Something novel has been discovered by Polish archaeologists working on the excavation of the Church of St. Francis of Assisi in Krakow; it is thought to be the first discovery of its kind in the nation. A first-of-its-kind medical prosthesis: a nearly 300-year-old device that helped a man with cleft palate live more comfortably with this condition.
Anna Spinek, an anthropologist at the Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy in Poland, explained the discovery to Live Science. “This is probably the first such discovery not only in Poland but also in Europe. No such devices exist in institutional and private collections (Polish and foreign).”
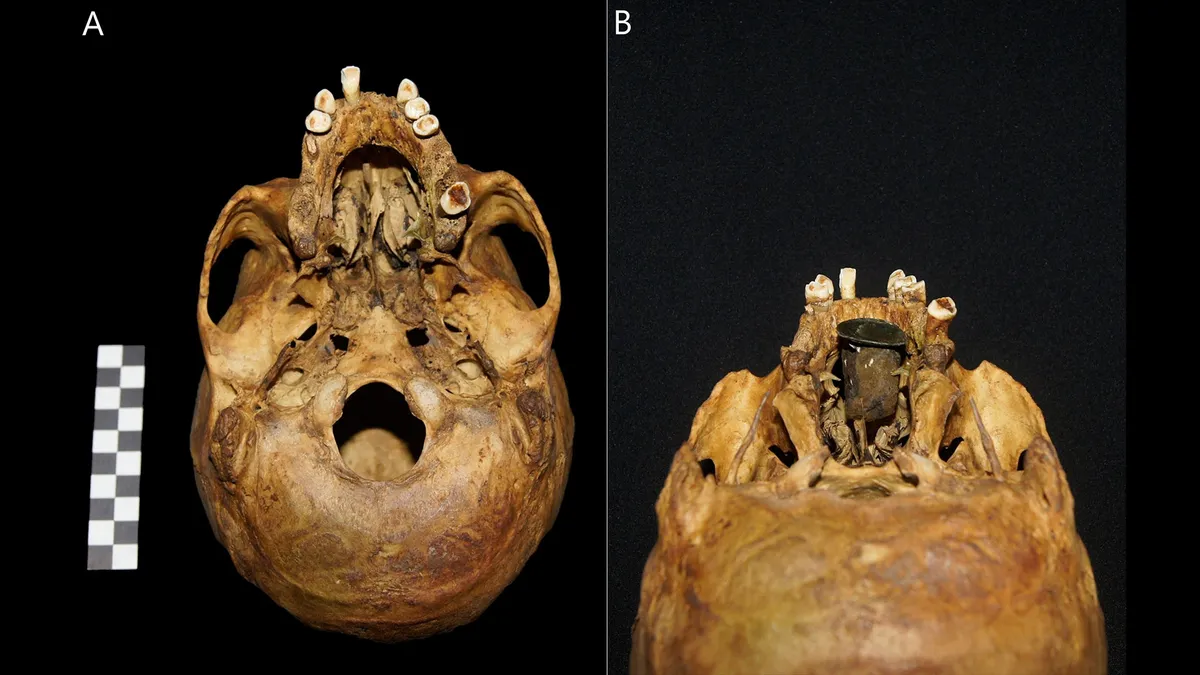
The device, described as a palatal obturator, was designed to fit into the roof of the man’s mouth. It would fit into the nasal cavity of the man replacing his hard palate.
Cleft palates arise when the hard palate, or roof of the mouth, doesn’t close during gestation. These days, cleft palates can be corrected surgically. However, this was not available to the man 300 years ago. Instead, he found another solution: this device, which was inserted into his mouth as a prosthetic.
The authors note in their paper, that the first attempts to replace missing palate parts were likely made in antiquity. Demosthenes (384-322 BC), a Greek orator, had a congenital cleft palate and may have filled open gaps in his mouth with pebbles.

The “exceptional” device consists of two parts. A metal plate that mimics the hard palate is attached to a wool pad, designed to secure the device comfortably when fitted into the mouth.
The hard palate prevents substances in the mouth from entering the nasal cavity, and it also helps with swallowing, breathing and talking, according to the study.
The 1.2-inch-long (3.1 centimeters) prosthesis, known as a palatal obturator, weighs around 0.2 ounce (5.5 grams), according to the study. The prosthetic is overall concave in shape and designed to arch up into the nasal cavity leaving a hollow in the mouth, just as a natural hard palate would.
To better understand the prosthesis’s composition, the researchers examined it under a scanning electron microscope and used X-ray spectroscopy, which analyzes the chemical composition of a sample. They discovered that the metal pieces were primarily composed of copper, with significant amounts of gold and silver. The wool was also tested and discovered to contain traces of silver iodide. This was most likely added to the pad because of its antimicrobial properties.

“Today, it is difficult to assess how well the obturator fitted or how tight a seal it provided,” the authors wrote in their paper. “However, modern-day patients struggling with similar health problems describe the use of a prosthesis providing improvements in speech (which becomes clearer) and increased comfort when eating.”
The study was published in the April issue of the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104443
Cover Photo: The skull of the man found in Poland from behind. On the left, the absence of a hard palate can be seen. The photograph on the right shows how the gold prosthesis was fitted. Source: Anna Spinek; © 2024 Elsevier Ltd / Live Science.