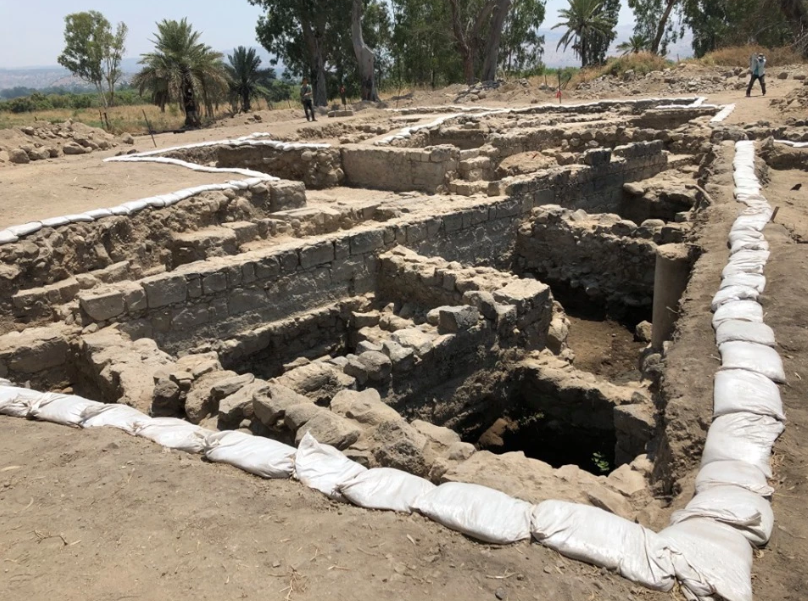
In a surprising twist of fate, a wildfire that swept through Israel’s Betiha Nature Reserve in late July has unveiled significant archaeological remains believed to be the biblical village of Bethsaida.
Long thought to be lost to time, this site, located along the northern shore of the Sea of Galilee, has been under excavation since 2016 at the official approval of the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. The recent blaze, while devastating to local flora and wildlife, has provided archaeologists with an unprecedented view of structures buried for centuries.
A Village Revealed by Fire
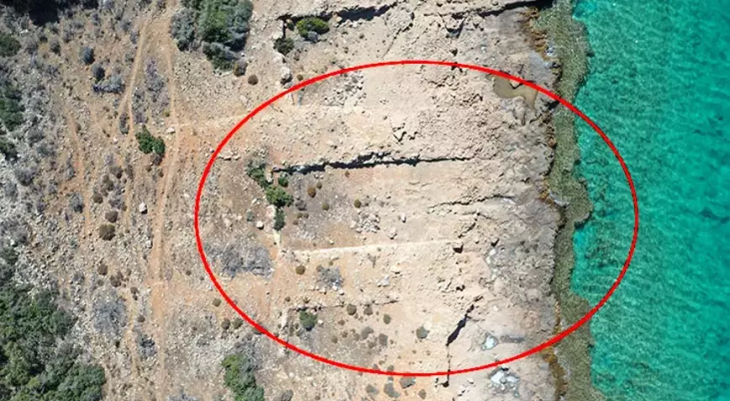
The wildfire, which raged for over 17 hours near Amnun Beach, forced the temporary closure of Highway 87 and sent beachgoers fleeing. When archaeologists returned to the blackened landscape, they discovered hundreds of small mounds scattered across the site of el-Araj.
“Each of these mounds is potentially an ancient room,” explains Mordechai Aviam, director of the excavation from Kinneret College. The cleared land exposed stone blocks, fragments, and even a pillar drum, suggesting the presence of public buildings alongside residential areas.
