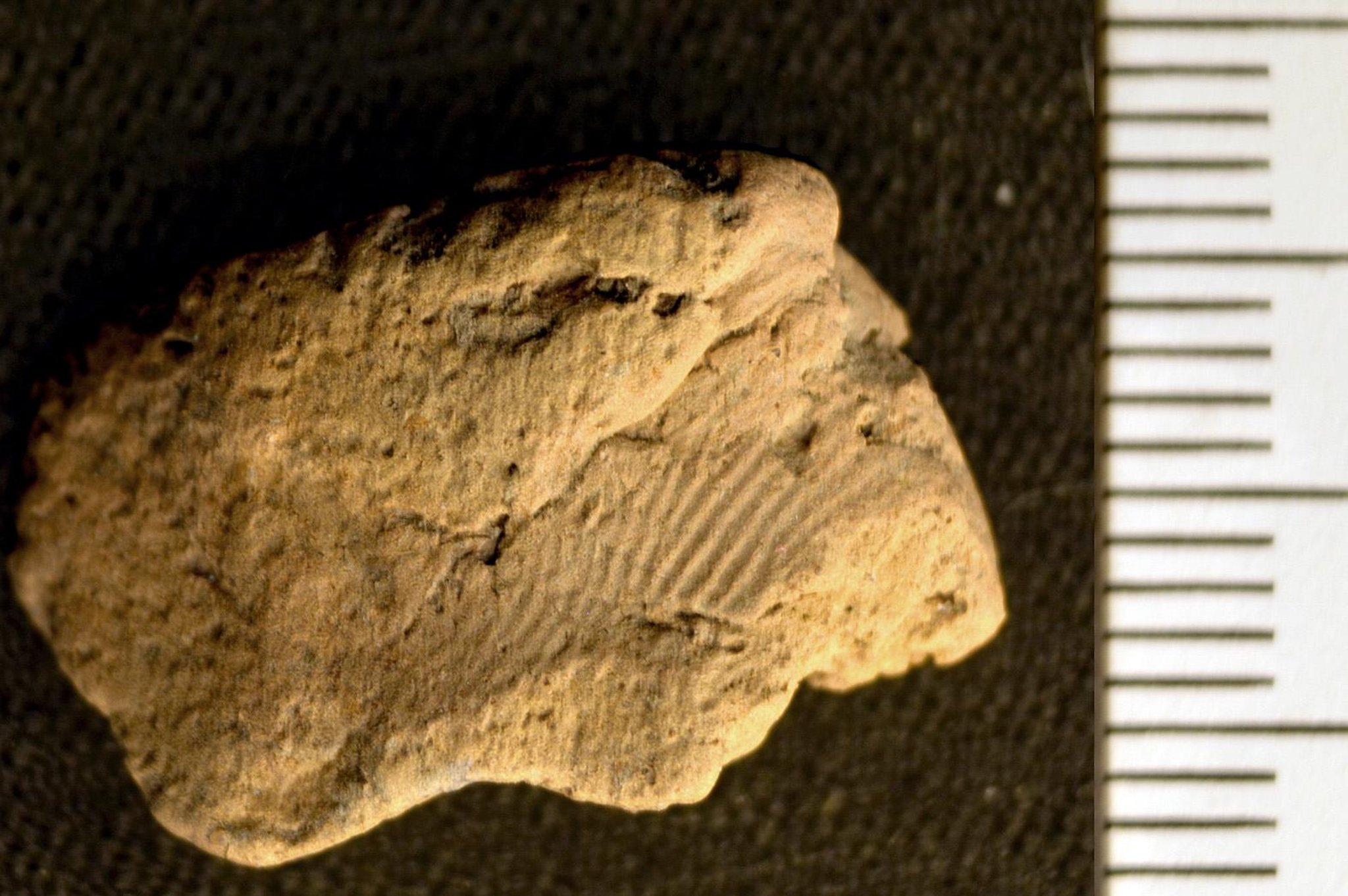
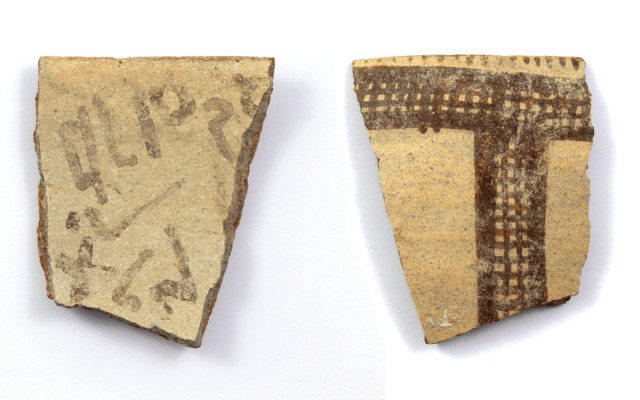
Details of the two young guys whose fingerprints were discovered on a fragment of a clay pot dating back over 5,000 years have now been revealed.
