Archaeologists have found a mysterious prehistoric site believed to be a 6,500-year-old Stone Age cemetery just 50 miles (80 kilometers) south of the Arctic Circle.
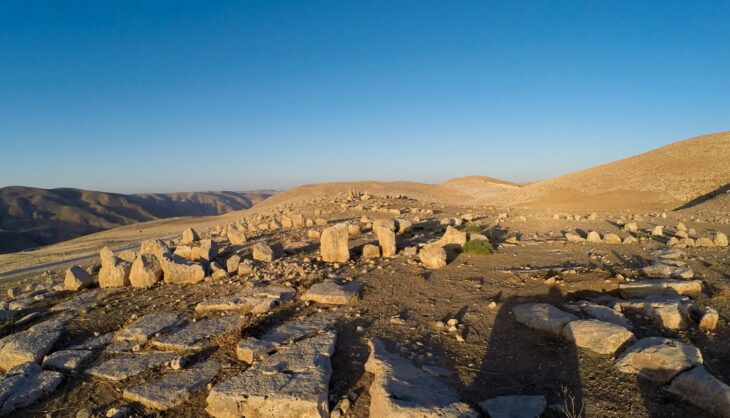
The prehistoric site is known as Tainiaro, located about 50 miles south of the Arctic Circle in the Finnish region of Lapland. Although the hypothesis that the Tainiaro site is a Stone Age cemetery remains unproven, if confirmed, it could drastically alter ideas about the history of Northern Europe. Furthermore, the proof would make Tainiaro the northernmost Stone Age graveyard in the world.
