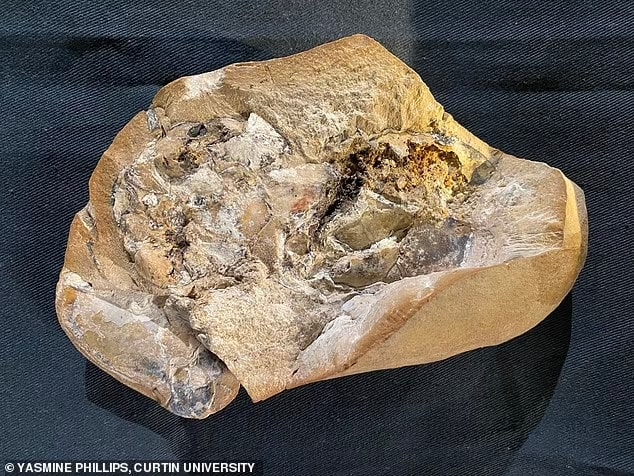
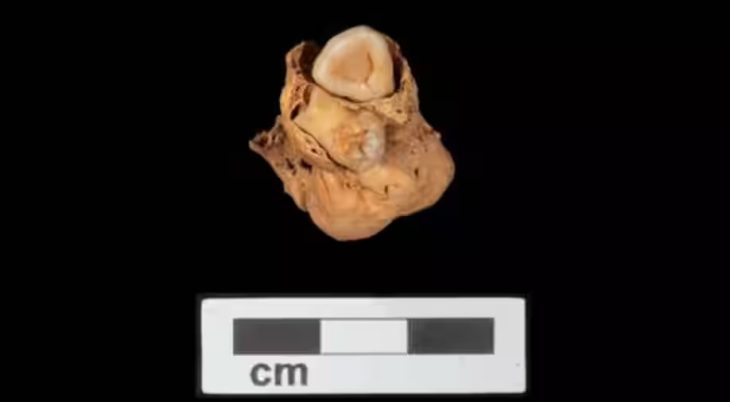
Researchers from Curtin University have discovered the world’s oldest heart in a ‘beautifully preserved’ ancient jawed fish fossil 380 million years old.
The heart was discovered alongside a separate fossilized stomach, intestine, and liver, with the organs arranged in a manner similar to modern shark anatomy.
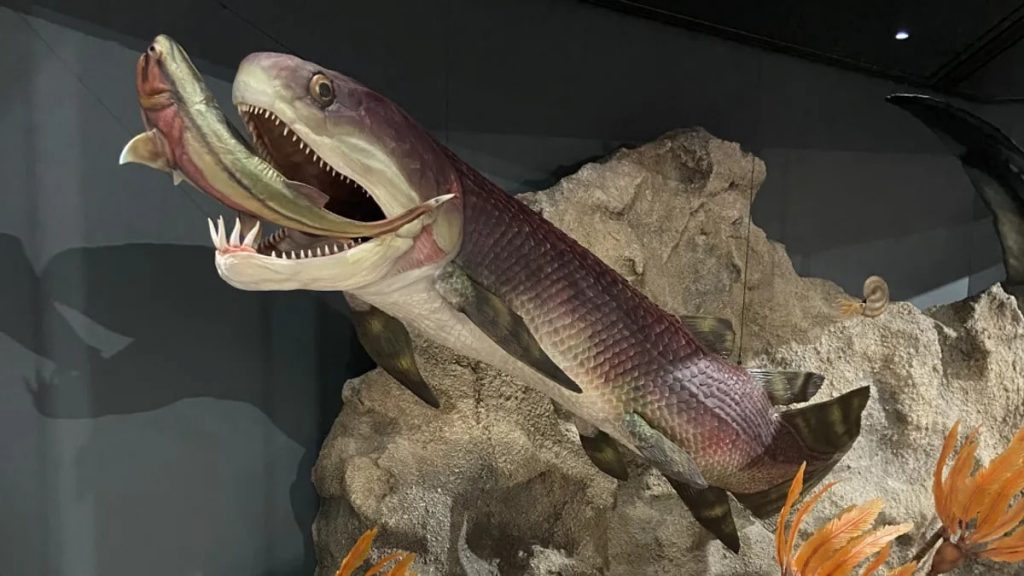
The new research, published today in Science, found that the position of the organs in the body of arthrodires – an extinct class of armored fishes that flourished through the Devonian period from 419.2 million years ago to 358.9 million years ago – is similar to modern shark anatomy, offering vital new evolutionary clues.
“Evolution is often thought of as a series of small steps, but these ancient fossils suggest there was a larger leap between jawless and jawed vertebrates,” said Professor Kate Trinajstic, lead researcher from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences and the Western Australian Museum, in a statement.