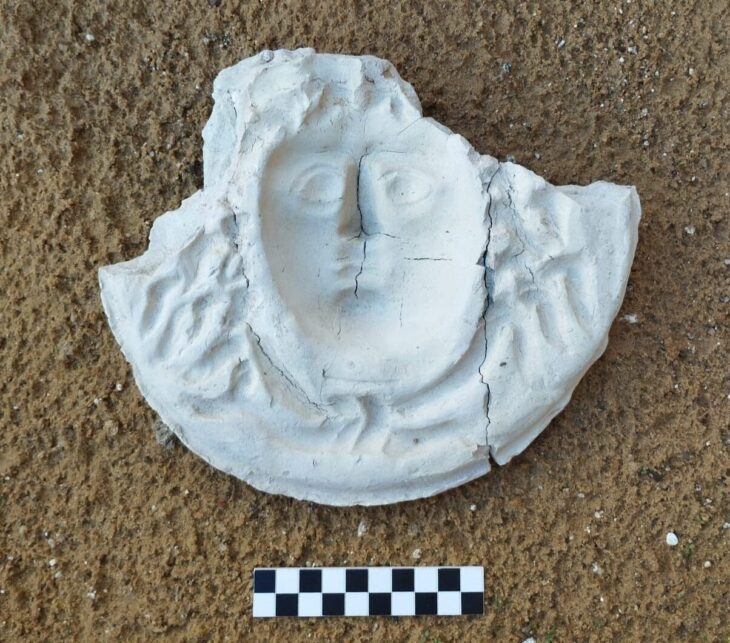
A fingerprint was discovered on a ceramic sherd recovered in April during the continuing University of the Highlands and Islands Archaeology Institute excavation of a Neolithic site on Orkney’s West Mainland.
Further examination of a digital model created by Jan Blatchford revealed two more prints, which were then examined by Professor Kent Fowler, director of the University of Manitoba’s Ceramic Technology Laboratory in Winnipeg, Canada.
Only two were detailed enough to analyze, but the results revealed it was two Neolithic males who left their mark on the wet clay vessel.
Professor Fowler was able to ascertain that one impression was made by an adolescent or adult man between the ages of 13 and 20, while the other was produced by an adult man between the ages of 15 and 22 since fingerprint components fluctuate according to age and sex.
Prof Fowler said: “Although the prints exhibit identical average ages, there is little overlap in the ridge values between the two measured prints. This suggests one print was made by an adolescent male and the other by an adult male.
