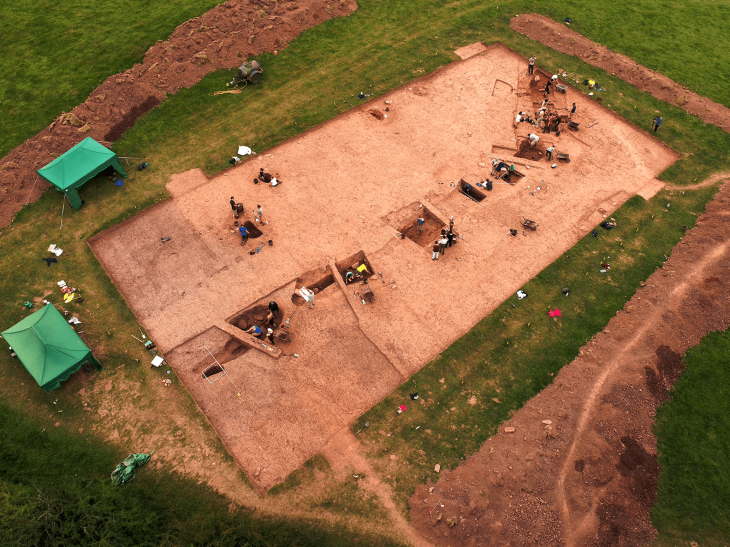
Recent research conducted by scholars from the Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB) and the Max Planck Institute for Social Anthropology has identified the economic and political boundaries that delineated El Argar, the first state structure in the Iberian Peninsula, approximately 4,000 years ago.
Recognized as the first state structure on the Iberian Peninsula, El Argar maintained intricate relationships with neighboring communities from the Bronze Age of La Mancha and Valencia, which had less centralized social systems. These interactions were characterized by a complex web of exchanges that influenced both economic practices and social hierarchies in the region.
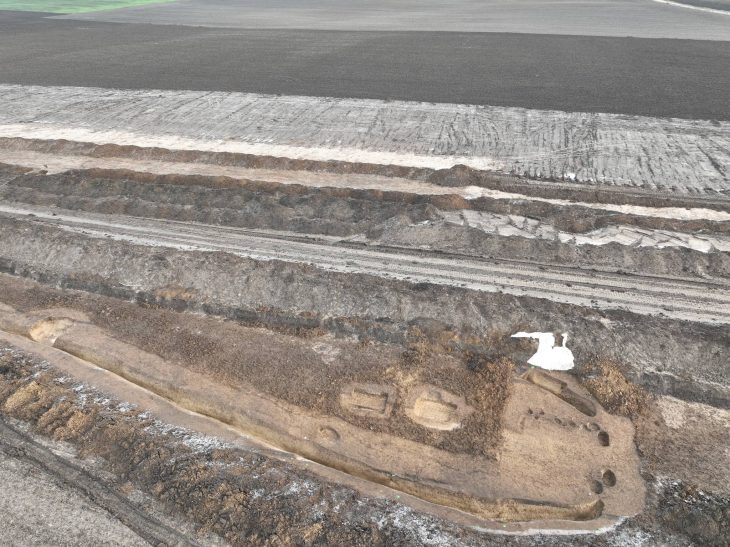
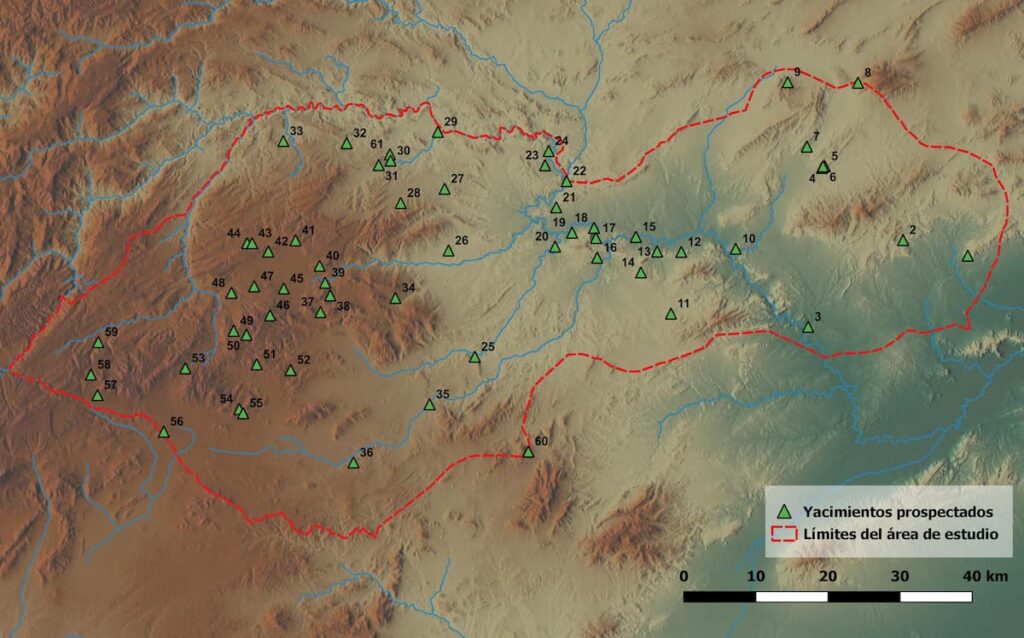
The research, published in the Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, utilized an innovative analysis of ceramic production and circulation in the northern province of Murcia. This methodology enabled scientists to reconstruct the interactions between these groups during the Early Bronze Age (2200-1550 BCE), effectively delineating border dynamics and their influence on social configurations of the time.
