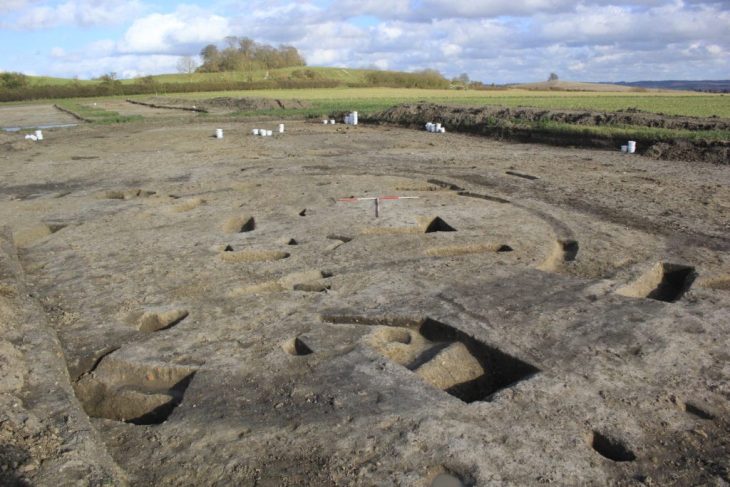
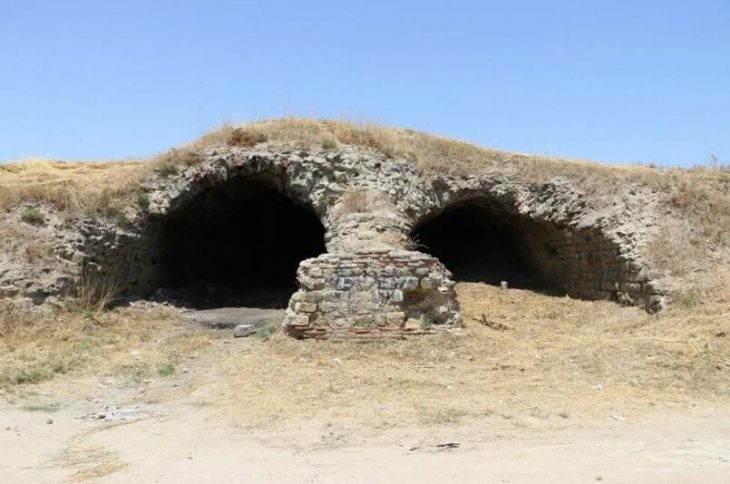
A colossal hall from the Bronze Age was discovered during excavations near the “royal grave” of Seddin (Prignitz district) northwest of Berlin, Germany. A colossal Bronze Age building remains thought to be the fabled meeting hall of King Hinz, a legendary figure purported to be interred in a golden coffin.
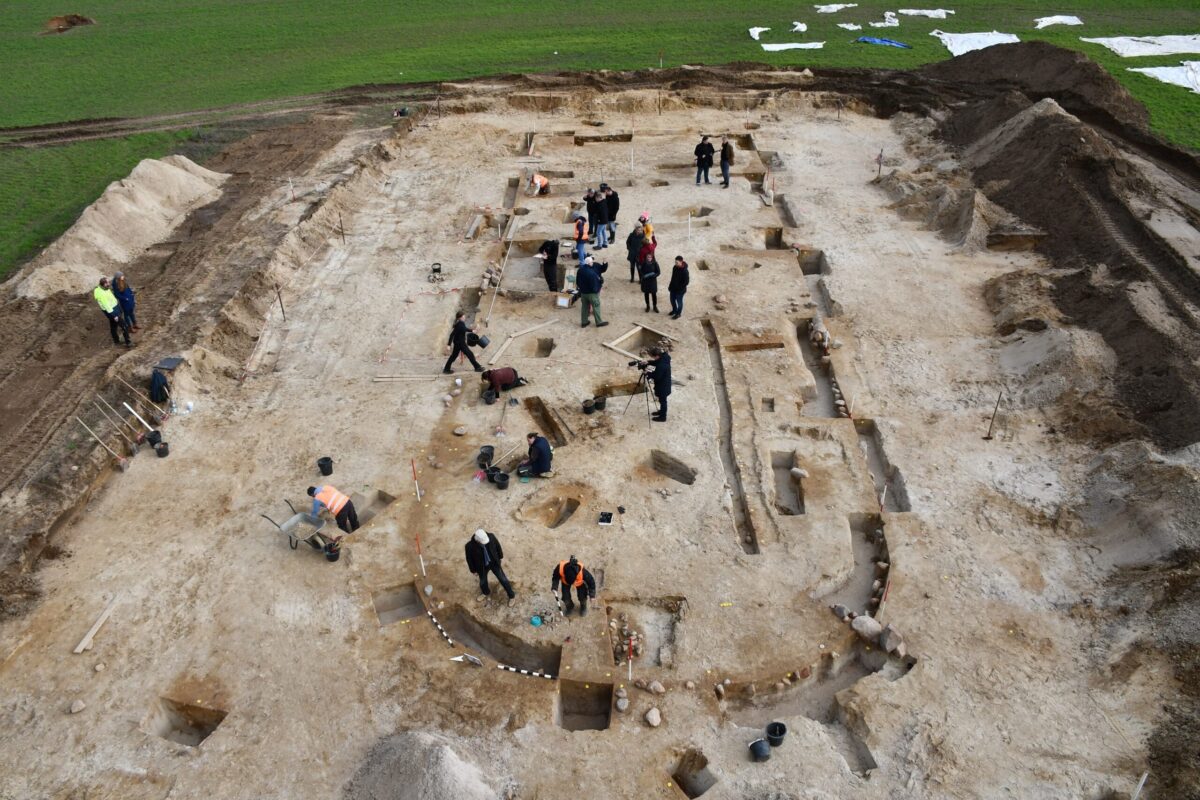
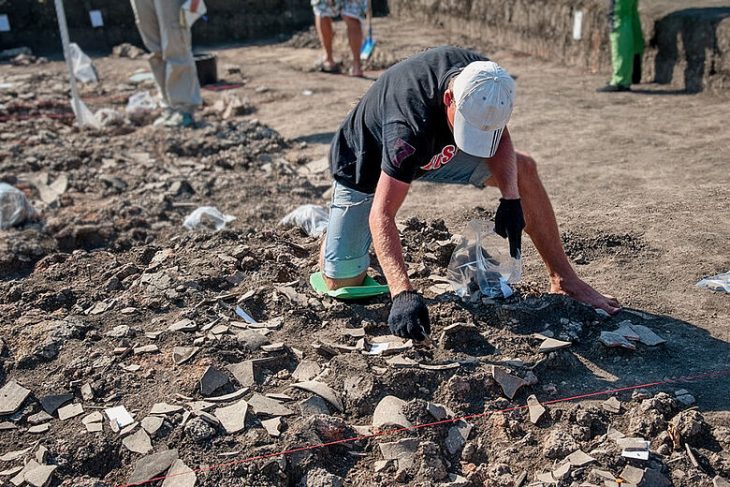