“These fish literally have their hearts in their mouths and under their gills – just like sharks today.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“For the first time, we can see all the organs together in a primitive jawed fish, and we were especially surprised to learn that they were not so different from us.”
“However, there was one critical difference – the liver was large and enabled the fish to remain buoyant, just like sharks today. Some of today’s bony fish such as lungfish and birchers have lungs that evolved from swim bladders but it was significant that we found no evidence of lungs in any of the extinct armored fishes we examined, which suggests that they evolved independently in the bony fishes at a later date.”
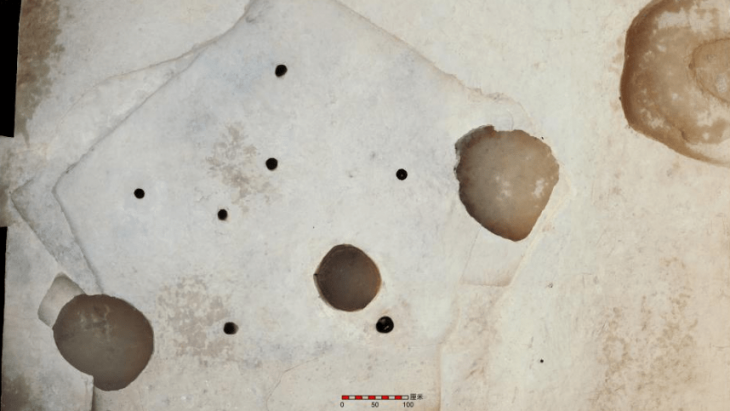
The specimen is not only remarkable in its age but also that it was preserved in its 3D form, something which the researchers didn’t become completely aware of until they were at the scanning stage.
Lead researcher John Curtin Distinguished Professor Kate Trinajstic, from Curtin’s School of Molecular and Life Sciences and the Western Australian Museum, said the discovery was remarkable given that soft tissues of ancient species were rarely preserved and it was even rarer to find 3D preservation.
“As a paleontologist who has studied fossils for more than 20 years, I was truly amazed to find a 3D and beautifully preserved heart in a 380-million-year-old ancestor,” Professor Trinajstic said.
“Evolution is often thought of as a series of small steps, but these ancient fossils suggest there was a larger leap between jawless and jawed vertebrates. These fish literally have their hearts in their mouths and under their gills – just like sharks today.”
This research presents – for the first time – the 3D model of a complex s-shaped heart in an arthrodire that is made up of two chambers with the smaller chamber sitting on top.
Professor Trinajstic said these features were advanced in such early vertebrates, offering a unique window into how the head and neck region began to change to accommodate jaws, a critical stage in the evolution of our own bodies.
The Gogo Formation, in the Kimberley region of Western Australia where the fossils were collected, was originally a large reef.

Enlisting the help of scientists at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation in Sydney and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility in France, researchers used neutron beams and synchrotron x-rays to scan the specimens, still embedded in the limestone concretions, and constructed three-dimensional images of the soft tissues inside them based on the different densities of minerals deposited by the bacteria and the surrounding rock matrix.
This new discovery of mineralized organs, in addition to previous finds of muscles and embryos, makes the Gogo arthrodires the most fully understood of all jawed stem vertebrates and clarifies an evolutionary transition on the line to living jawed vertebrates, which includes the mammals and humans.
Co-author Professor John Long, from Flinders University, said: “These new discoveries of soft organs in these ancient fishes are truly the stuff of palaeontologists’ dreams, for without doubt these fossils are the best preserved in the world for this age. They show the value of the Gogo fossils for understanding the big steps in our distant evolution. Gogo has given us world firsts, from the origins of sex to the oldest vertebrate heart, and is now one of the most significant fossil sites in the world. It’s time the site was seriously considered for world heritage status.”
Co-author Professor Per Ahlberg, from Uppsala University, said: “What’s really exceptional about the Gogo fishes is that their soft tissues are preserved in three dimensions. Most cases of soft-tissue preservation are found in flattened fossils, where the soft anatomy is little more than a stain on the rock. We are also very fortunate in that modern scanning techniques allow us to study these fragile soft tissues without destroying them. A couple of decades ago, the project would have been impossible.”
The Curtin-led research was a collaboration with Flinders University, the Western Australian Museum, the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility in France, the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation’s nuclear reactor, Uppsala University, Monash University’s Australian Regenerative Medicine Institute, and the South Australian Museum.
Journal reference:
Trinajstic, K., et al. (2022) Exceptional preservation of organs in Devonian placoderms from the Gogo lagerstätte. Science. doi.org/10.1126/science.abf3289.