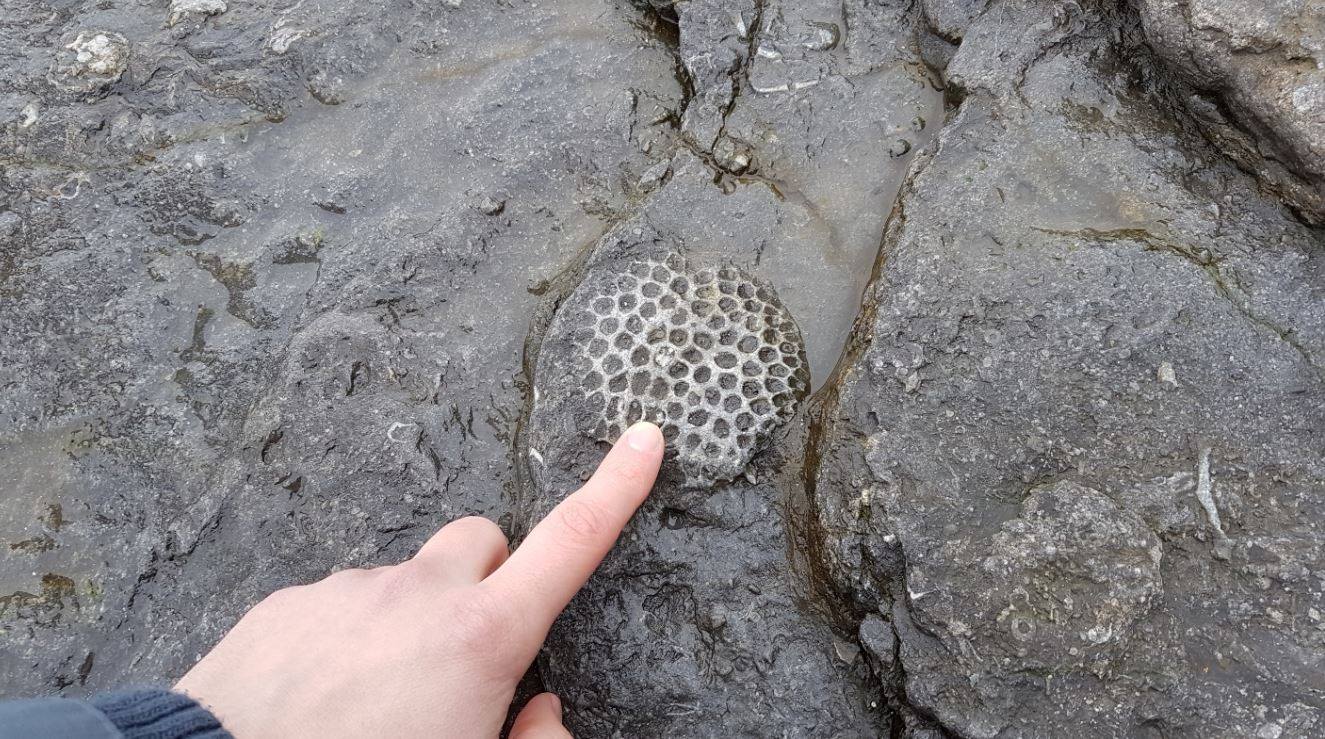
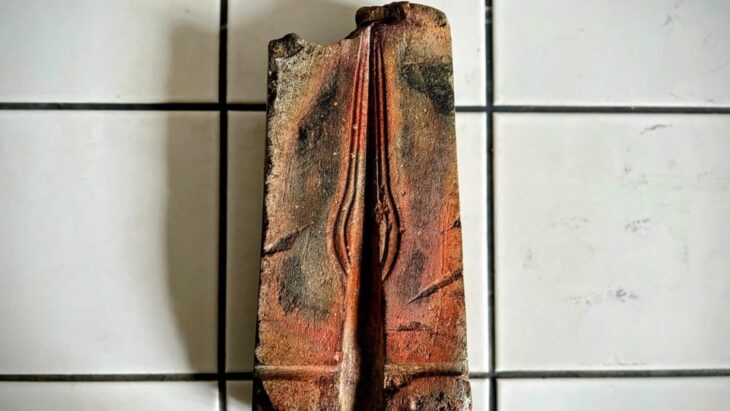
890-million-year-old fossil sponges found in the “Little Dal” limestones of northwest Canada may be the oldest animal ever found.