Since the spring, the Brandenburg State Office for Monument Preservation and archaeologists from the University of Göttingen have been carrying out large-scale excavations around the legendary royal grave of Seddin.
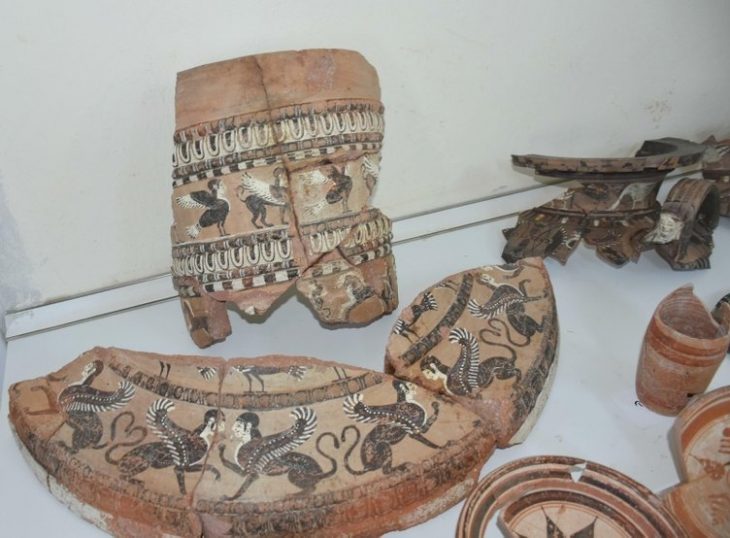
The “King’s Grave” near Seddin near Groß Pankow is considered the most important grave complex of the 9th century BC in northern Central Europe. It was discovered in 1899 during stone extraction work.
