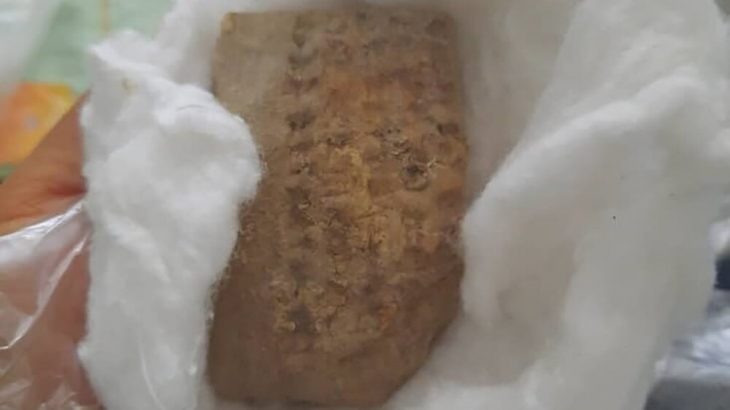
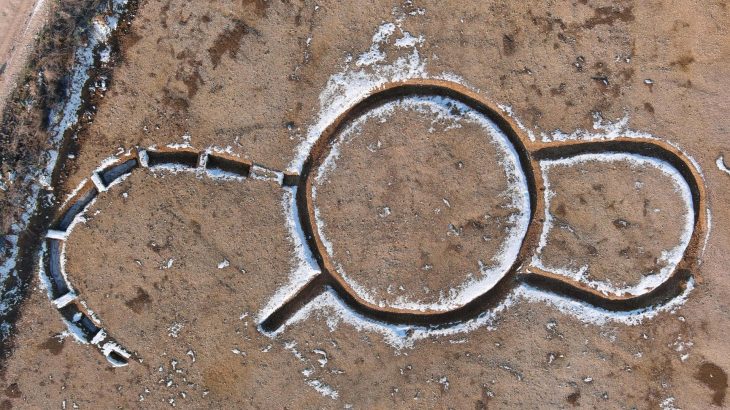
Archaeologists excavating at Villa del Mitra in Cabra, Spain, have uncovered a sanctuary dedicated to the god Mithras, along with the remains of ritual banquets.
Mithraism rose to prominence as a cult religion that became popular in the Roman Empire in the late 1st century AD. Worship was a Romanised form of the Indo-Iranian god Mithra. In Roman Empire during the 2nd and 3rd centuries, this deity was honored as the patron of loyalty to the emperor.
The Villa del Mitra, located within the Roman city of Licabrum, dates from the first century AD. The villa was named after a Mitra de Cabra sculpture discovered in situ in the second century AD, depicting Mithras sacrificing a bull (a symbol of death and resurrection).
Archaeologists from the University of Málaga, the Carlos III University of Madrid, and the University of Córdoba have, in the most recent excavations, uncovered the remains of a Mithraic sanctuary dating to the second century AD, with a second phase of construction from the end of the third century AD.
