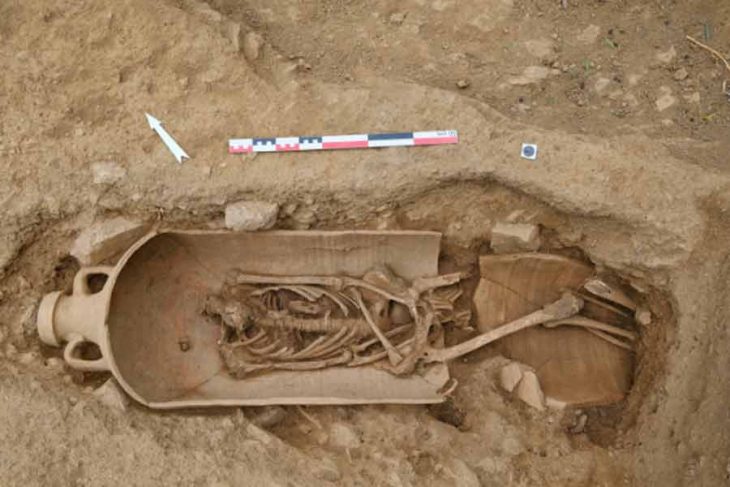
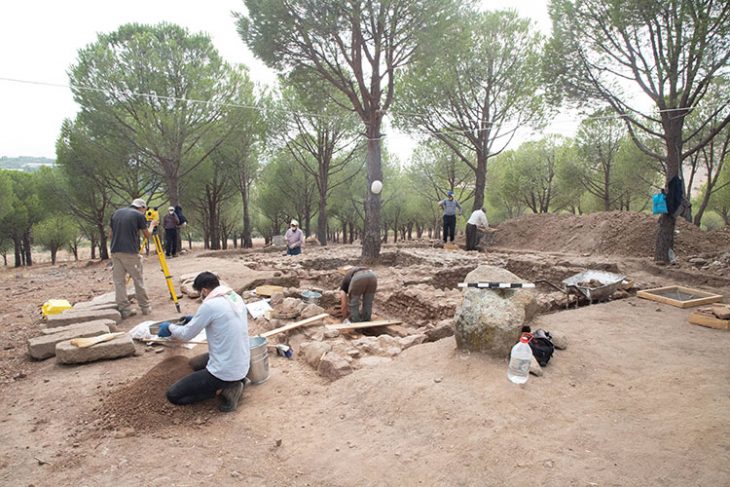
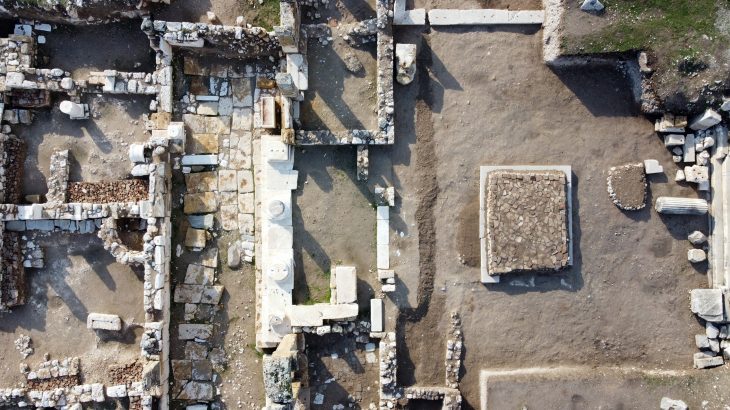
Jerash is a magnificent old Roman city located around 50 kilometers from Amman, Jordan. Jerash is considered the most well-preserved Roman ruins outside of Italy.
King’s Highway was vital to commerce in the Middle East, linking Egypt to Damascus via the Red Sea’s Gulf of Aqaba. There was no major empire headquartered along this road, but the cities along it grew rich through commerce as traders carrying grain from Egypt, incense from Yemen, pearls from the Red Sea, and spices from India passed through.
