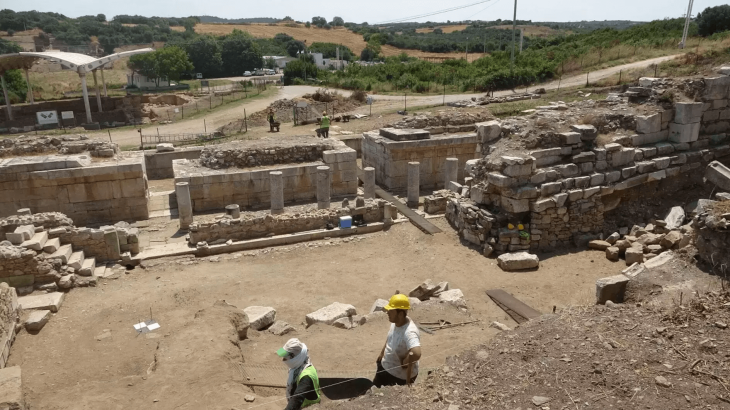
The restoration of Augustus’ colossal tomb, which is expected to be opened in 2014, has been completed. The Augustus mausoleum is expected to open to the public in March 2021.
Restorations complete in two stages cost over 10 million Euros (12 million dollars).
Funded by Fondazione TIM, the social arm of Telecom Italy, restructured the interior was restructured for tours. Fondazione TIM spent about 6 million euros on the interior.
For the restoration, a project was designed to include not only the original work but also all later structures.
Augustus had big plans for his tomb. He had started working on this structure before he was awarded the title of “Augustus”.Probably in 28 BC, this monument had developed the idea of the tomb. As a commander who wrote history and a man of management, he wanted the history he wrote to be reflected in the future in a glorious way.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
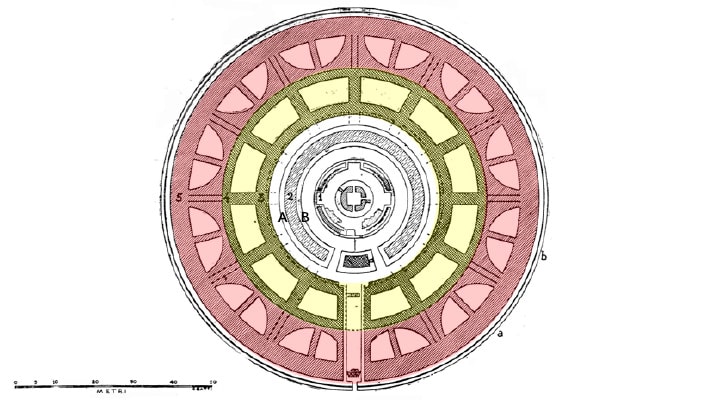
The memorial tomb is the world’s largest circular tomb with a diameter of 90 meters and a height of at least 45 meters. Only a third of the original monument is standing today. Its massive size made it as big as the nearby Pincian hill, and it is positioned on the Tiber side so it can be seen from most of the city.
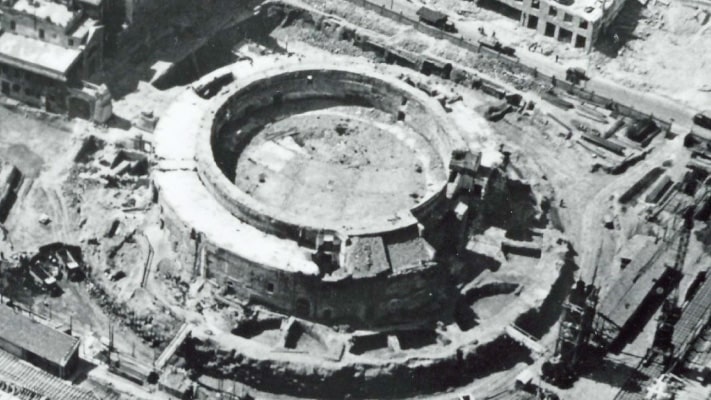

The mausoleum was built in the form of a ring divided into 12 semicircular rooms and 12 trapezoidal rooms behind the outermost wall surrounding the innermost ring. The semicircular walls of the outermost rooms and the radial walls of the trapezoidal chambers are necessary to support the weight of the entire building. The chambers of both rings had filled with earth to make the mausoleum stronger.
Although the walls of the mausoleum appear to be made of brick only today when it was first built it was covered with travertine marble.
A castle was built on residues in the Middle Ages but was destroyed in 1241. After that, the marble of the monument was gradually dismantled for reuse in building construction.
In the 16th century, the owners of a nearby palace turned the inside of the tomb into a garden. In the 1780s it was used as an amphitheater for bullfighting and spear fighting. In the 19th century, it was covered with a glass dome and used for theater performances; In the 20th century, the Auditorium Augusto was being used as a concert hall.
In 1939, the monument was able to breathe a sigh of relief as the regime demolished modern buildings in order to harmonize with ancient Rome.
Although the restoration work was interrupted during World War II, it started again in the 1950s.
It seems that Emperor Augustus did not receive the attention he expected from his people after his death. For Augustus, who consolidation the Roman Empire, and most importantly, made Rome a monumental city, Rome was far from being a loyal place.
The site will open in March 2021 and will accept free visitors for 50 minutes. Tickets must be pre-booked at mausoleodiaugusto.it.
















