When it comes to Rare Diseases, what almost all of us think of is that this disease has affected very few people. Probably, this disease is one of the diseases that affects 1 to 5 people in 10,000. Rare diseases are nowadays a special field in medical-pharmaceutical research and treatment.
Is it possible to diagnose these rare diseases as ancient rare diseases only from human skeletons?
Working as a physical anthropologist at the Kiel University Clinical Molecular Biology Institute, Dr. Katharina Fuchs explored this question.
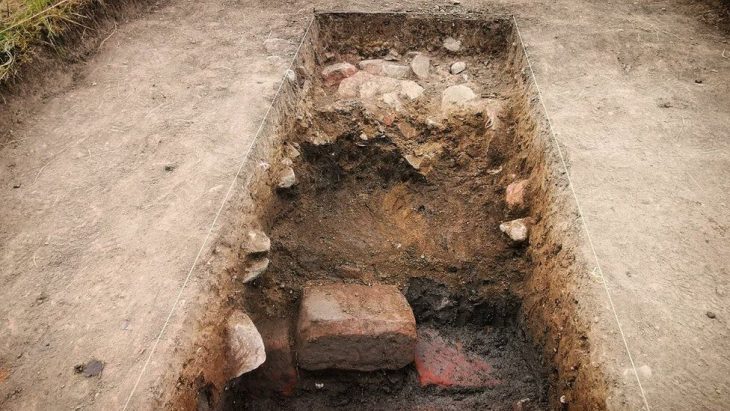
Using the medical history of male individuals from the North Caucasus Bronze Age (approximately 2200 to 1650 BC), she came to the conclusion that the standards of rare diseases used today cannot simply be transferred to the past. A recent study published in the International Journal of Paleopathology shows that not only the diagnosis of rare diseases but also the calculation of incidence and prevalence (i.e. incidence) are challenging for researchers. The level of personal barriers and social integration and support is also difficult to rebuild.
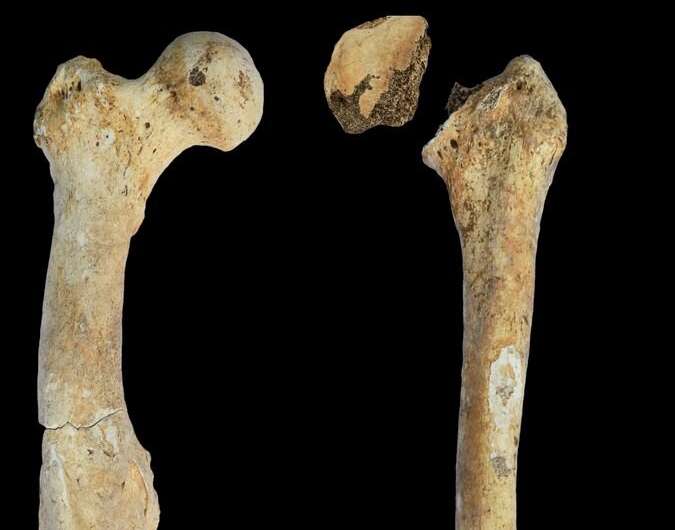
There are many conclusions that anthropologist K. Fuchs can draw from the skeleton of a Caucasian man she studied in her research: From his youth, he suffered from rare hip disease, Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease, and he had a limp gait due to that inward twisted leg. In addition, as an adult, he suffered severe skull and thigh fractures. In addition, the signs of wear on his teeth indicate that he was using them as tools during the working processes, as was customary. Also, from the objects with which he was buried, it can be concluded that he did not occupy a particularly high social position.
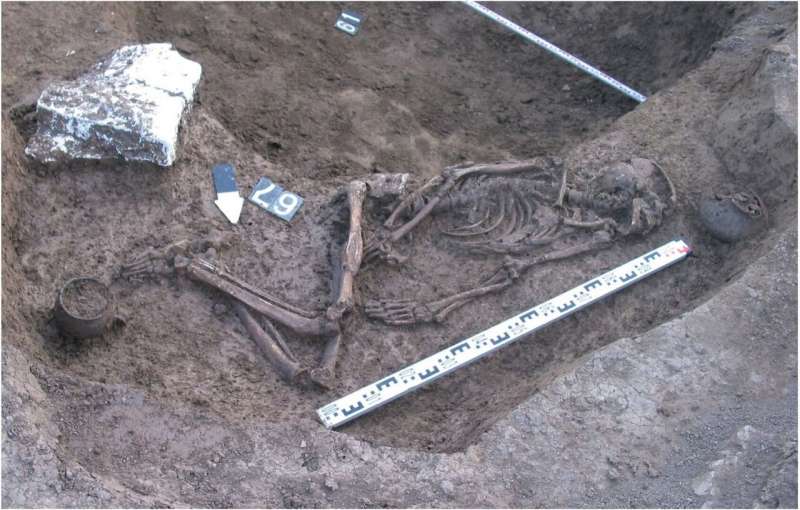
“Taken together, the results show that this man was important to society. The fractures he suffered required a high level of care. He probably survived his injuries because his fellow human beings cared for him. This gives us an idea of how the people in the North Caucasus were treated 4,000 years ago and how they treated someone who was physically limited for most of their life. ”Fuchs explains. Such considerations go beyond the topic of ancient rare diseases but illustrate the social dimension of their research.
Another result of the research is that the “rare” criteria related to ancient rare diseases cannot be defined by strict thresholds. The fact that a disease is rare today does not necessarily mean that it was rare in the past. Depending on the cause of the disease, the cause, occurrence, disappearance and most interestingly, the transition from a rare disease to a common disease is all affected by social and human ecological dynamics. This is a discovery of modern medicine, which identifies lifestyle and external influences as important components.
Therefore, research on rare diseases in the past is also related to our understanding of current diseases. One of the co-authors of the study, Dr. Julia Gresky from the German Archaeological Institute, stresses: “Since its foundation in 2019, the research of the “Ancient Rare Diseases’ workgroup also has the task to reach people who are affected today. We hope to contribute to public awareness by pointing out that humankind has always been confronted with rare diseases—but also that being affected does not have to mean social isolation.”