A recent study of Leonardo da Vinci’s family tree indicates that the renowned Renaissance artist, inventor, and anatomist had 14 surviving male cousins. The new family tree might one-day aid academics in determining if the Italian genius’s bones are placed in a French church.
Historians Alessandro Vezzosi and Agnese Sabato have spent over a decade tracking the ancestors of famous painter.
Their map spans 690 years, 21 generations, and five family branches, and will be critical in assisting anthropologists in sequencing da Vinci’s DNA by sequencing the DNA of his ancestors, according to the researchers.
Beyond determining the identity of his possible remains, scientists hope that sequencing the artist’s DNA will help them better understand “his extraordinary talents — notably, his visual acuity, though genetic associations,” according to representatives from the Leonardo Da Vinci DNA Project, a project that aims to use genetic data to create 3D images of da Vinci through a process called DNA phenotyping.
In recent research, Vezzosi and Sabato traced the five branches of the da Vinci family tree using historical records from archives and direct recollections from surviving ancestors. Leonardo belonged to the sixth generation of da Vincis, according to historians.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Only one of da Vinci’s parents can be fully traced, making family history research challenges. Leonardo da Vinci was the son of Florentine lawyer Ser Piero da Vinci and a peasant woman named Caterina. He was born out of wedlock in the Tuscan hamlet of Anchiano. At age 5, the young da Vinci was taken to his family estate in the town of Vinci (from which his family took their surname ) to live with his grandparents.
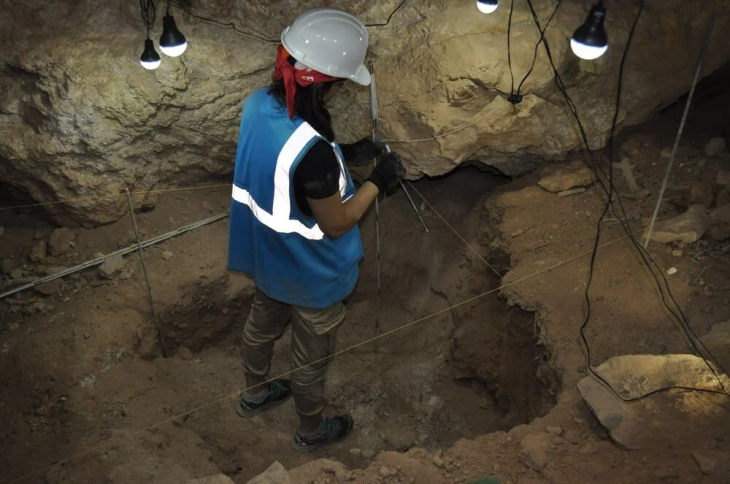
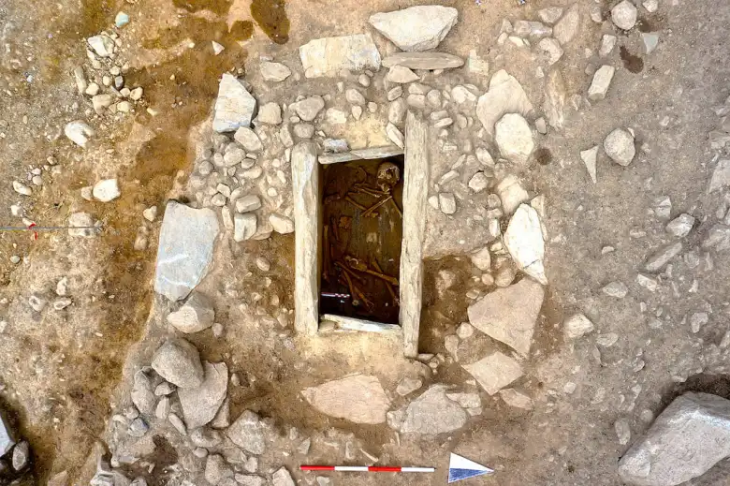
Da Vinci had no known offspring when he died on May 2, 1519, at the age of 67, and his bones were lost, thus there was no trustworthy DNA to examine. As a result, several aspects of his lineage are shrouded in obscurity.
Leonardo was buried at the church of Saint-Florentin in the Chateau d’Amboise, a manor house in France’s Loire Valley. After the French Revolution, the church was left to rot and was ultimately destroyed. According to contemporary reports, a whole skeleton was excavated from the spot and relocated to the adjacent Saint-Hubert church, although whether or not these are Leonardo’s bones remains unknown.
The new family tree, which begins in 1331 with family patriarch Michele, showed 14 surviving relatives with diverse vocations such as office employees, a pastry chef, a blacksmith, an upholsterer, a porcelain vendor, and an artist.
The researchers will compare the Y chromosome in the human remains from the Loire Valley chapel to the Y chromosome in da Vinci’s male relatives to establish whether the human remains from the Loire Valley chapel belong to da Vinci. According to the experts, the Y chromosome is passed down from father to son and can remain virtually unaltered for up to 25 generations.
Furthermore, discovering remnants of da Vinci’s genetic code might assist art historians in determining the validity of artworks, notes, and diary entries allegedly made by the Italian Renaissance artist by matching his discovered DNA with DNA traces found on the items.
The researchers published their findings July 4 in the journal Human Evolution.
Originally published on Live Science.