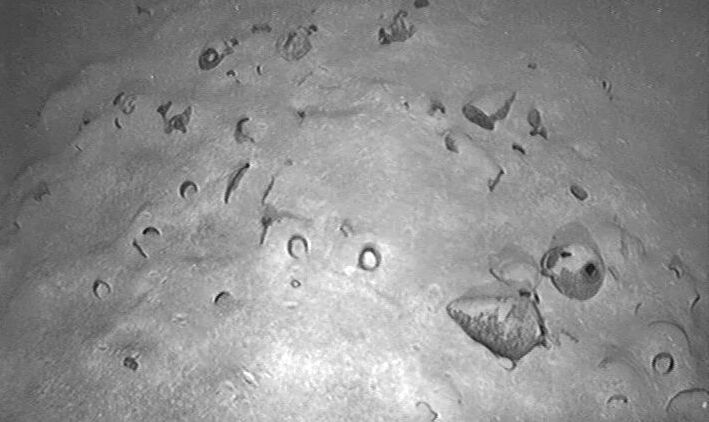
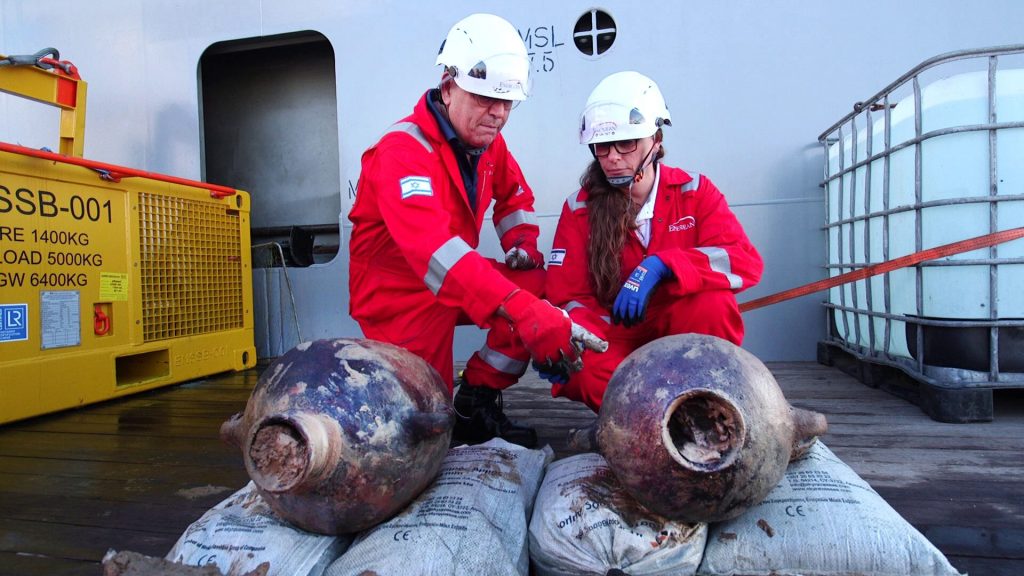
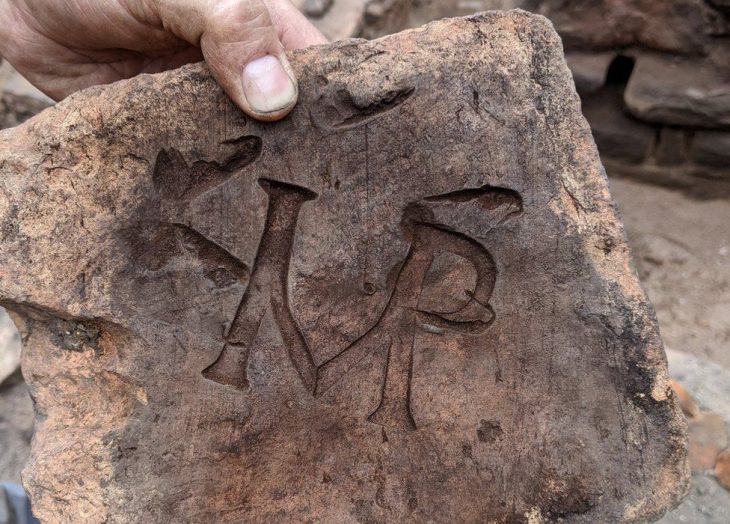An Energean natural gas surveying vessel operating about 90 kilometers (56 miles) off the coast of Israel discovered a ship filled with hundreds of intact containers dating from about 3300-3400 years old (14th-13th centuries BC) at an astonishing depth of 1.8 kilometers.
