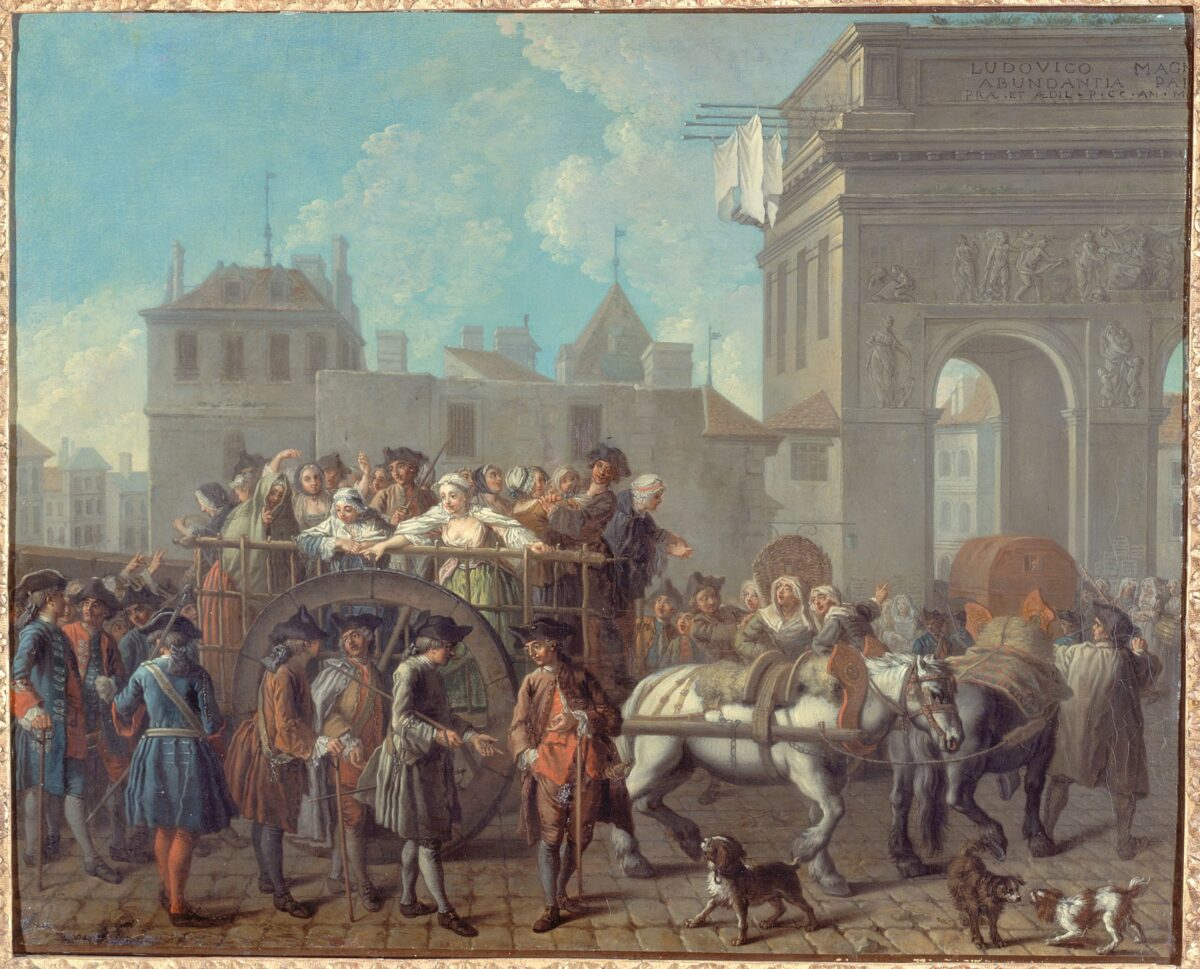
A medieval brothel in Belgium yields a discovery that forces historians to confront forgotten tenderness in places long seen only through the lens of sin.