Jerash, created when Greek civilization expanded over the region, was one of the biggest cities. Jerash, which was enriched by commerce, was molded by waves of invaders until it was incorporated by Rome’s eastward advance.
According to inscriptions, Jerash, or Gerasa, was named for its first inhabitants: the old soldiers—gerasmenos means elderly people in Greek—of Alexander the Great’s campaigns in the early fourth century B.C.

Having carefully chosen this lucrative spot on the King’s Highway, the Seleucids started work on their new city with a flurry of building, dedicating temples to various gods in the Greek pantheon. As well as competing with other Hellenized towns and cities in prestige and trade, Jerash also maintained close ties with them, including Philadelphia (now the Jordanian capital Amman) and Heliopolis (today Baalbek in eastern Lebanon).
Nabataean caravans passed through Jerash on the way to Damascus and Palmyra, leaving their own cultural mark on the city.
As the Seleucids fell out of favor, another strong civilization aspired to conquer Jerash and the trade that flowed through the King’s Highway. In 102 B.C., Alexander Jannaeus, monarch of Judaea’s Hasmonaean dynasty, acquired control of Jerash. The Hasmoneans governed the city until 63 B.C., controlling what is now modern Israel, the Palestinian territories, and western Jordan.

That same year, Pompey the Great of Rome defeated the Pontus ruler, Mithridates VI Eupator, who ruled over regions in what is now Turkey. Mithridates’ death allowed Rome to establish a firm footing in the eastern Mediterranean and develop throughout the region.
Pompey seized Syria’s region to the north of Jerash in 63 B.C. Rome singled out Jerash and its nearby Hellenistic cities for particular attention as oasis of classical culture in a country dominated by Semitic traditions.
When Emperor Nero conquered the Nabataean Kingdom in the first century A.D., its capital, Petra, was tied ever closer to the Roman world.

Although the profitable commercial flow was disrupted by Rome’s larger economic crises in the third century, Jerash’s capacity to adapt guaranteed it enjoyed a second flush of success when it fell under the protection of the Byzantine Empire in the fourth century.
Today it is one of the best-preserved Roman cities in the Middle East and is a popular destination for those who would like to witness the majesty of Roman architecture, marvel at extraordinarily well-preserved mosaics and carvings.
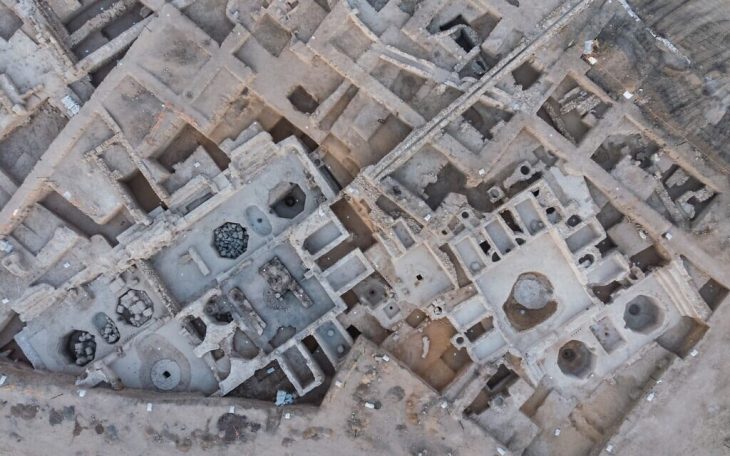
The site covers a huge area, the ruined city of Jerash is Jordan’s largest and most interesting Roman site. Its imposing ceremonial gates, colonnaded avenues, temples, and theatres all speak to the time when this was an important imperial center.

Most of the ancient city of Gerasa was destroyed in an earthquake in 749 AD, leading to comparisons to another great Roman city: Pompeii. The ruins were re-discovered in 1806 by German explorer Ulrich Jasper Seetzen.
Today Jerash is considered to be among the best-preserved of all Roman ruins in the Middle East; the city’s remains are prized by UNESCO as an “ancient meeting place of East and West.