Roberto Risch, a professor in the Department of Prehistory at UAB and coordinator of the study, emphasized the importance of understanding how borders were created and maintained in the context of the first state entities. Despite the significance of borders in archaeology, they have received relatively little attention until now.
The analysis revealed clear patterns of interaction between El Argar and its neighboring communities, highlighting active zones of exchange and negotiation. Adrià Moreno Gil, a researcher at the Max Planck Institute and lead author of the study, noted that pottery vessels were not merely everyday objects but also reflected the economic and political networks of the era.
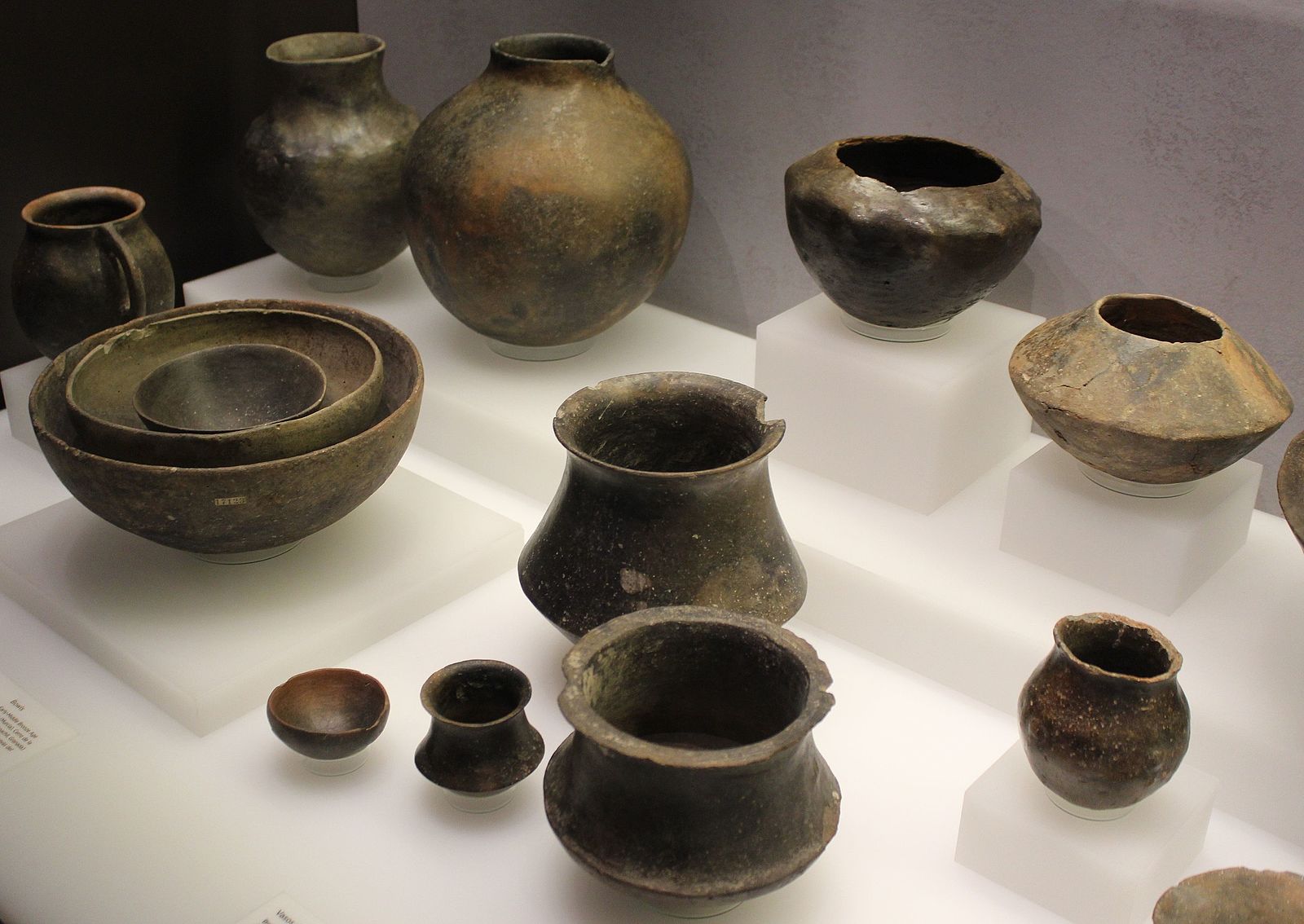
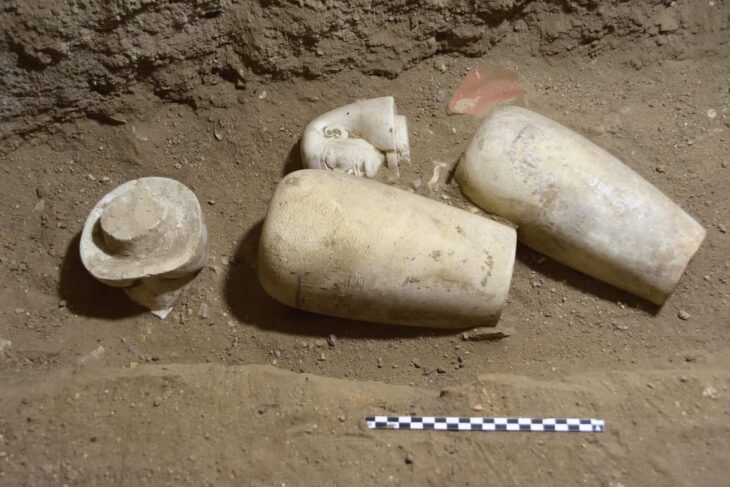
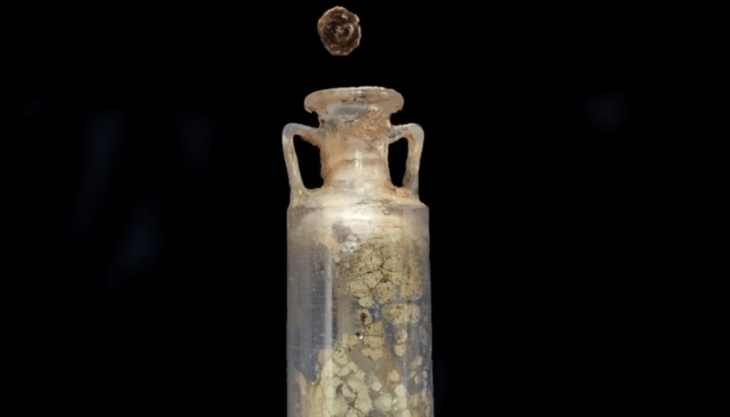
The study focused on ceramic production in the Segura River basin, where Argaric ceramics were predominantly found in the southern settlements, indicating a regional-scale distribution network likely controlled by El Argar. In contrast, the northern part of the territory exhibited numerous small pottery workshops utilizing local clays, suggesting distinct economic systems between the communities.
This disparity in ceramic production and distribution underscores the existence of asymmetrical relationships among the southeastern Iberian groups. El Argar’s dominance extended beyond strategic resources like metals to everyday items such as ceramics, reinforcing a center-periphery system that favored Argaric society.