El-Araj has long been under investigation as a potential site for Bethsaida, historically recognized as the hometown of apostles Peter, Andrew, and Philip. Until recently, the village’s precise location had been debated, with the nearby site of e-Tell traditionally accepted despite its distance from the lake and elevated terrain — characteristics inconsistent with a first-century fishing village.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
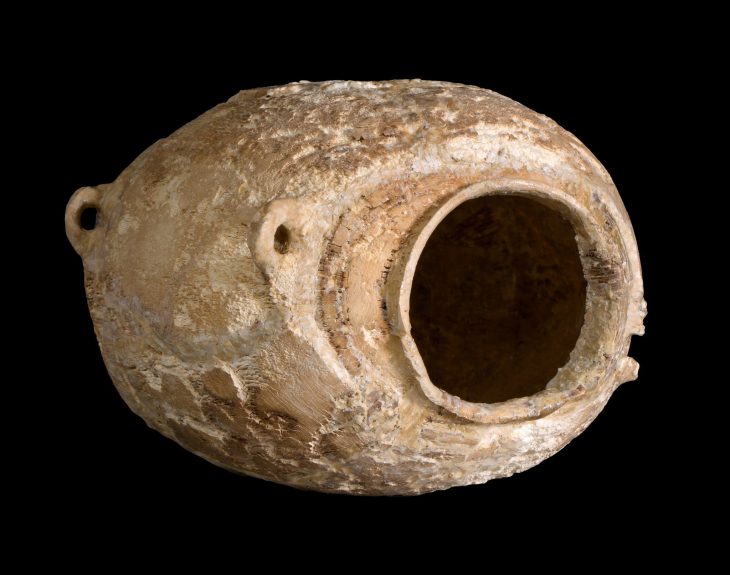
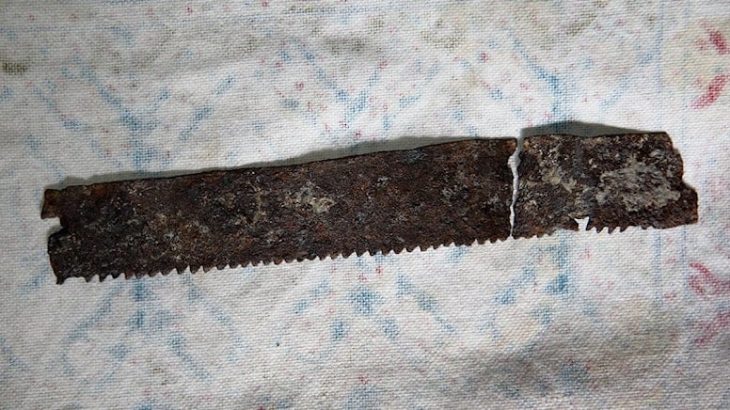
Excavations at el-Araj, however, have revealed fishing tools, Roman-era pottery, and remnants of a Roman bathhouse, all pointing to a thriving lakeside community in the time of Jesus.

Layers of History Beneath the Ash
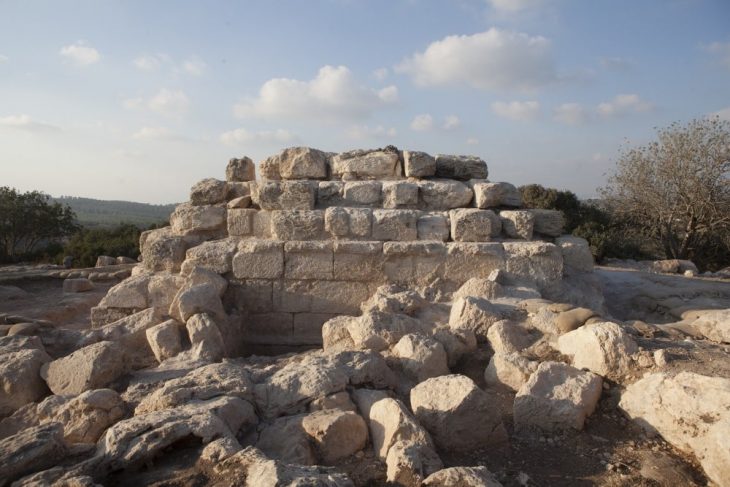
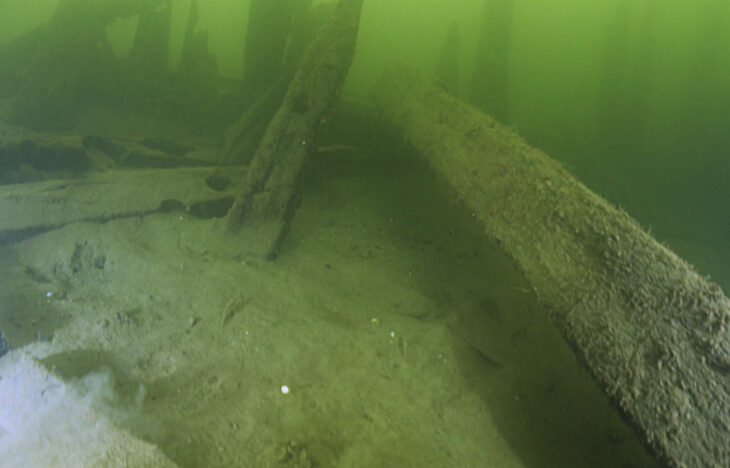
The archaeological site at el-Araj is layered with history. Beneath the surface lies the Roman-era settlement, topped by a Byzantine church and monastery from the 5th century. Crusaders later repurposed the church into a sugar factory in the 12th or 13th century.