What can I see?
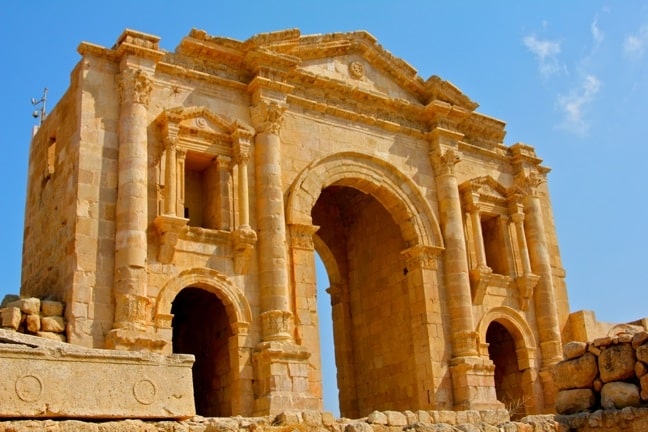
The stunning Hadrian’s Arch, also known as the Triumphal Arch, is at the extreme south of the site and was erected in AD 129 to commemorate Emperor Hadrian’s visit. Behind the arch is the hippodrome, which hosted chariot races in front of up to 15,000 spectators.
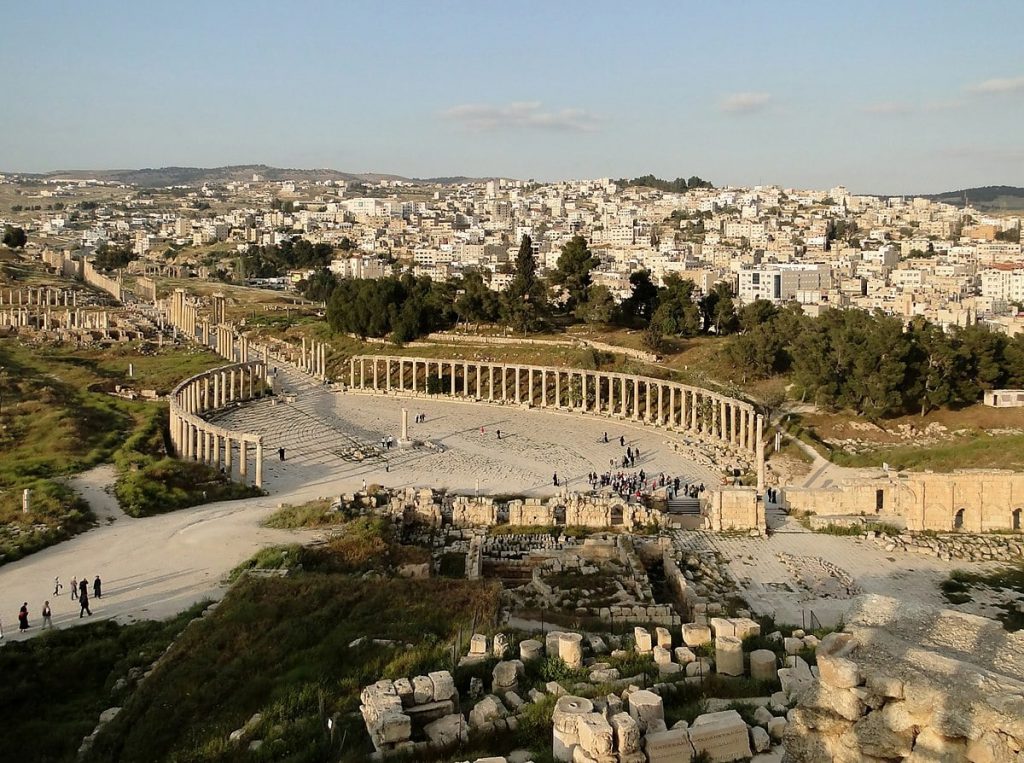

The South Gate, which was erected around 130 and was once one of four along the city wall, leads into the city proper. The forum, one of Jerash’s most unique landmarks, is peculiar because of its shape and size (90m long and 80m at its widest point). The paved limestone plaza is surrounded by fifty-six Ionic columns that connect the cardo Maximus to the Temple of Zeus.
