A group of paleontologists from the University of Tehran has discovered traces of fossilized crabs in the Iranian which may hint at a hotbed of biodiversity dating 15 million years ago in the region that is today the Zagros Mountains.
The paleontologists have discovered fossils of a species of crab in different parts of the country that suggests the Zagros Mountains were once sea waterways through which the Indian and Atlantic Oceans intersect some 10 to 15 million years ago, and Iran has been one of the hotspots of biodiversity on Earth, ISNA reported on Sunday.
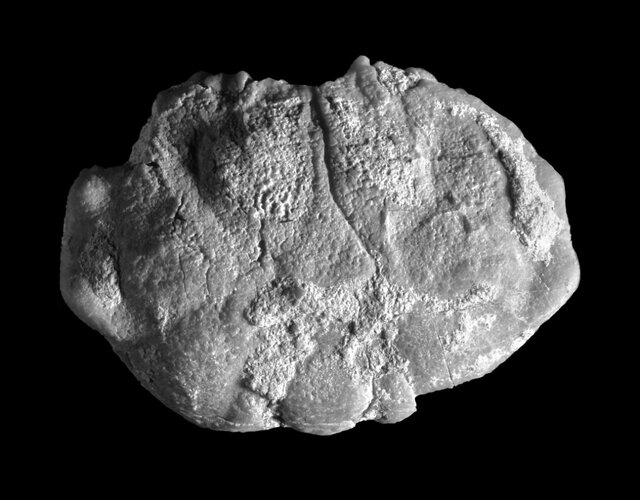
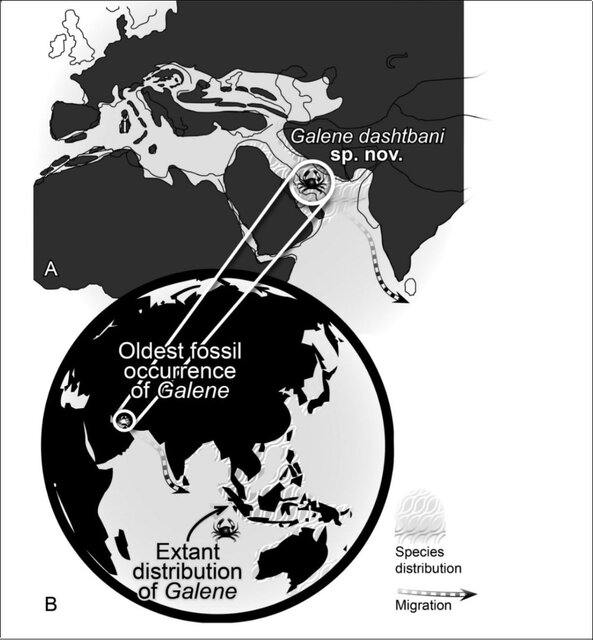
“A new species of Galene de Haan from the Mid Miocene (Langhian) strata of the Mishan Formation has been exposed at two localities in Hormozgan province, Zagros Mountains, Iran,” according to a new study conducted by Erfan Khosravi, Alireza Sari, Majid Mirziee-Ataabadi, Hossein Gholamalian, Mat Hyn, Reza Naderloo.
The Galene species, (“named as Galene dashtbani”), is considered the oldest representative of the genus and simultaneously the westernmost occurrence of all fossil and extant congeners known to date.

As mentioned by the researchers, the genus is currently limited to the Indo-West Pacific region. The present fossil occurrence of the genus suggests a Tethyan origin and subsequent migration eastward.
“The finding raises new debates about the importance and role of biodiversity hotspots and the importance of their conservation. In addition, it doubles the importance of paleontological research and shows the extent to which the study of fossils can enhance our understanding of the current living world and the environment,” the report says.
Speaking to ISNA, Khosravi considers crab fossils to be much, much rarer than fossils such as oysters and snails, which are very difficult to find.
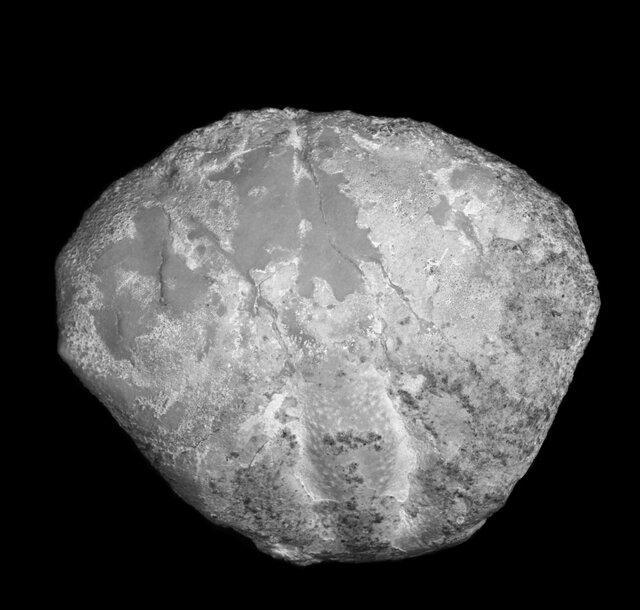

“Because they are found in much more specific environments than oysters, and because they do not have hard outer parts like shells and snails, their complete preservation in fossils is rare. In addition, it is much more difficult to identify and examine them; Because many crab fossils are just pieces of the crab’s armor backplate.”
In response to the question that if the crabs found in the study are more or less similar to modern crabs found in rivers, he explained: “During the (recent) years, we found several new species of crabs from different parts of Iran, all of which species lived in the sea. Fossils of river crabs are very rare, even when they are no longer available in some parts of the world.”
Elsewhere in his remarks, the paleontologist noted they discovered fossils of sea crabs from different regions of the country including Shahroud, Garmsar, Isfahan, Kurdestan, Bandar Abbas, and Kazerun.
“A few years ago, as I was trying to identify some new fossils, I noticed that one of these fossils did not look like any I had seen before. Many fossils are more or less the same species still found in the Persian Gulf today, but this new species of crab was one of the species that, although recorded once or twice in the Persian Gulf, is mostly found in Southeast Asia around countries such as the Philippines, Indonesia, Taiwan, and Australia.”
In addition to its living representatives, fossils of this crab have been reported only from the same region of Southeast Asia, and those fossils are at most one to two million years old, he said.

“Significantly, this [fossilized] crab is at least 10 million years older than all other similar specimens found in Southeast Asia.”
These crabs and a few other specimens that have been discovered in previous studies on Iran’s Zagros, as well as similar sediments from the Tethys in Austria, all of which have newer and more modern similarities in Southeast Asia, lead us to the hypothesis that from the current habitat, the hotspot of biodiversity in Southeast Asia has been here in the Tethys Sea deposits.
“We have discovered more than a thousand specimens of crab fossils from all over Iran, and gradually the information extracted from these fossils will be published in the form of articles.”
Because studies show that there are several dozen new species among these fossils and some rare species that have been described by paleontologists from other regions but are discovered for the first time in Iran.
