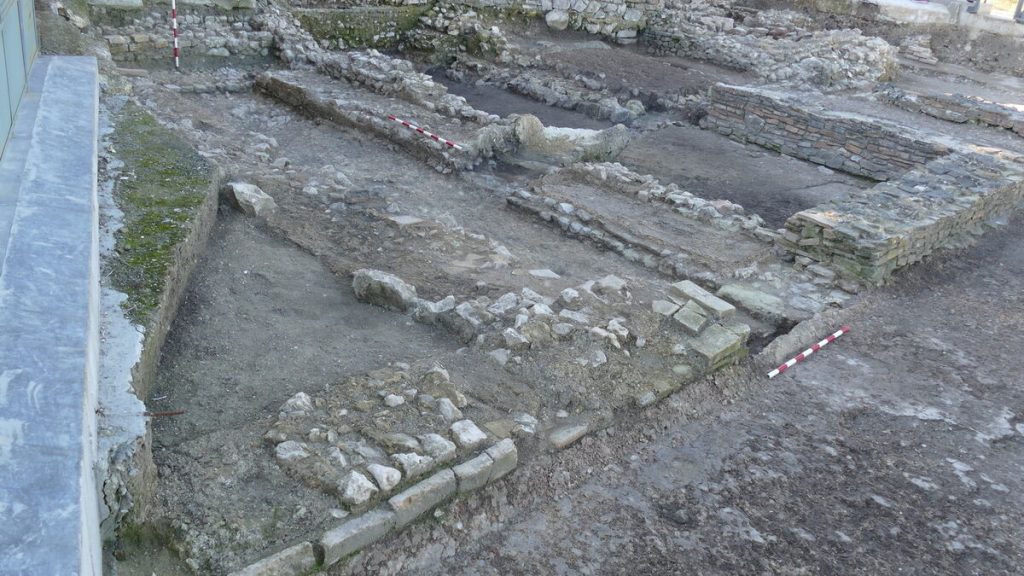

The sanctuary is a rectangular room located to the southwest of the Domus, measuring 7.2 by 2.5 meters (24 by 8 feet). It has a narrow entrance, that descends several steps leading into the sanctuary that has two flanking stone benches. On the right is a small water tank measuring 1.70 by 0.65 meters.
The research team believes that these benches were used by worshipers who sat to perform rituals and feasts in Mithras’ honor. The walls have fragments of Roman bricks, one of which has two holes or niches which would likely have held a tauroctony sculpture.
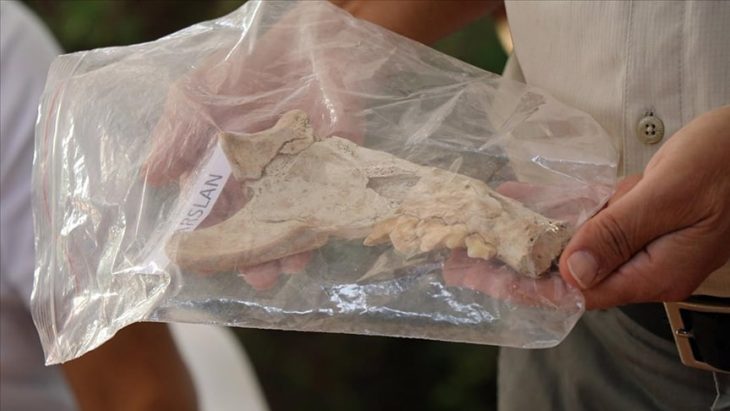
The floor is covered in a dark burnt layer that, upon closer inspection, revealed fragments of pigs, birds, and rabbits, indicating evidence of cooking during the ritual banquets.
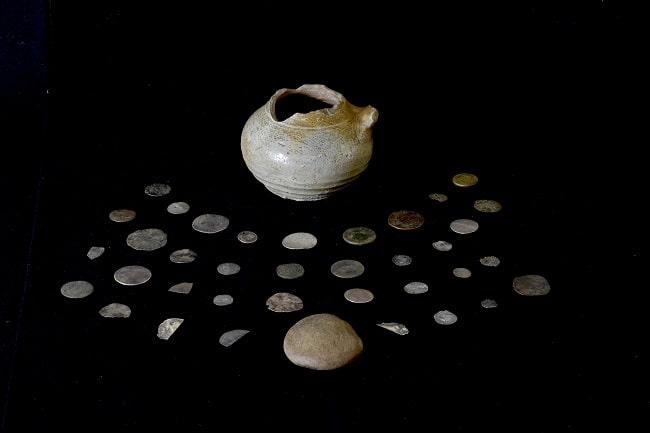
The villa was originally excavated between 1972 and 1973, during which time a courtyard with a pond and several adjacent rooms with mosaic flooring was found. Later excavations in 1981 uncovered the remains of a hypocaust, or subfloor heating system, as well as coins depicting Philip the Arab, Diocletian, and Valentinian II.