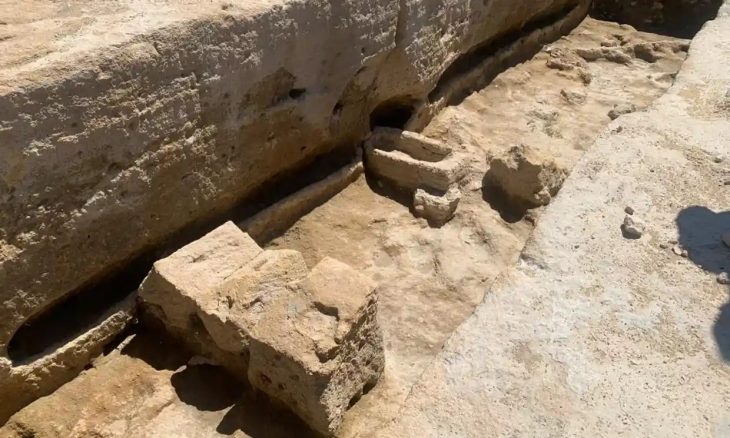
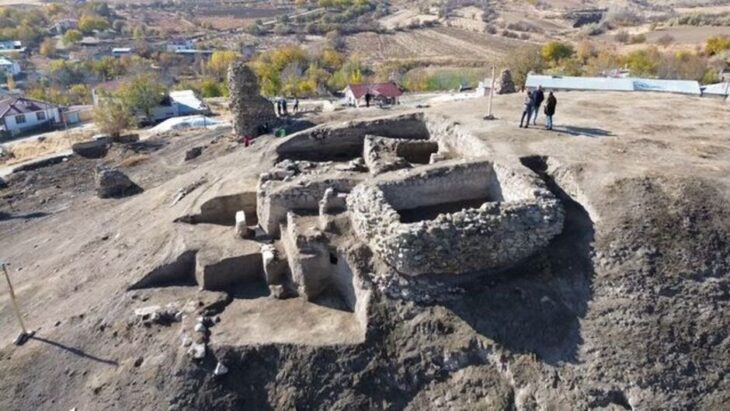
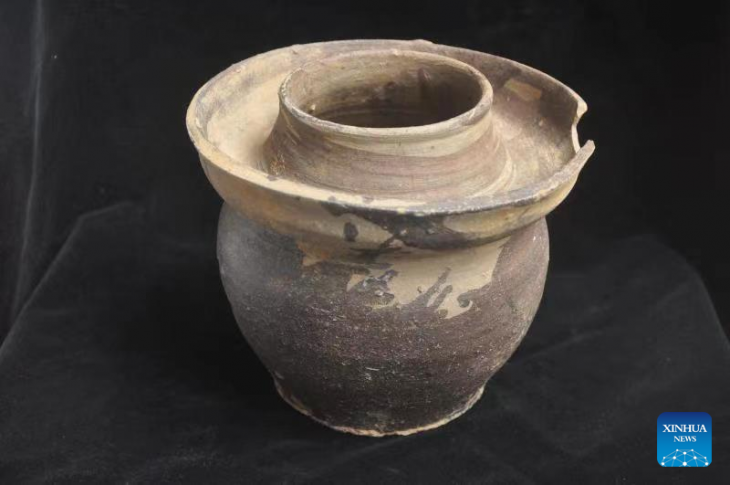
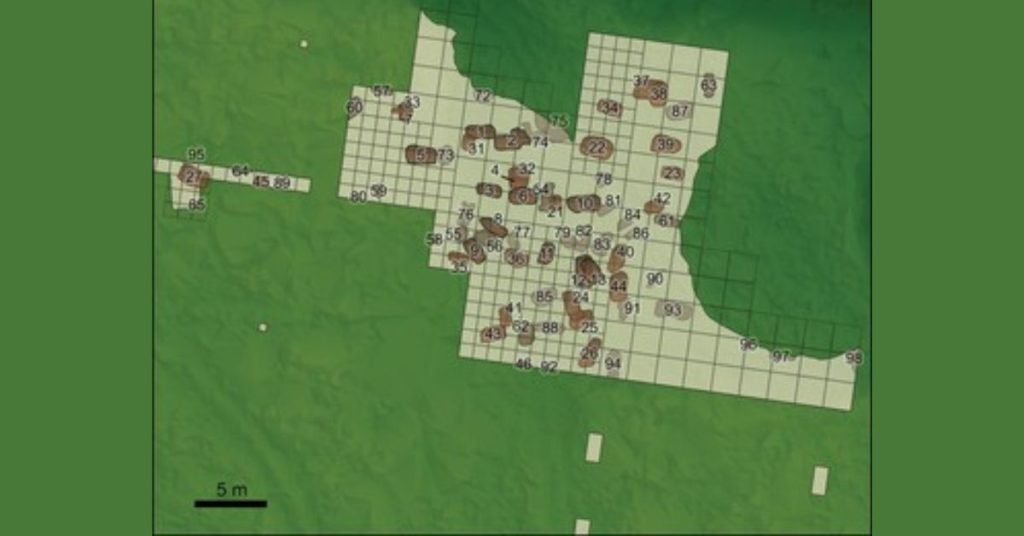
Back in 1959, local workers came across stone tools in Simo, which is situated near the Baltic Sea’s northern edge, just 80 kilometers to the south of the Arctic Circle. The site, named Tainiaro, underwent partial excavations in the 80s. This led to the revelation of thousands of artifacts, including pottery, stone tools, and animal bones.