Excavation director Aviam explains that uncovering the Roman layer — the period contemporary with Jesus and his apostles — requires meticulously documenting and sometimes removing the upper layers of Byzantine and Crusader structures.
In a statement to Haaretz’s Ruth Schuster, Aviam said, “The fire, while tragic, has allowed us to survey areas that were previously inaccessible due to thick vegetation.
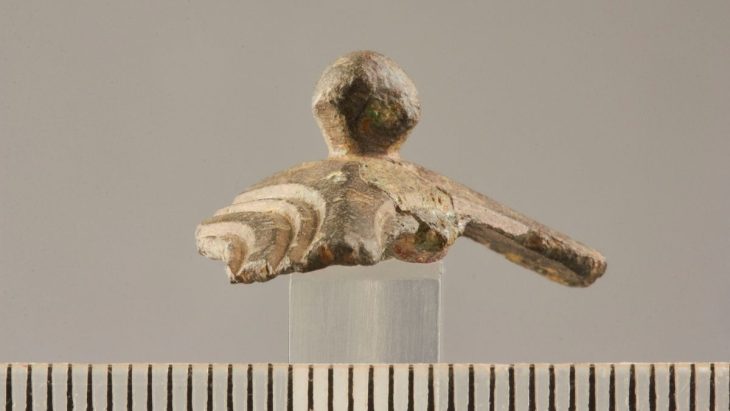
Among the finds, one of the most remarkable discoveries was an early inscription associated with the Apostle Peter. Volunteers uncovered ancient Greek letters hinting at Peter’s presence, reinforcing the identification of el-Araj as his hometown.
The site’s artifacts and architectural remains collectively provide a more accurate representation of a first-century fishing village than e-Tell, supporting the long-standing biblical accounts.

International Collaboration and Volunteer Efforts
The excavation project at el-Araj has attracted volunteers from around the world, including Hong Kong, under the supervision of R. Steven Notley, dean of Religious Studies at Pillar College, Newark. Among the youngest participants is Yohan Wong, who has been visiting the site since he was two years old.
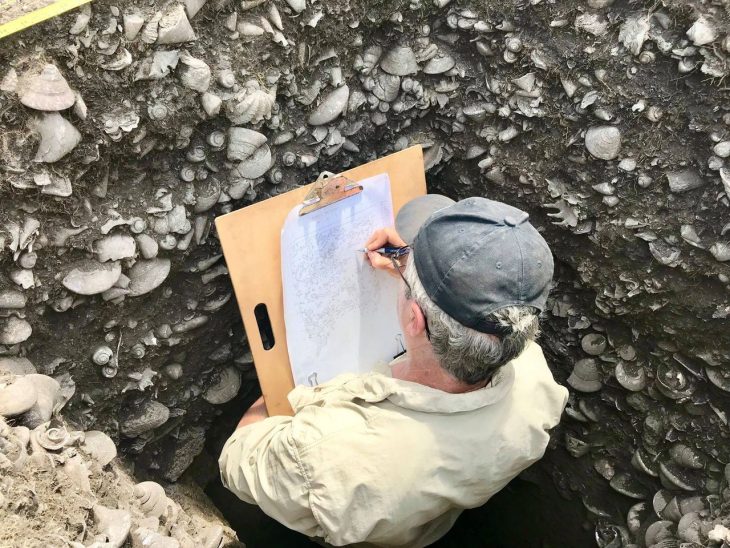
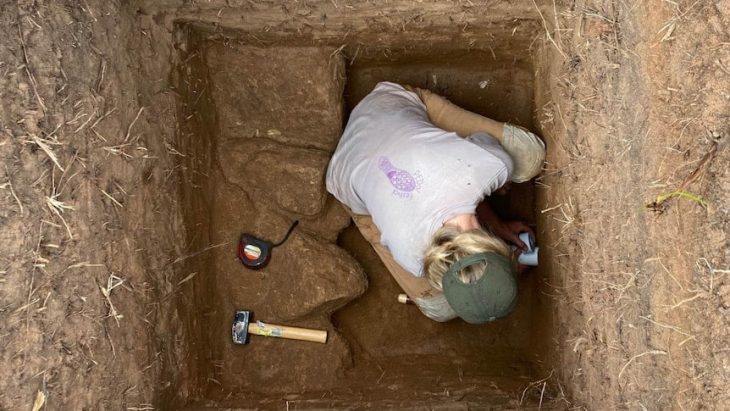
Families and volunteers play an active role in unearthing artifacts, cleaning mosaics, and documenting findings, creating a vibrant, hands-on learning environment.
