During excavations at Kastel Fortress, the national monument of Bosnia and Herzegovina, students and professors of Archaeology and History found an ancient coin and, more importantly, they think they have discovered an ancient necropolis.
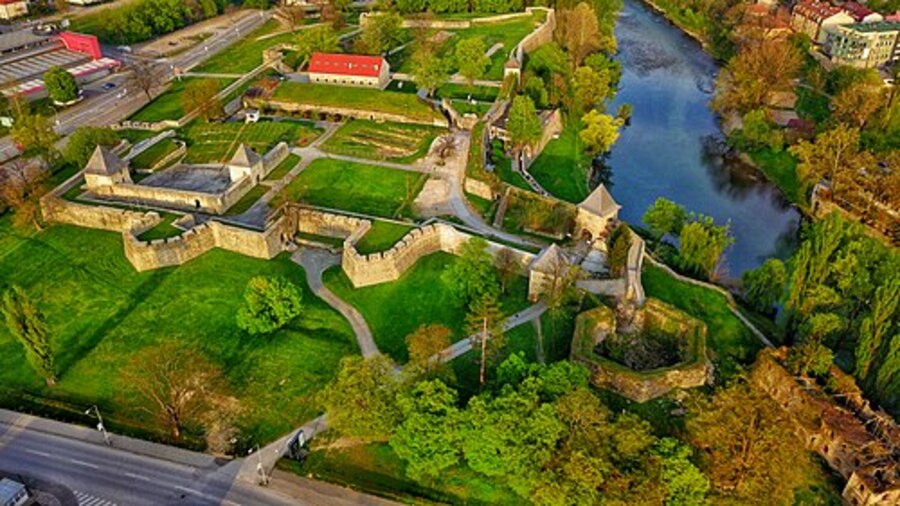
Kastel Fortress the oldest historical monument in Banja Luka, is situated on the left bank of the Vrbas River, between the City Bridge and the month of the Crkvena River. It is believed to have been constructed on the remains of a Roman settlement known as Castra.
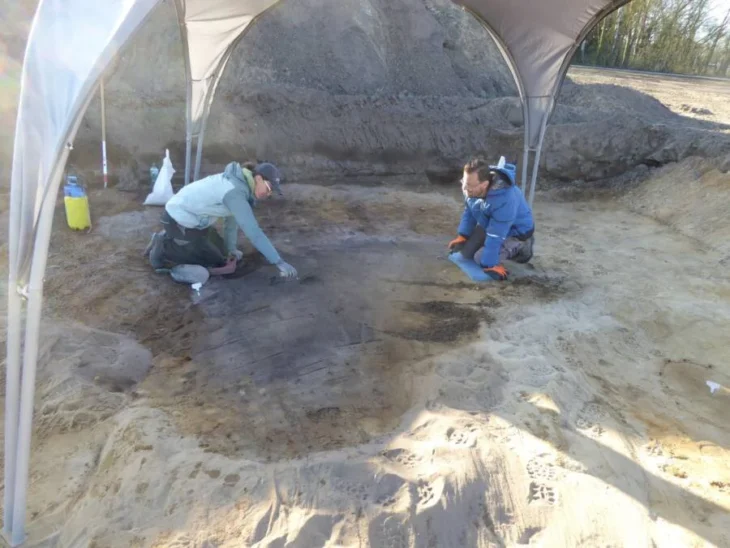
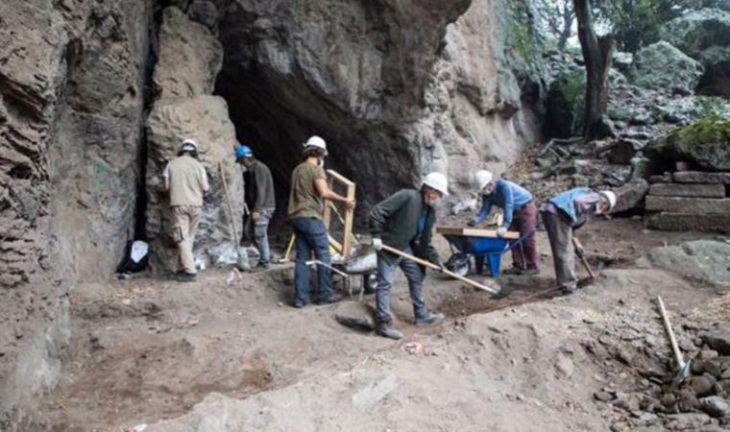
Boris Radic, Senior Associate at the Republican Institute for the Protection of Cultural and Historical Heritage, told Sarajevo Times that the discovery took place at an archaeological school attended by students of Archaeology and History from both public universities in Republika Srpska (RS).