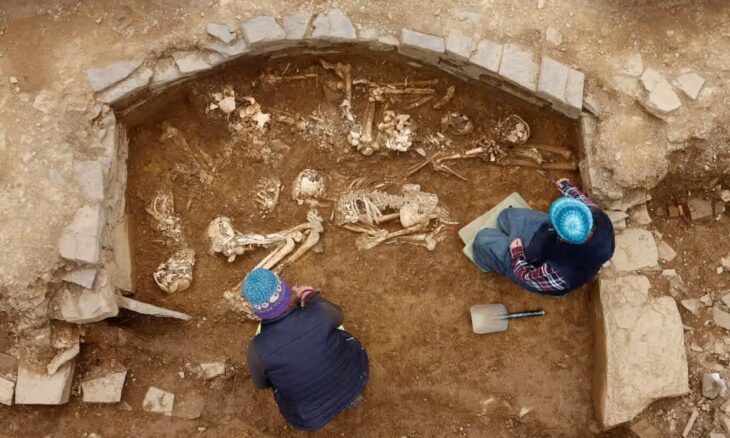
A remarkable archaeological discovery in Aalst, Belgium, is challenging long-held assumptions about motherhood, childcare, and the lives of medieval sex workers. Recent scientific analyses of the remains of a baby buried inside a 14th-century brothel reveal that the infant was breastfed and cared for—offering a different perspective on family life in one of the most marginalized corners of medieval society.
For centuries, historians assumed that infants born to sex workers in medieval Europe were often abandoned or even killed due to the social stigma surrounding their mothers’ profession and the severe economic hardship they faced. However, a new study, published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences in 2025, paints a different picture using cutting-edge bioarchaeological techniques, including ancient DNA (aDNA) and stable isotope analysis.
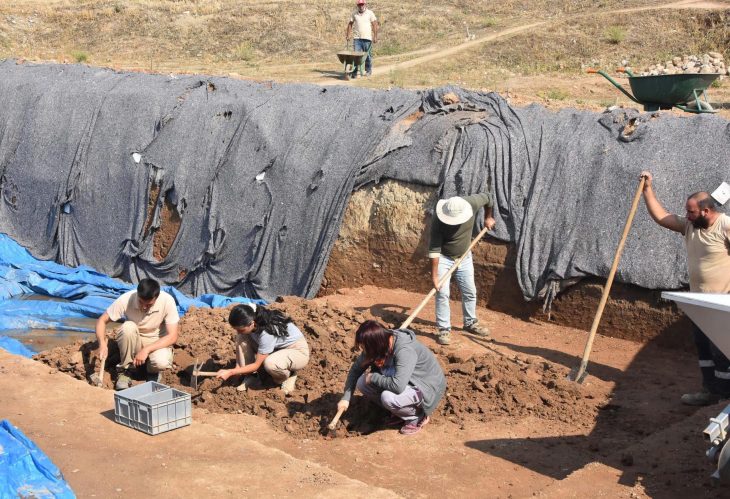
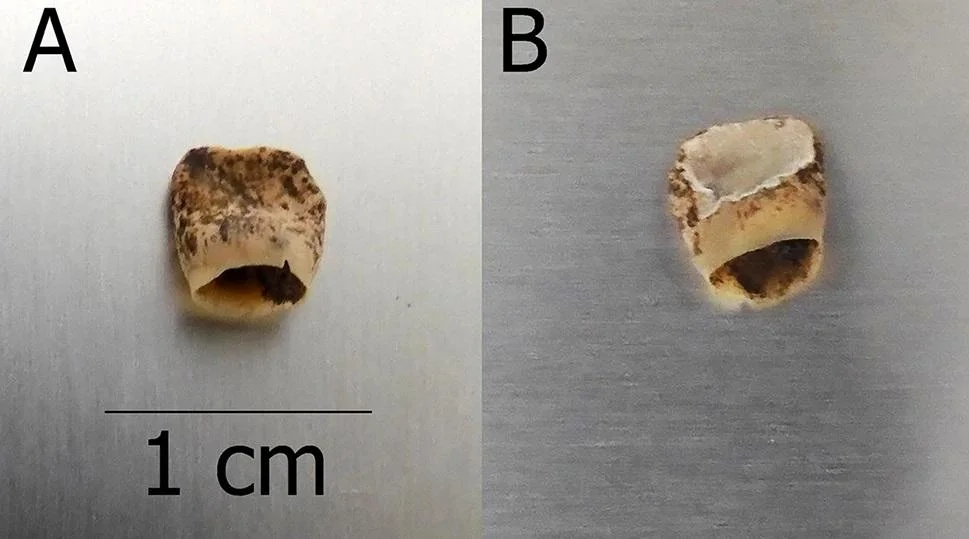
The remains of the infant were discovered during excavations in 1998 at a site in Aalst, a city in modern-day Belgium. Archaeologists identified the location as a 14th-century brothel, based on architectural features and artifacts found there. Among the most unexpected discoveries was a single infant burial located within one of the building’s rooms—a highly unusual context for medieval burials, which typically occurred in churchyards or cemeteries.