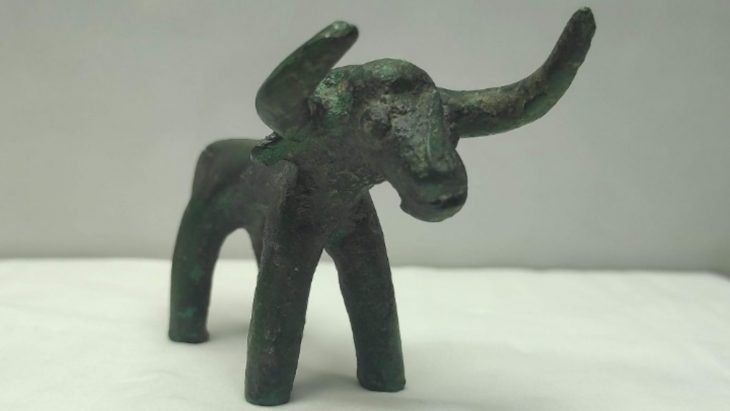
Despite the intense heat and post-fire conditions, the team remains dedicated. Archaeologist Achia Kohn-Tavor highlights the significance of recent discoveries, including fragments of limestone vessels typical of Second Temple-period Jewish homes, further supporting the site’s identification as Bethsaida.
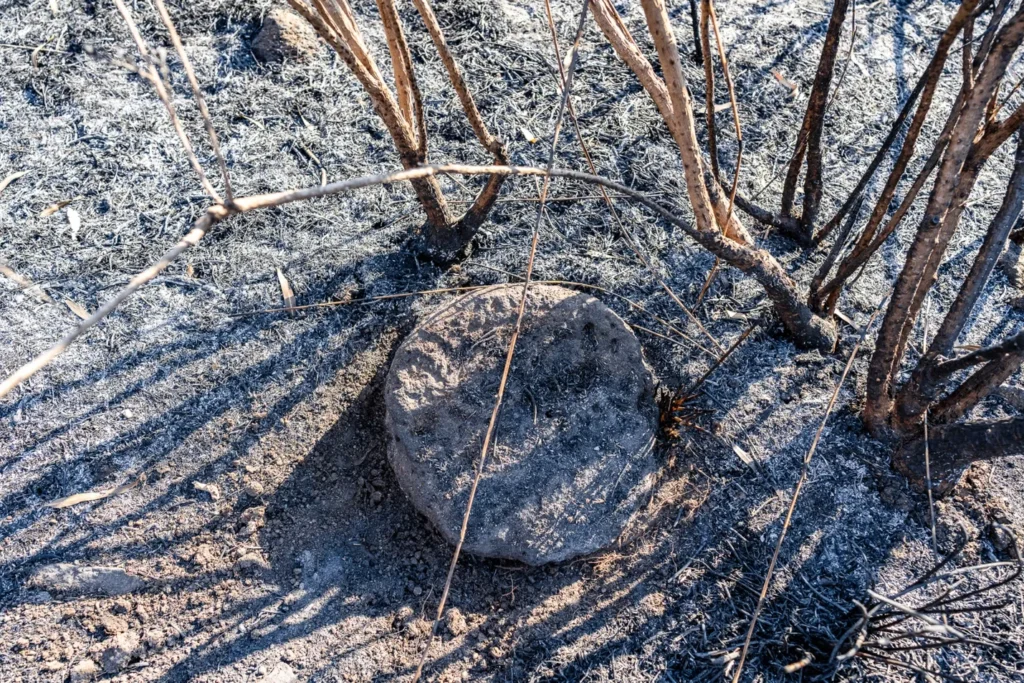

The Fire’s Silver Lining
While the wildfire destroyed much of the reserve’s vegetation, it inadvertently enhanced the archaeological work. The cleared land allowed researchers to locate structures more efficiently and plan future excavation strategies. Remarkably, the early Byzantine church and its protective coverings were spared from the flames, preserving vital evidence of the site’s layered history.