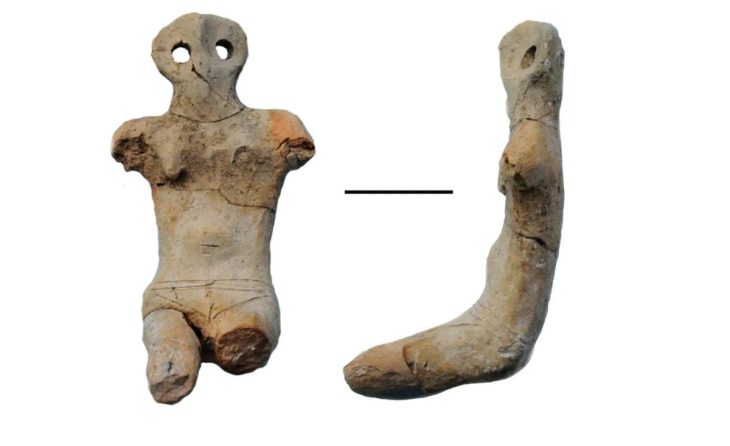
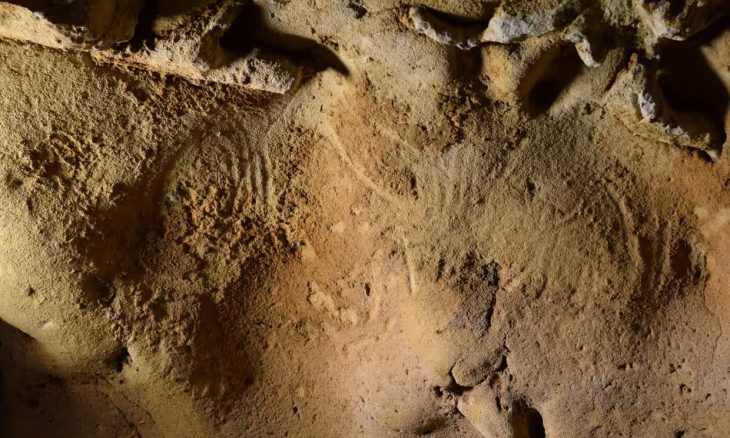
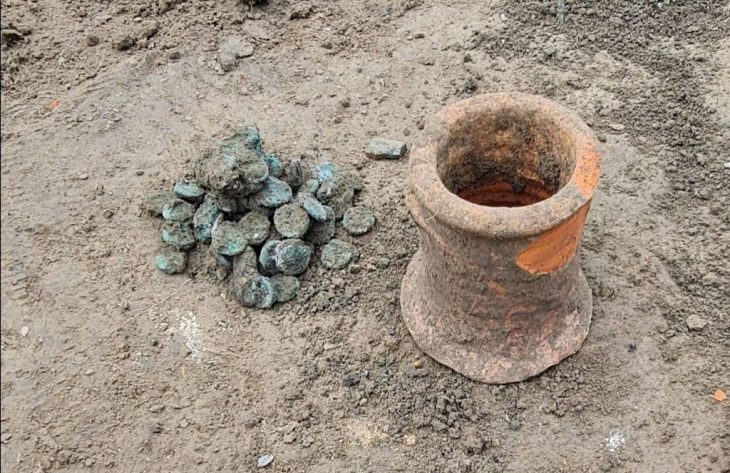
According to Boris Radic, they found an ancient cemetery in Kastel, the existence of which was not even known. The exact results will become clear after Carbon 14 dating. The excavations also uncovered a late antique coin from the 4th century.
Excavations were carried out at the site in the 1980s. On-site, flint tools from the Gravettiena period—the youngest stage of the upper Paleolithic period, which spanned from the XIX to the first quarter of the XII millennium BCE—were discovered. Also, a settlement was discovered, dating back to the Eneolith period, containing ceramics of the Baden culture group and a small number of ceramic fragments from the Vučedol culture. Later, on the basis of methodological studies, ancient geographical maps, and mostly accidental discoveries, it was established that an ancient Roman settlement called Castra existed here.