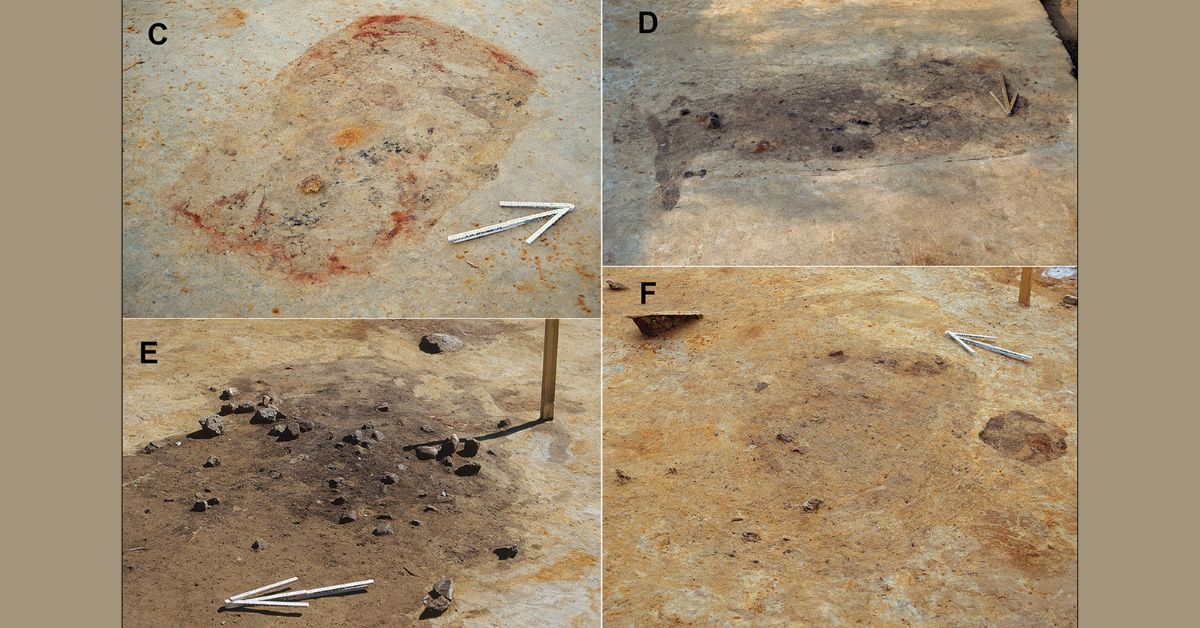
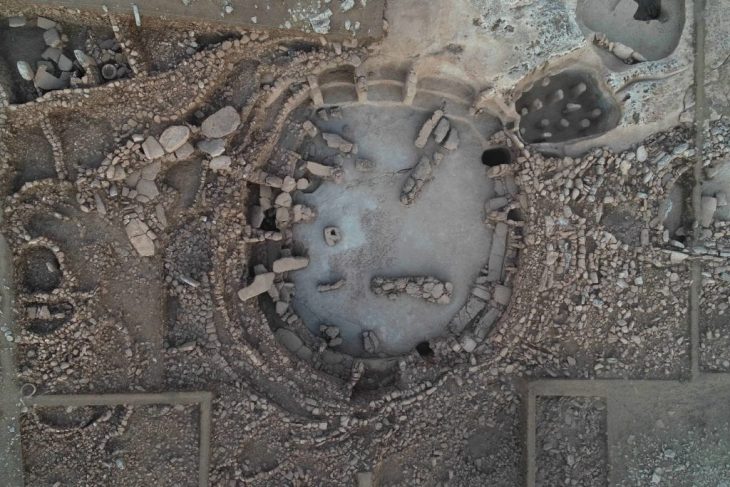
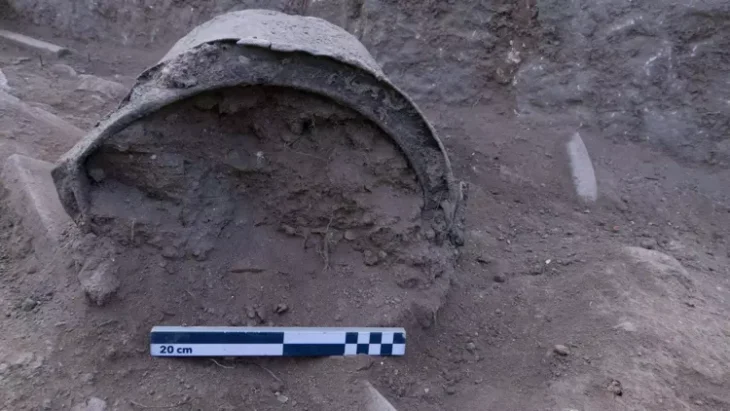
The archaeologists were also able to notice 127 possible pits of different sizes that could have been sediment-filled. Some had burning evidence, while others had red ochre traces. Red ochre is a natural iron pigment that is crucial to several burials of the Stone Age. However, without skeletal evidence, which quickly decayed in the acidic soil of this region, the Taniaro’s identification as a cemetery was never confirmed.