“The fire was an unfortunate event, but it has given us a rare opportunity to study the site with minimal obstruction,” Aviam notes.
The excavation’s next steps focus on uncovering additional Roman-era homes and public buildings, which could provide further insights into the daily lives of Bethsaida’s inhabitants and the community that shaped early Christianity.
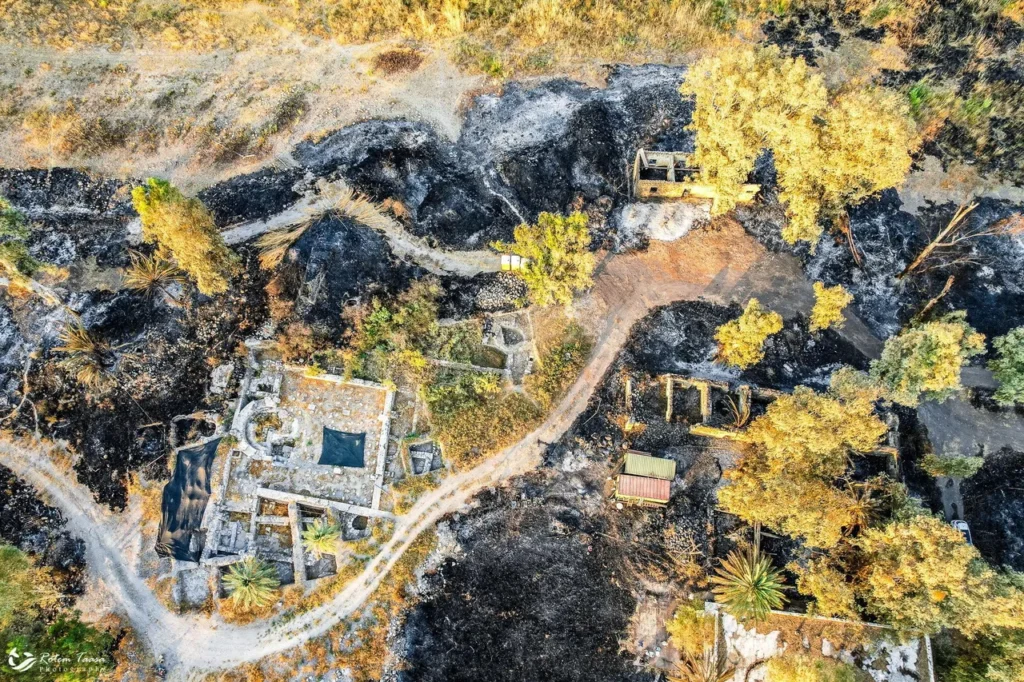

A Glimpse Into the Past
El-Araj stands as a testament to resilience — both human and environmental. Green shoots already emerge from the blackened earth, signaling life’s return.
Meanwhile, archaeologists continue to peel back centuries of history, one layer at a time, offering the world a tangible connection to biblical times. With each new discovery, the lost village of Bethsaida slowly reclaims its place in history, revealing stories that have been buried under soil, ash, and time for nearly two millennia.
Cover Image Credit: The main excavation site (Area A) at el-Araj. Photo Credit: El-Araj Excavation Project