Assuming that the site had been completely excavated in the 1980s, the archaeology school started out as a cleaning project six years ago.
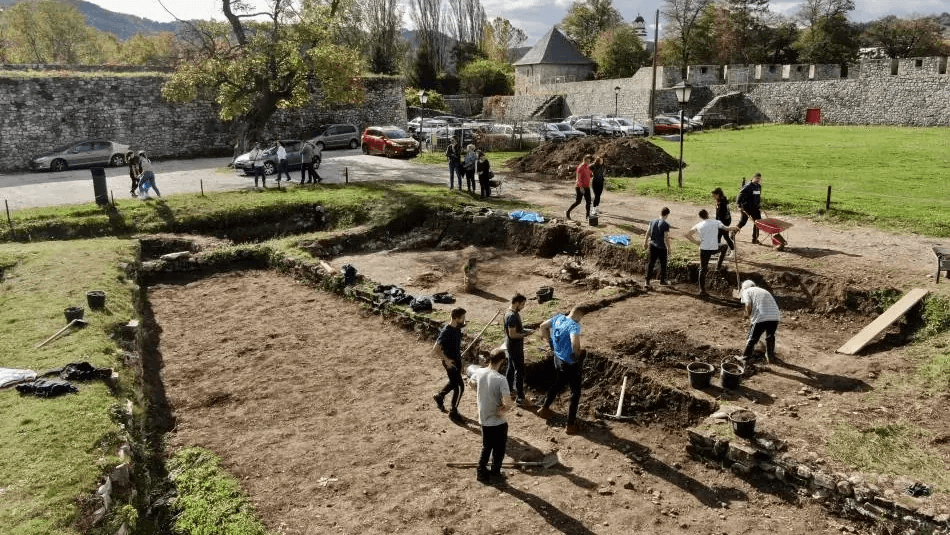

“During the first cleaning, six years ago, we found that it was not fully examined and that additional archaeological layers remained. We then decided to make this a regular archaeology school, which now serves as practical instruction for History and Archaeology students,” explains Radic.
He points out that because Kastel was continuously inhabited, both professors and students have the chance to observe how the layers mix there, but it also makes their job challenging because it is challenging to distinguish between the layers.
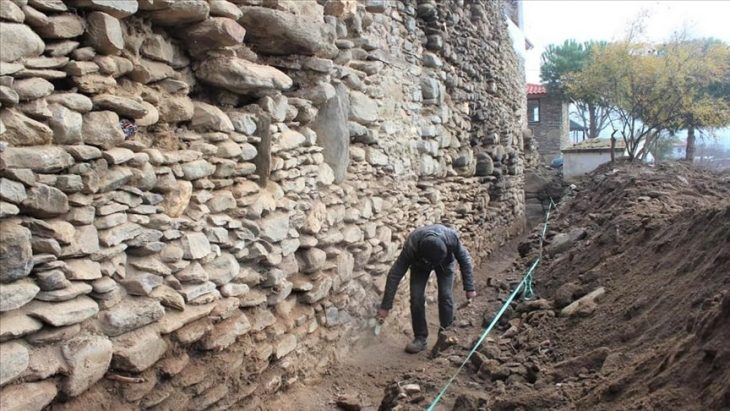
“So now we unexpectedly came across a necropolis, and each year, we come across human skeletons. This isn’t a conventional cemetery; based on the orientation of the deceased, we assume they are from an earlier period, as they do not align with Christian or Muslim burial customs. Moreover, these graves are embedded into ancient walls, and this year, we discovered that people disregarded the walls, digging graves and thereby destroying walls that could date to the 2nd century,” Radic said.
However, it is not possible to say anything definite until the Carbon 14 dating results are determined. The researcher stated that there were also many ancient pottery in the layer they uncovered, but they were mixed with Turkish pottery. They also found a 4th-century coin, but this alone does not mean anything.
This project was carried out in cooperation with the Museum of Republika Srpska, the Association of Archaeologists of Republika Srpska, the Faculty of Philosophy of the University of Banja Luka, and the Faculty of Philosophy of the University of East Sarajevo. The project was co-financed by the Ministry of Education and Culture of Republika Srpska and the city of Banja Luka.
Cover Image Credit: Tomas Damjanovic Banjaluka – CC BY-SA 4.0