The beautiful ruins of the Temple of Zeus, erected about 162, are accessible from the forum. The South Theatre, next door, was erected in the first century and has a seating capacity of 5000 people.
The Cardo Maximus, the city’s major road, also known as the colonnaded street, is located northeast of the forum.
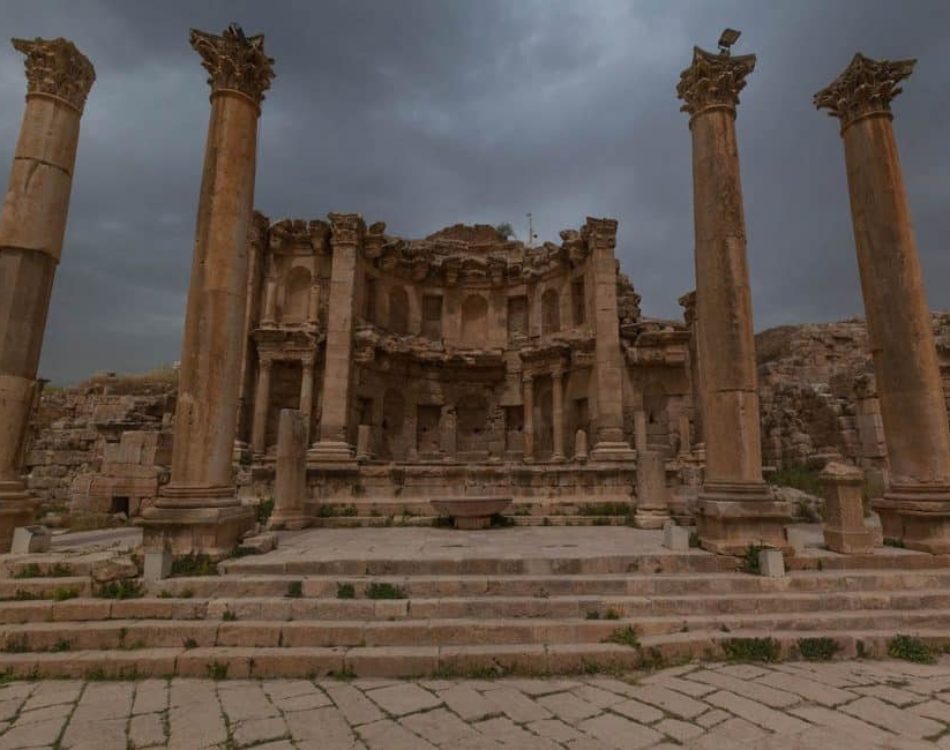
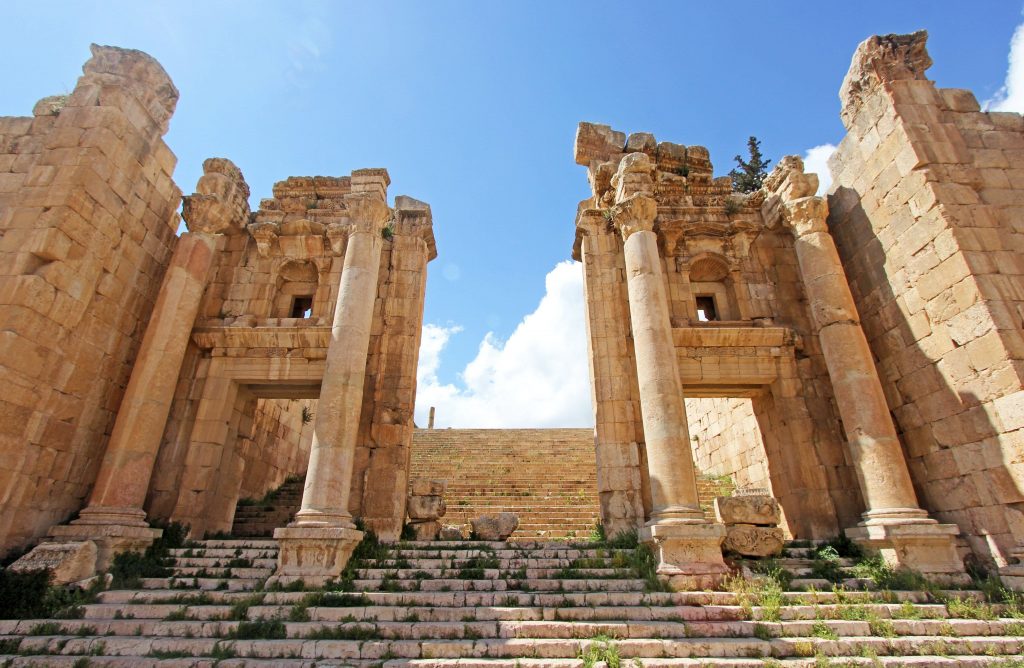
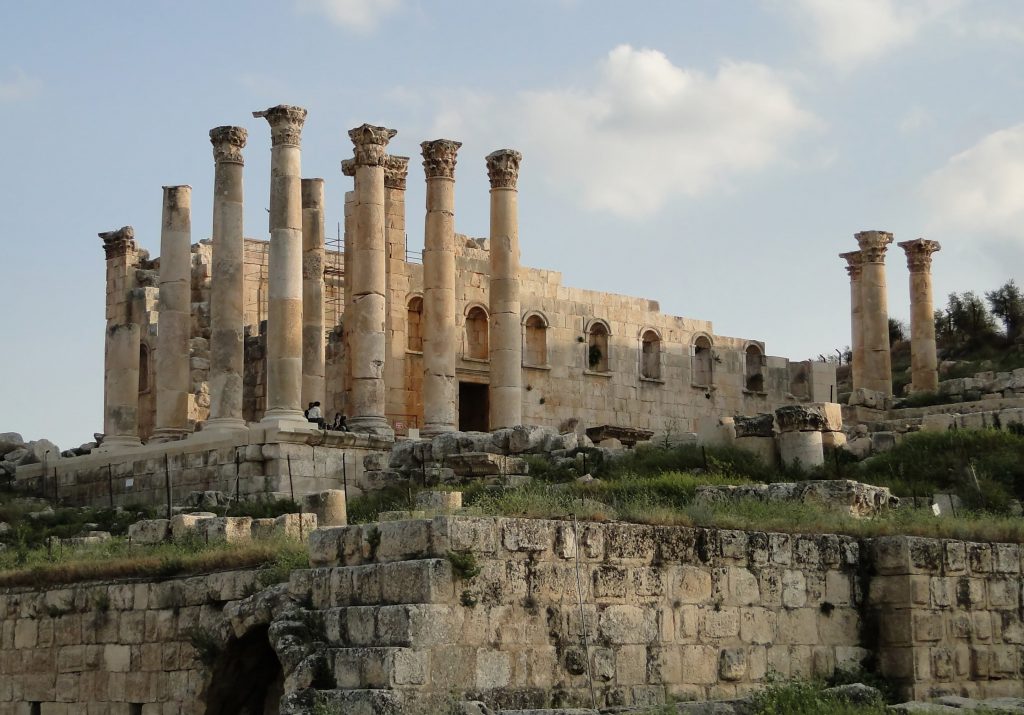
The colonnaded boulevard is interrupted by the city’s major fountain, the nymphaeum, before giving way to a magnificent propylaeum (monumental doorway) and a stairway. The Temple of Artemis, which towered over Jerash at the top of the stairs, was devoted to the city’s patron goddess, but it was demolished in 386 to furnish masonry for new churches under Theodosius.
Further north is the North Theatre, built-in 165 and now restored to its former glory.