As the Brandenburg State Office for Monument Preservation announced on Wednesday in Wünsdorf, it is the largest building of its kind from the Nordic Bronze Age (approx. 2200-800 BC). It was said that the meeting hall of the legendary “King Hinz” was probably excavated with the 31 by 10 meter (102 by 33 feet) floor plan.
According to state archaeologist Franz Schopper, it is a “really big, spectacular find”.
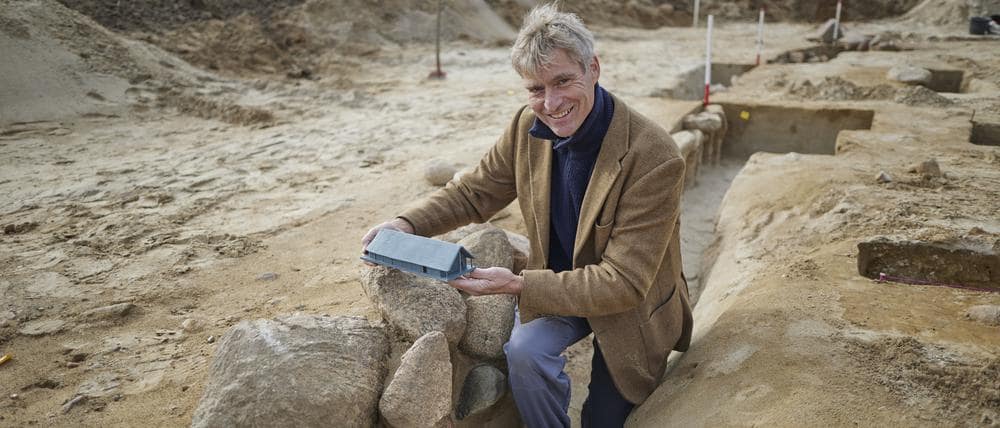

“Houses in prehistory were usually built in such a way that they were six to seven, sometimes eight meters wide. We’re at ten meters here, that’s what’s unusual,” explains Dr. Immo Heske, a leading archaeologist at the University of Göttingen.
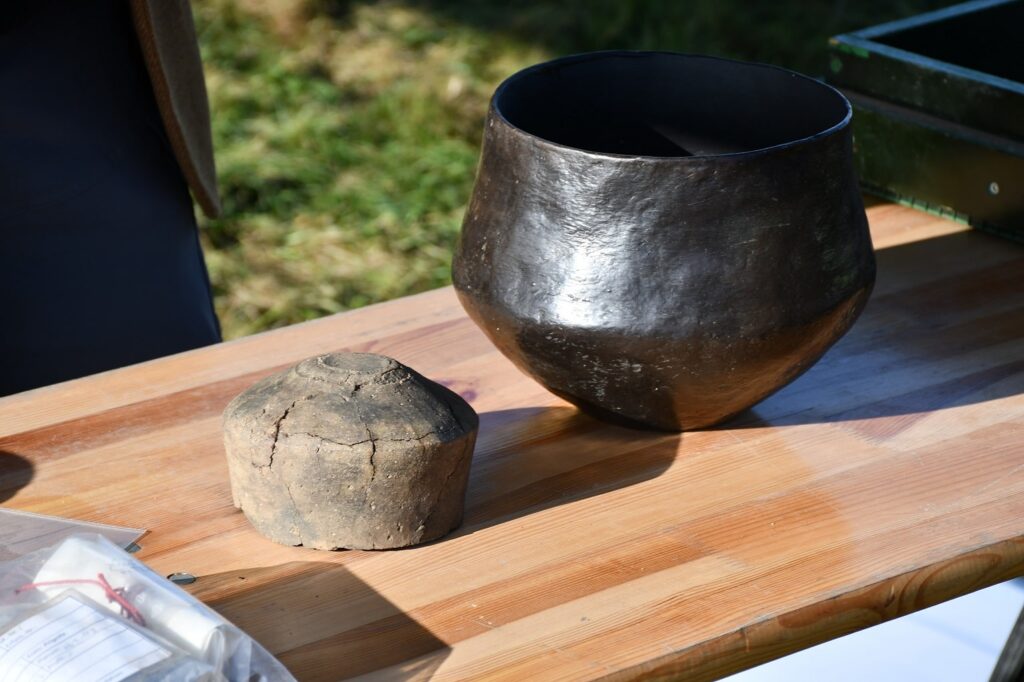
The walls of the building consisted of wooden planks and wattle and daub with clay plaster. The roof was covered with thatch or straw. Due to the estimated building height of seven meters, it is assumed that there were additional floors for living and storage. There was a fireplace centrally located inside the western half of the building. A miniature vessel was recovered on the northern long wall, which is interpreted as a ritual sacrifice.
The experts also found two outer walls of the hall made of piled-up field stones in the Prignitz soil. A completely atypical construction method for Northern Europe in the Bronze Age.
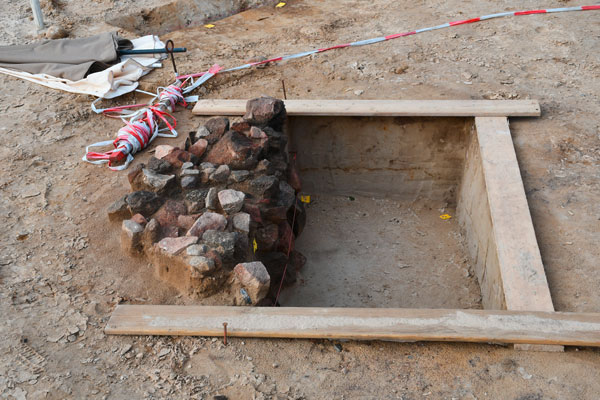

For Immo Heske it is clear: the builder or user of the house was inspired by his travels: “If we think about the European networks, you can imagine that on his travels south he may have seen how to work with stone built it.”
The archaeologist Immo Heske dates the building to between the 10th and 9th centuries BC. Due to its enormous size, it was probably a ruler’s seat. In the period from 1800 to 800 BC there were only two other buildings of this type between Denmark and southern Germany, said Heske.
