extreme depth has protected the wreck from natural degradation and looting, preserving it as a near-intact time capsule from the 1500s.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This extraordinary find, now designated as “Camarat 4,” presents a unique opportunity for scientific research and historical analysis. Planned initiatives include complete photogrammetric mapping, selective artifact recovery, and interdisciplinary study by a panel of experts—ranging from naval architecture and artillery specialists to ceramologists and conservators.
Raising Awareness and Preserving the Deep
The discovery also underscores the importance of protecting marine environments. Despite its remote location, the wreck is not immune to pollution, with both micro- and macroplastics found on-site. This highlights the need for increased public awareness around ocean conservation and cultural preservation.
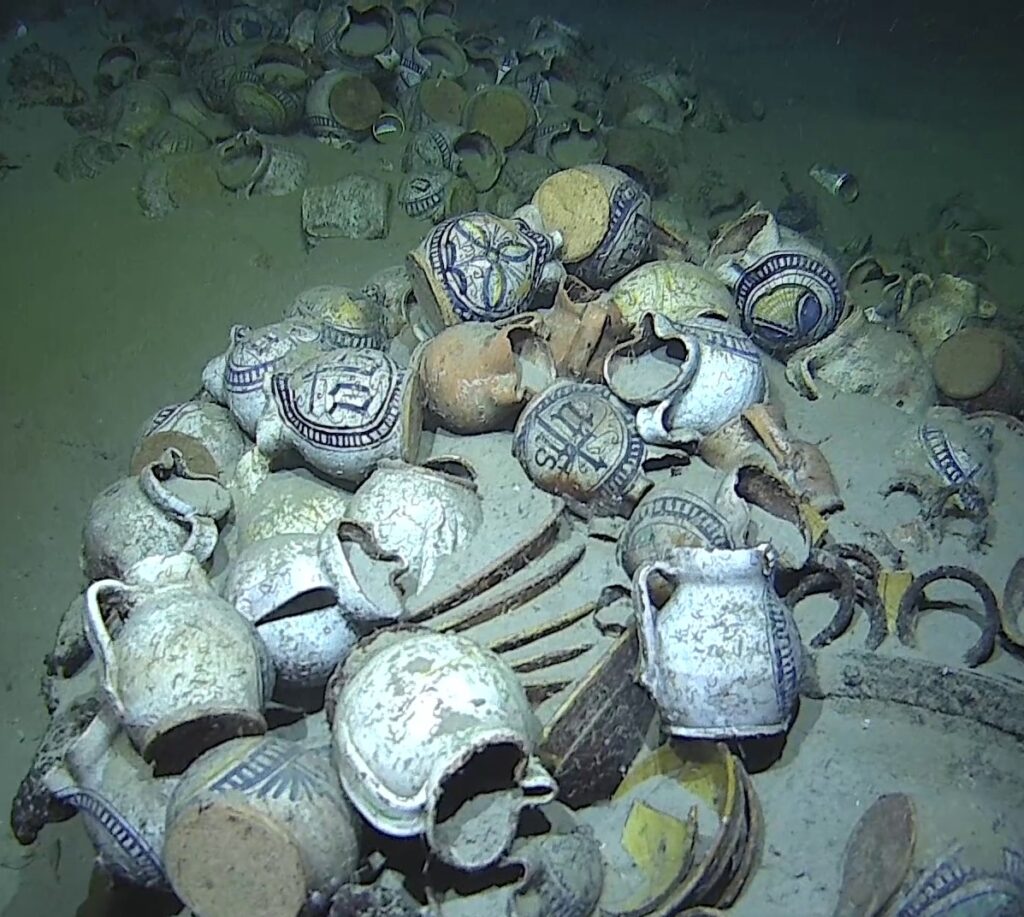

As France deepens its capabilities in underwater exploration, the Camarat 4 wreck marks a significant step in uncovering the secrets of the deep sea—offering scholars, scientists, and the public a window into maritime history hidden beneath the waves.
Cover Image Credit: Drassm – Marine Nationale