The 3,300-year-old vessel and its cargo of hundreds of intact amphorae (storage vessels) were found on the Mediterranean seafloor, as reported in today’s joint press release from the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) and Energean.
The amphorae are of a Late Bronze Age type, dating to the 14th century B.C.E. They are best associated with port cities along the coast of the Levant during a time when international maritime commerce—particularly with this region (and even faraway Britain)—flourished. Two representative vessels have been recovered by the Energean team from the 12- to 14-meter-long wreck.
Jacob Sharvit, director of the Marine Unit of the Israel Antiquities Authority, expressed that the ship apparently sank amid a crisis, possibly due to a storm or a pirate attack, both common events in the Late Bronze Age.
What makes this wreck especially exciting is its location—“both the first and the oldest ship found in the Eastern Mediterranean deep sea, 90 kilometers from the nearest shore,” Sharvit says. He further explained:
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“This is a truly sensational find. Only two other shipwrecks with cargo are known from the Late Bronze Age in the Mediterranean Sea—the boat from Cape Gelidonya and the Uluburun boat; both found off the Turkish coast. Yet both of those shipwrecks were found relatively near the shore and were accessible using normal diving equipment. Based on these two finds, the academic assumption until now was that trade in that time was executed by safely flitting from port to port, hugging the coastline within eye contact. The discovery of this boat now changes our entire understanding of ancient mariner abilities: It is the very first to be found at such a great distance with no line of sight to any landmass. There is tremendous potential here for research: The ship is preserved at such a great depth that time has frozen since the moment of disaster—its body and contexts have not been disturbed by human hand (divers, fishermen, etc); nor affected by waves and currents which do impact shipwrecks in shallower waters. …”
This find reveals to us as never before the ancient mariners’ navigational skills …. To navigate they probably used the celestial bodies, by taking sightings and angles of the sun and star positions.
Up until now, trade was thought to be carried out along the visible coastline. But this ship, discovered ninety kilometers from the closest coast, shows that prehistoric seafarers could travel great distances without being able to see land.
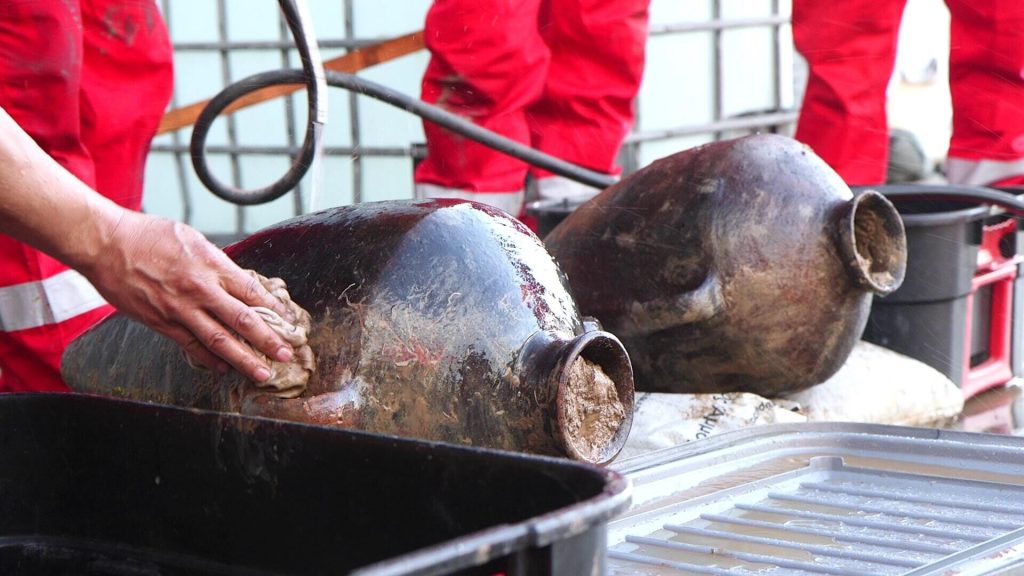

Dr. Karnit Bahartan, head of Environment at Energean, explained that the discovery was a surprise during one of their routine studies. Using an advanced submersible robot, the team identified what appeared to be a pile of jars on the seabed. Collaboration with the Israel Antiquities Authority confirmed it was a significant archaeological find.
Eli Escusido, director of the Israel Antiquities Authority, highlighted the importance of these findings, announcing that the extracted Canaanite containers will be exhibited at the Archaeological Campus, allowing the public to learn about the history of this ship before the official opening of the visitor center in two years.
Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA)
Cover Photo: The world’s oldest known deep-sea ship cargo. Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA)