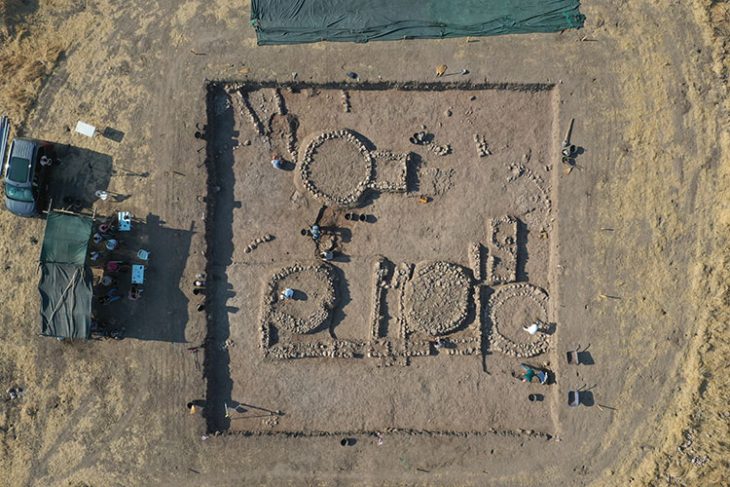Archaeologists from the Czech Institute for Egyptian Science have discovered a cache of artifacts related to the practice of Egyptian mummification during excavations inside a group of burial wells dating back to the era of the 26th Dynasty.
The location of this discovery is located in the western part of Abu Sir cemetery, the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities announced.
Mummification was an important part of the rituals for the dead in Ancient Egypt, involving the preservation of the body to ensure the departed was welcomed into the afterlife. The Ancient Egyptians thought that when a person died, the soul, ka, which signified life, left the body. Only if the corpse is properly embalmed will the ka return, allowing them to live in the afterlife eternally.
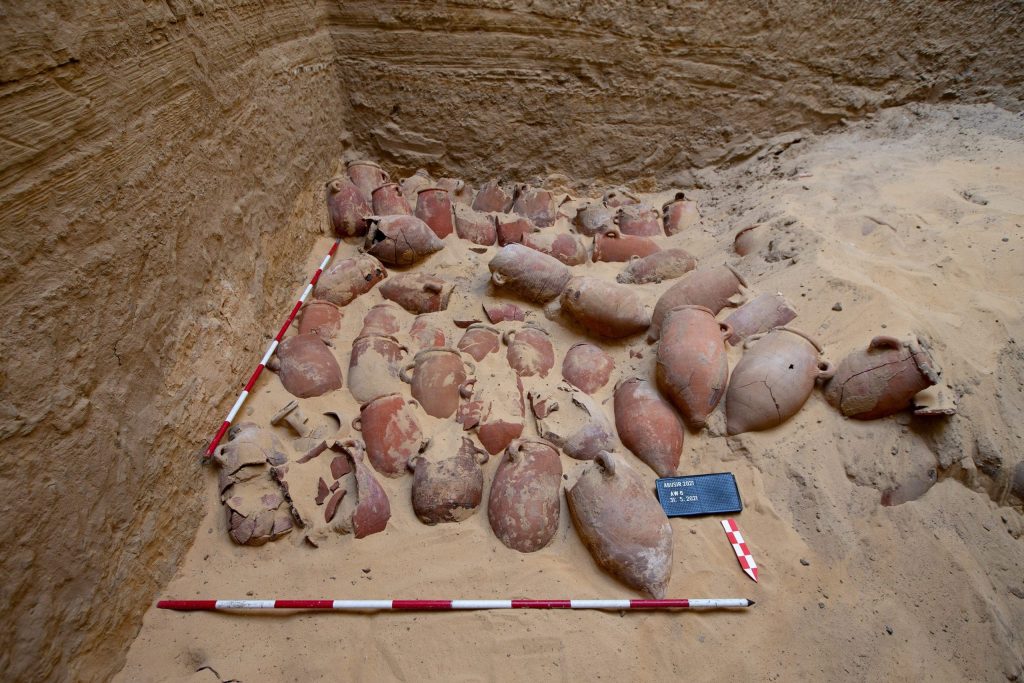

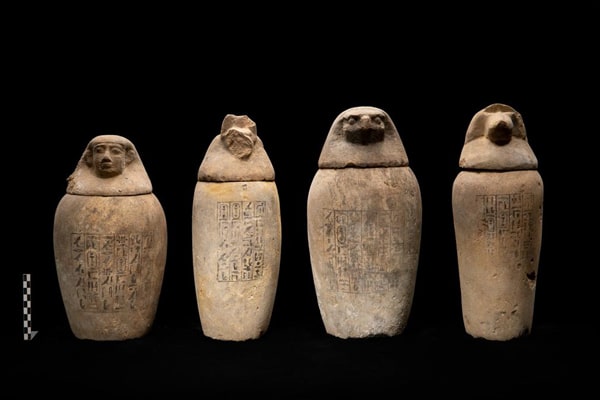
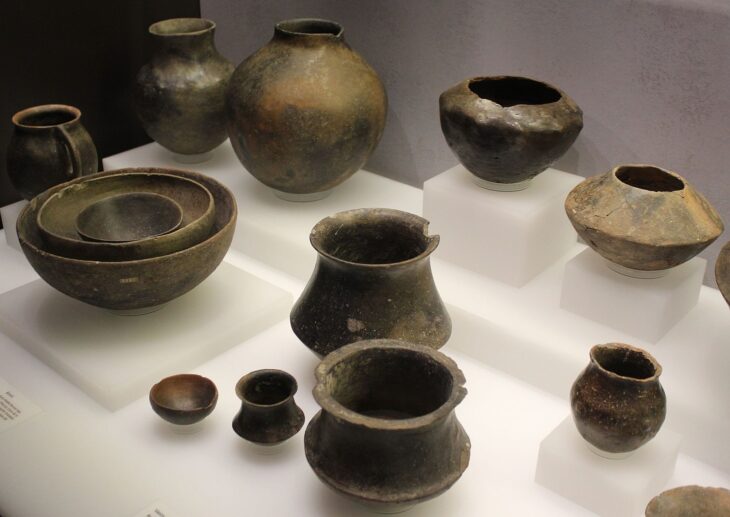
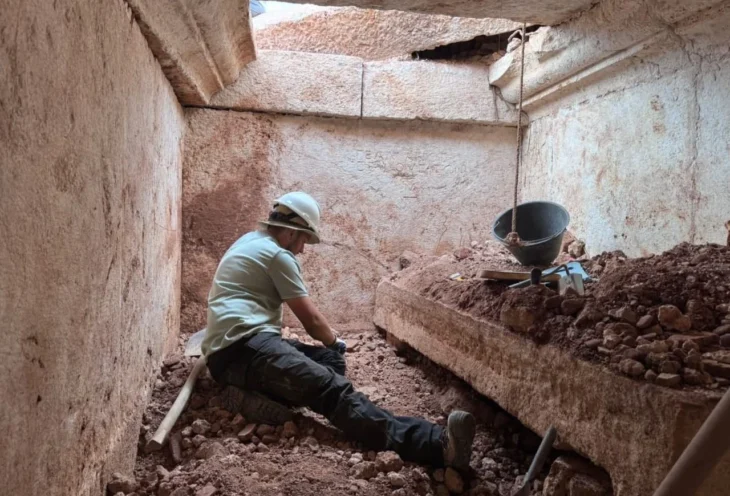
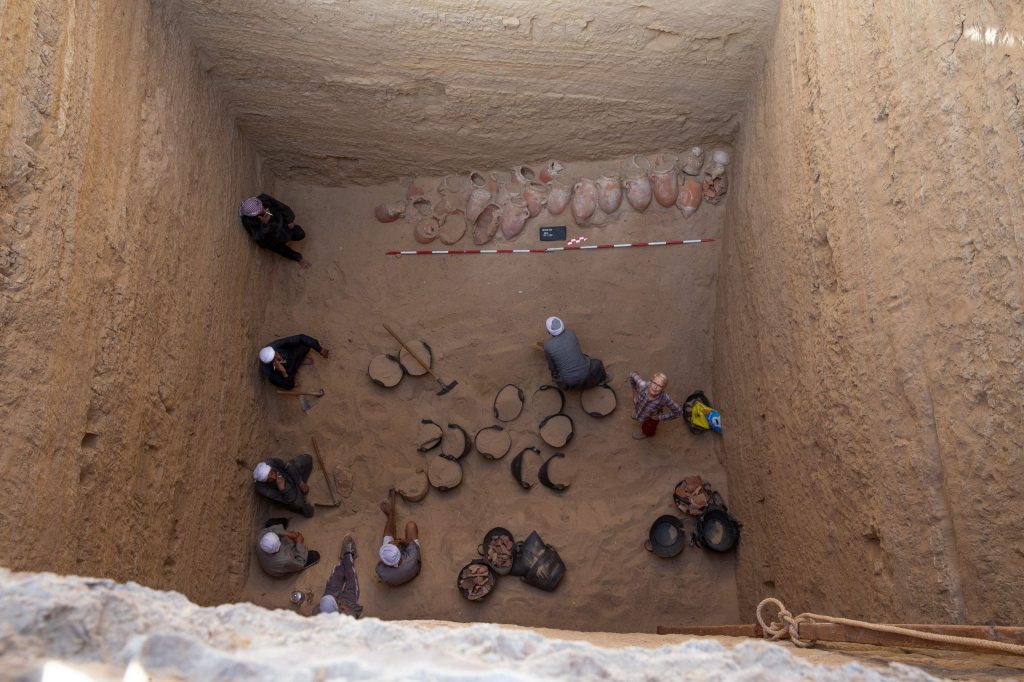
The cache was found inside a huge well measuring 5.3 x 5.3 meters, and more than 14 meters deep, containing unique embalming materials, consisting of 370 large-sized pottery vessels divided into 14 groups.
Each set contains from seven to 52 pots, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities Mostafa Waziri explained.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He added that these pots contain remnants of materials that were used during the mummification process.
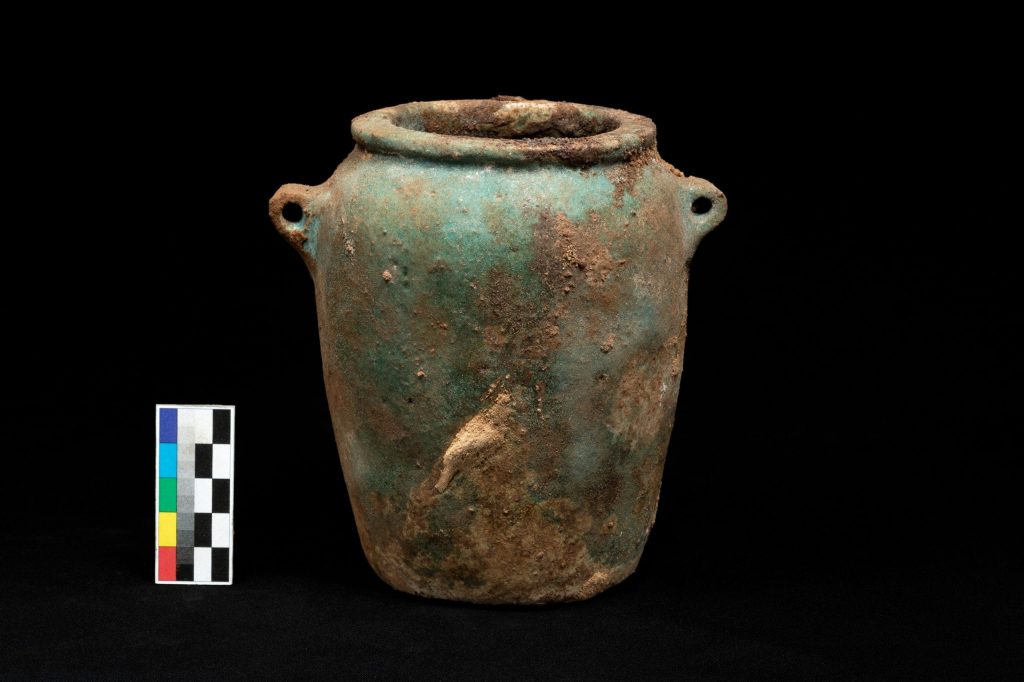

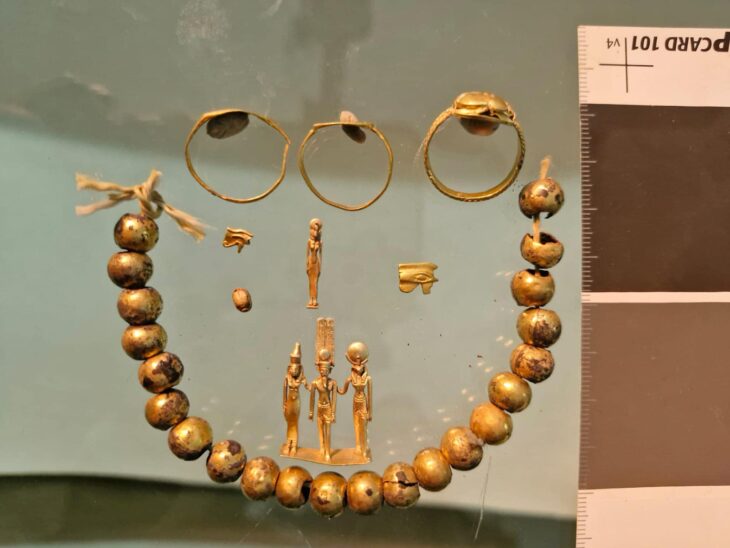
The researchers have identified ceramic vessels, containing the remnants of materials used in the mummification process, in addition to four empty limestone Canopic jars engraved with hieroglyphic texts that name an individual called ‘Wahibre’. According to the texts inscribed on them, the canopic jars belonged to a certain Wahibre-mery-Neith, son of the Lady Irturu.
Director of the mission to Abusir, Prof. Miroslav Bárta notes that “The season of 2021 was part of a long term project aiming at excavation and interpretation of monuments dating to a period when Ancient Egyptian society was looking for new means how to maintain their unique identity which was challenged by the Greek, the Persian and the Nubian armies”. The shaft tombs of Abusir, built in a similar fashion like the famous burial of Djoser, founder of the Old Kingdom, played a major role in a unique way of cultural expression by the Egyptian elites of the period.”

“Although a number of dignitaries of this name are known from this period, none of them can be identified as the owner of these canopic jars, as different mothers are attested for all of them. Judging from the size of the embalming deposit and, mainly, from the dimensions and arrangement of the nearby tomb, the owner of the tomb (and of the deposit) must have belonged to the highest dignitaries of his time, together with his closest neighbours in the cemetery – the famous admiral Udjahorresnet and general Menekhibnekau,” Prof. Ladislav Bareš, one of the leading experts on the period, said.
Deputy Director of the Czech mission, Mohamed Megahed confirmed that during 2022, archaeological excavations will continue in the area.
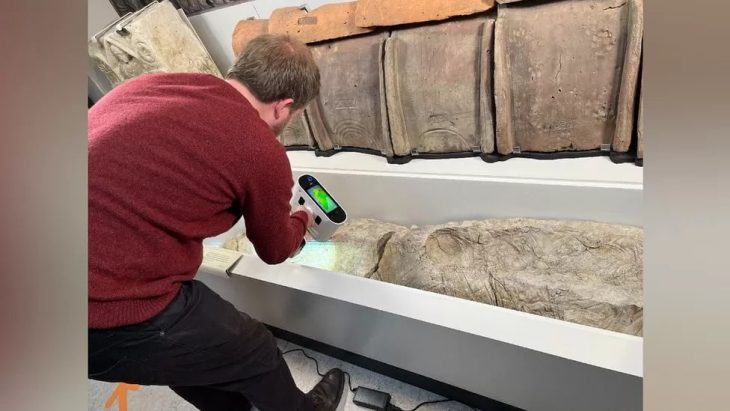
At the same time, studies and analysis of the contents of the pottery vessels will be started using modern scientific methods.
The excavations of the Czech Institute of Egyptology, Faculty of Arts, Charles University are supported by the Charles University Progres and Cooperation programs, the KREAS project (OPVVV), and the VEG of the Ministry of Education, Youth, and Sports.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Czech Institute of Egyptology, https://cegu.ff.cuni.cz/en/2022/02/09/the-largest-embalming-cache-ever-found-in-egypt-unearthed-at-abusir/