According to research published in the journal Nature, mesh-like structures in an ancient reef may represent 890-million-year-old sponges. The rocks were found by geologist Elizabeth Turner in a remote location of the Northwest Territories accessible only by helicopter, where she has been digging since the 1980s. Thin sections of rock contain three-dimensional structures that resemble modern sponge skeletons.
If research confirmed, the fossilized sponges found in the “Little Dal” limestones of northwest Canada would predate the earliest undisputed fossils of any animal by more than 300 million years.
Joachim Reitner, a geobiologist and sponge expert at the University of Gottingen in Germany, who was not involved in the study, said “I believe these are ancient sponges – only this type of organism has this type of network of organic filaments,”
“What’s most stunning is the timing,” said Paco Cardenas, an expert on sponges at Sweden’s Uppsala University, who was not involved in the research. “To have discovered sponge fossils from close to 900 million years ago will greatly improve our understanding of early animal evolution.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Many experts believe the first animal groupings contained soft sponges or sponge-like organisms that lacked muscles and nerves but possessed other characteristics of basic animals, such as differentiated cells and sperm.
To be fair, there is very little scientific unanimity or confidence about anything extending back a billion years, so other experts will most certainly continue to scrutinize and argue Turner’s results.
“I think she’s got a pretty strong case. I think this is very worthy of publishing – it puts the evidence out there for other people to consider,” David Bottjer, a paleobiologist at the University of Southern California who was not involved in the study, concurred.
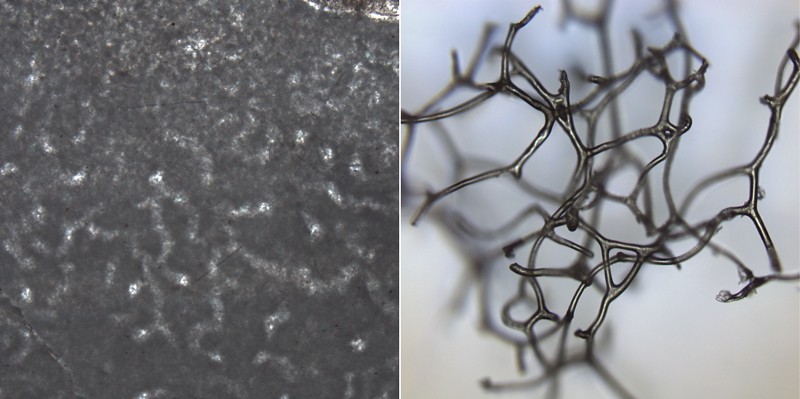
Life on Earth, according to scientists, began approximately 3.7 billion years ago. The first animals came considerably later, although the precise date is still contested. The earliest undisputed fossil sponges date back to about 540 million years ago, during the Cambrian period.
However, scientists adopting a line of reasoning known as the molecular clock – in which they evaluate the pace of genetic changes to backdate when two species are likely to have separated – claim that existing evidence leads to sponges arising far earlier, about a billion years ago. Despite this, no supporting physical evidence has been discovered to date.
“This would be the first time that a sponge fossil has been found from before the Cambrian, and not only before, but way before – that’s what’s most exciting,” said Uppsala University’s Cardenas, adding that the research seems to confirm the molecular clock estimates.
The 890 million-year-old date is noteworthy because, if the sponge’s identification is verified, it reveals that the earliest animals developed before the quantity of oxygen in the atmosphere and ocean reached what scientists formerly thought was essential for animal existence. However, a new study indicates that certain sponges can survive with very little oxygen.
“I don’t think this is the end of the story. This is just the beginning of a really interesting phase,” said Robert Rıdıngunıversity of Tennessee, Knoxville.
Cover Photo: Fossilised Sponge, Source: Hook Peninsula
