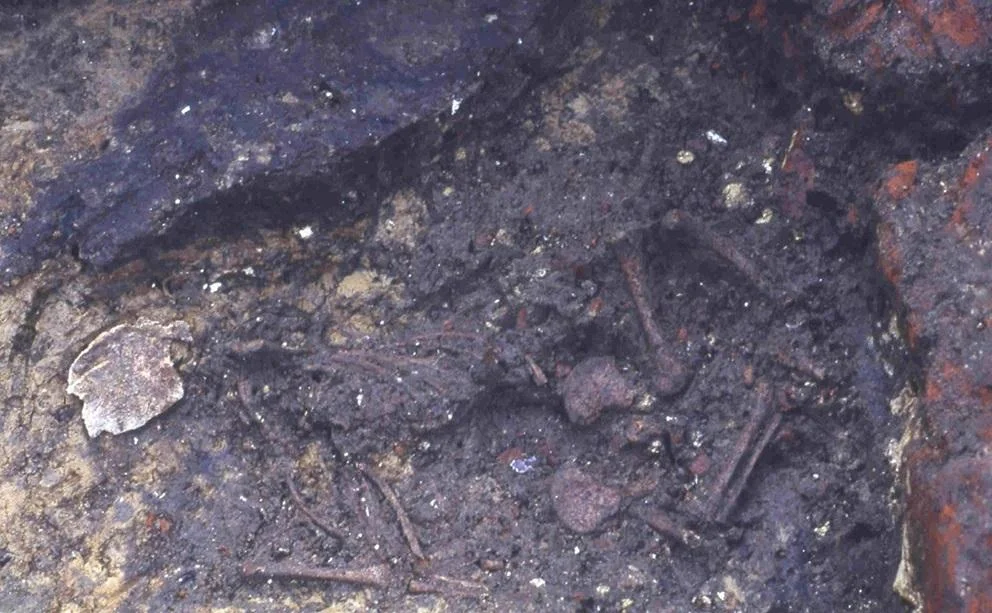

Advanced ancient DNA testing allowed researchers to determine the infant’s sex and familial lineage, while stable isotope analysis of the bones and teeth revealed that the baby had been breastfed for some time before death. These findings ruled out immediate infanticide and indicated active maternal care. This is the first known case in medieval archaeology where biomolecular evidence has been used to directly trace breastfeeding in such a context.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Lead researcher Dr. Maxime Poulain, a specialist in medieval bioarchaeology, explained the significance of the findings: “This infant’s story shows that, even in the context of a brothel, there was room for motherhood and caregiving. The burial was not hidden or ashamed; it was within the community of the women who lived and worked there.”
The implications of the discovery go beyond a single infant’s fate. They offer new insight into how sex workers in the Middle Ages might have lived—challenging the image of the brothel as a place of social abandonment and isolation. Instead, it becomes a more nuanced setting, where women formed bonds, raised children, and cared for each other in deeply human ways.
By applying modern scientific methods to ancient remains, archaeologists are uncovering stories that traditional historical records have long ignored. Written documents from the Middle Ages often stigmatize or overlook sex workers, but bioarchaeology can fill in those silences, offering a more complete picture of medieval life.
The study encourages a reassessment of commonly held beliefs about women, family, and marginalized communities in the past. According to the researchers, these findings underscore the importance of approaching history with both empathy and scientific curiosity. They emphasize that such discoveries reveal a deeper humanity in historical contexts that have often been overlooked or misunderstood.
The Aalst brothel site continues to yield valuable insights into urban medieval life, including the architecture, social structures, and daily lives of people on the margins. This particular discovery—a single infant, buried among working women—adds an unexpected layer of tenderness and complexity to that narrative.
Poulain, M., Bon, C. & Palmer, J. (2025). Born in a brothel: new perspectives on childcare with medieval sex workers. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 17, 105. doi:10.1007/s12520-025-02218-2
Cover Image Credit: French prostitutes being taken to the police station; painting by Étienne Jeaurat. Credit: Public Domain