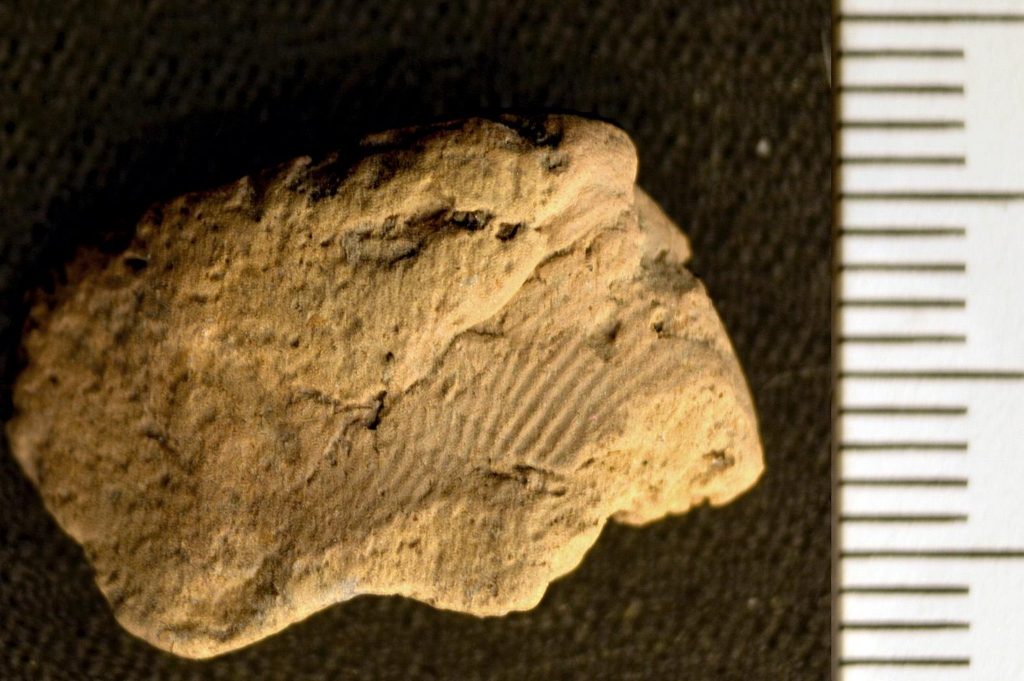

“Ethnographic and experimental accounts of hand-building techniques indicate that hands are normally only placed within closed-form vessels when fashioning roughouts and while manipulating the object to modify the exterior by wiping, smoothing burnishing.
“External prints can accrue during shaping or when handling the vessel after the roughout is completed, but when the clay is still leather hard and will accept prints. In this instance, it is most likely there were two print makers and the interior print was left by the potter.
“At this stage we cannot determine whether the older or younger potter was responsible for shaping operations.”
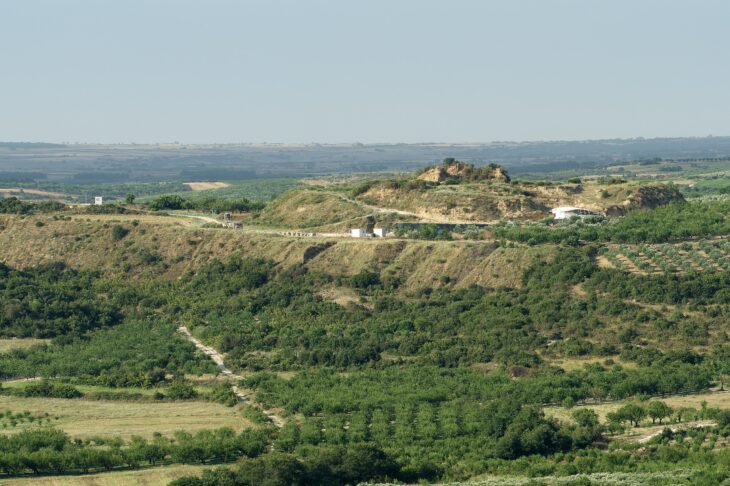
The Ness of Brodgar is the name of the thin strip of land, in the West Mainland of Orkney, that separates the lochs of Harray and Stenness.
Part of the Heart of Neolithic Orkney World Heritage Site, the Ness is covered in, and surrounded by, archaeology. An excavation in 2002 revealed a massive complex of monumental Neolithic buildings along with associated artwork, including pottery, bones and stone tools.
Nick Card, the director of the Ness of Brodgar excavation, said: “With well over 80,000 pottery sherds found at the Ness of Brodgar, it can be all too easy to lose sight of the people behind them.
“This single sherd has brought two back into the spotlight and given us an unparalleled glimpse into life at the Ness complex 5,000 years ago. It also raises many questions.
“The creation of this pot involved an adolescent boy – did he fashion the vessel or was he just involved in the manufacturing process, perhaps overseen by a more experienced potter?
“Were all children engaged in the creation of pottery from an early age or was it a task that involved a select few? Were different types of vessel created by different people within the household or community?
“The analysis has much wider implications in the study of Neolithic ceramics, but we will need many more fingerprint examples before any firm conclusions can be drawn.”
Source: Scotsman