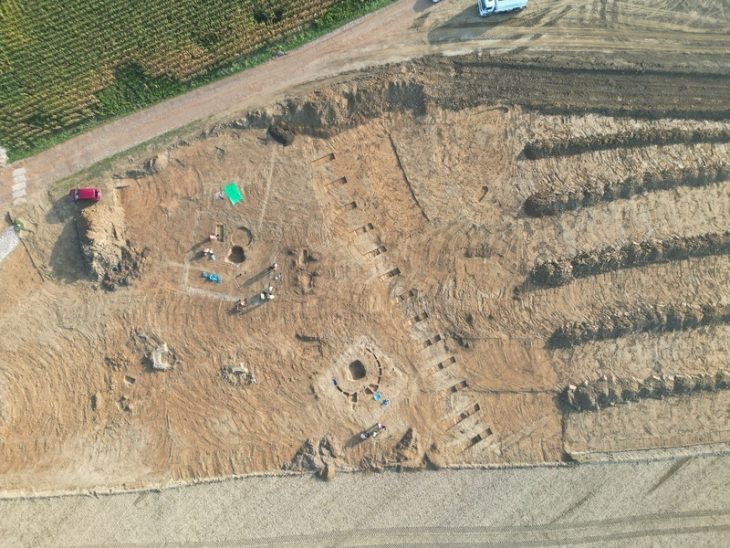
Employing a novel approach that combined archaeological surveys, petrographic analysis, and geographic information systems (GIS), the research team mapped ceramic production and circulation areas with unprecedented detail. Carla Garrido García, a doctoral researcher at UAB and co-author of the study, stated that ceramic analysis is crucial for understanding economic exchanges and social relationships in prehistoric contexts.
The implications of this research extend beyond El Argar, as the methodology could be applied to study other contemporary cultures, such as the Únětice culture in Central Europe and the Minoan civilization in Crete, to explore their border structures and relationships with neighboring groups.
Funded by the Max Planck Institute for Social Anthropology, the Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies (ICREA), and the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities, this study represents a significant advancement in the understanding of prehistoric frontiers and the formation of early state societies.
Autonomous University of Barcelona
Moreno Gil, A., Garrido García, C., Bonora Soriano, B. et al. Bronze Age Frontiers and Pottery Circulation: Political and Economic Relations at the Northern Fringes of El Argar, Southeast Iberia, ca. 2200–1550 BCE. J Archaeol Method Theory 32, 36 (2025). doi.org/10.1007/s10816-025-09702-y
Cover Image Credit: Argaric ceramics. Wikipedia Commons