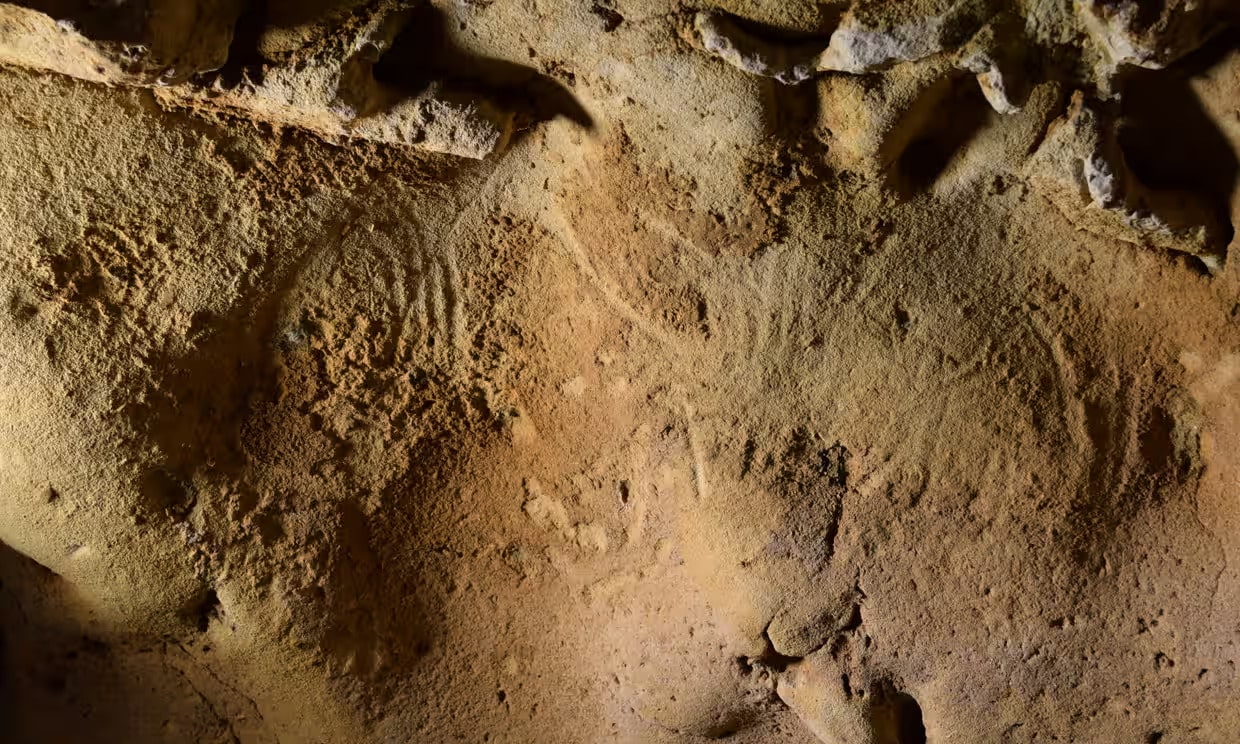
According to a recent study published, the oldest engravings made by Neanderthals have been discovered on a cave wall in France.
Hundreds of faint stripes, dots, and wavy lines at the Loire Valley site were created more than 57,000 years ago, say researchers.
Hundreds of faint stripes, dots, and wavy lines that adorn a cave wall in central France are the oldest known engravings made by Neanderthals, according to Jean-Claude Marquet of the University of Tours in France and colleagues, who analyzed ancient markings.
Authors of study published in PLOS One analyzed, plotted, and 3D modeled these intriguing markings and compared them with other wall markings of all types to confirm that they are the organized, intentional products of human hands.
The team also dated deep sediment layers that had buried the cave’s opening to reveal that it was sealed up with the engravings inside at least 57,000 and as long as 75,000 years ago—long before Homo sapiens arrived in this part of Europe.
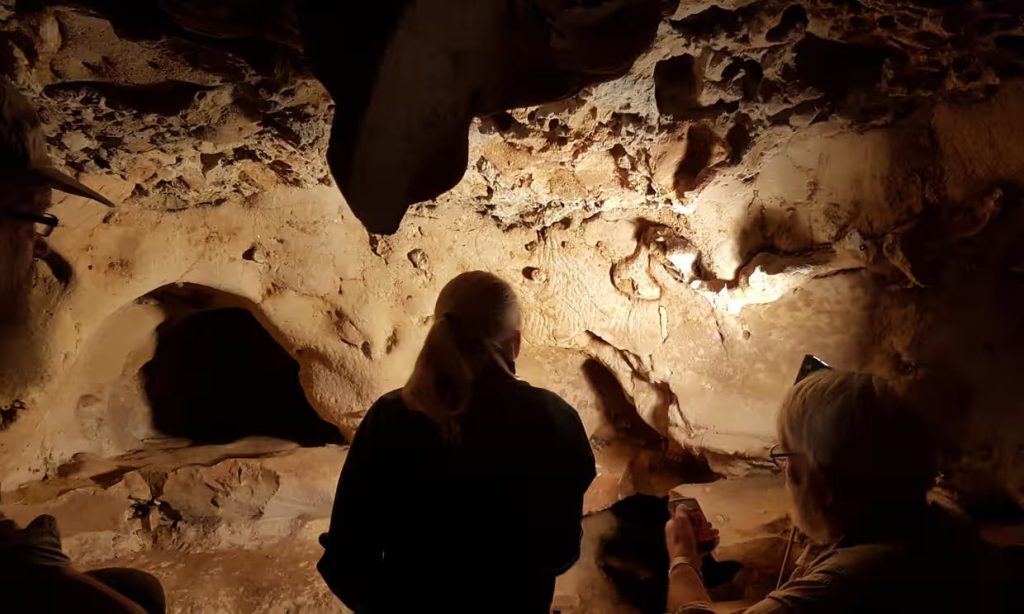

The authors said: “Fifteen years after the resumption of excavations at the La Roche-Cotard site, the engravings have been dated to over 57,000 years ago and, thanks to stratigraphy, probably to around 75,000 years ago, making this the oldest decorated cave in France, if not Europe!”
Over the past few decades, research has shed light on the cultural sophistication of Neanderthals. However, our understanding of their symbolic and artistic expression remains limited. Only a short list of symbolic productions is attributed to Neanderthals, and the interpretation of these is often the subject of debate.
This, combined with the fact that stone tools within the cave are only Mousterian, a technology associated with Neanderthals, is strong evidence that these engravings are the work of Neanderthals.
Because these are non-figurative symbols, the intent behind them is unclear. However, they share a similar age with Homo sapiens engravings found in other parts of the world. This adds to the mounting evidence that Neanderthal behavior and activities were as complex and varied as those of our own ancestors.
“For a long time it was thought that Neanderthals were incapable of thinking other than to ensure their subsistence,” notes archaeologist and study co-author Jean-Claude Marquet, of the University of Tours, France. “I think this discovery should lead prehistorians who have doubts about Neanderthal skills to reconsider.”
La Roche-Cotard is an ancient cave nestled on a wooded hillside above the Loire River. It was first uncovered in 1846 when quarries were operated in the area during the construction of a railroad line.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286568
Cover Photo: Examples of engravings discovered in the La Roche-Cotard cave (Indre et Loire – France). On the left, the “circular panel” (ogive-shaped tracings), and on the right the “wavy panel” (two contiguous tracings forming sinuous lines). Credit: Jean-Claude Marquet, CC-BY 4.0