The experts are therefore certain: no simple farmer lived in the large assembly hall, which was used for receptions and other celebrations. Rather, there is much that points to the legendary King Hinz in Prignitz, who is said to have been buried just a few meters away – also in the 9th century BC – in the royal grave just a few meters away.

“It is very conceivable that the king lived here and held his meetings and consultations,” explains Brandenburg state archaeologist Franz Schoppe. But it could also have been a predecessor of King Hinz. One thing is clear: the house also dates back to the period between the 10th and 9th centuries BC and it stood for a good 80 years.
With the find there is now another piece of the puzzle about life in the Bronze Age, says Brandenburg’s State Secretary for Science Tobias Dünow: “Here we have the opportunity – like hardly anywhere else in Europe – to gain an insight into the way of life, the culture, the building of houses and to get the burial culture in the Bronze Age.”
The finds and house outlines will be secured and documented by the end of the week. The excavation site will then be closed again. However, the research is not yet complete.
The excavation site could be reopened in the next few decades so that new technology or special DNA tests can be used to get to the bottom of history and learn more about the lives of the people around the royal tomb of Seddin. And the archaeologists from the University of Göttingen and the Brandenburg State Office for Monument Preservation will also be carrying out extensive excavations around the royal grave over the next two years as part of the funding project.
Brandenburg State Office for Monument Preservation
Cover Photo: Prignitz district
















Thank you.