The team of archaeologists working on the site has published its findings and theories in the Cambridge University Press archaeological journal Antiquity in the paper entitled “A large fifth-millennium BC cemetery in the subarctic north of the Baltic Sea.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
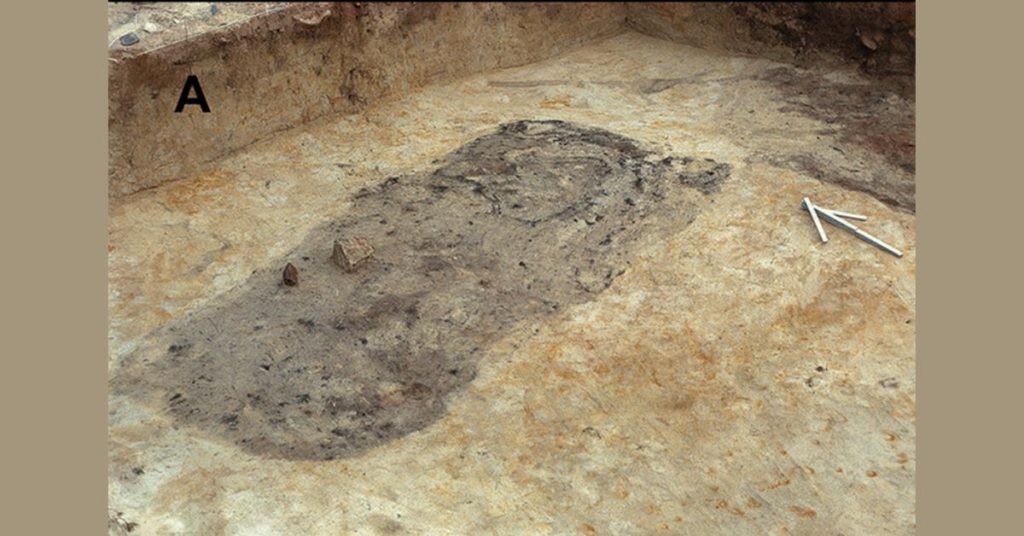

Archaeologists were initially unsure whether the pits were graves, hearths, or a combination of the two. To determine the nature, the team examined the contents and sizes of the pits and compared them to hundreds of Stone Age graves in 14 cemeteries. The archaeologists were then able to determine that at least 44 of these could have housed human burials. Furthermore, the pits’ rounded-edge rectangular shape, red ochre traces, and occasional artifacts suggest that they were graves.
The authors note in the study that Tainiaro should be considered a cemetery despite no skeletal material surviving in the area was found.
Their research paper mentions, “Despite the absence of skeletal evidence, dozens of fifth-millennium BC pits have been tentatively interpreted as burials… Many of the pits are consistent in form with those used for inhumation at contemporaneous sites suggesting that Tainiaro is one of the largest Stone Age cemeteries in northern Europe and raising questions about the cultural and subsistence practices of prehistoric societies in the subarctic.”
While elsewhere it would have been possible to find human remains in these pits, which would have confirmed the Stone Age cemetery hypothesis, the soil in Finland is so acidic that nothing organic buried in the ground could survive for more than a thousand years.
” We’re talking more than six millennia here. So the outlines of pits and their inner traces are all that local archaeologists have to go by. But there was not even a map of the place,” Aki Hakonen, an archaeologist with the University of Oulu in Finland and one of the authors of the paper, said in a statement to Newsweek.
Archaeologist Aki Hakonen, who led the team, explains that based on the burial pit shapes at other areas, the dead in Tainiaro could have been buried on their sides or backs, with bent knees. He notes that furs could have been present and that the dead could have been wrapped in the skins of seals. Hakonen also notes that red ochre and grave goods may have been mixed into the fill dirt or the grave.
Excavations have only been done on one-fifth of Tainiaro. This means that the number of graves could actually be more than 200.
















