In Rutland, archaeologists discovered an ‘unusual’ skeleton of a Roman slave, who might have been a criminal sentenced to death.
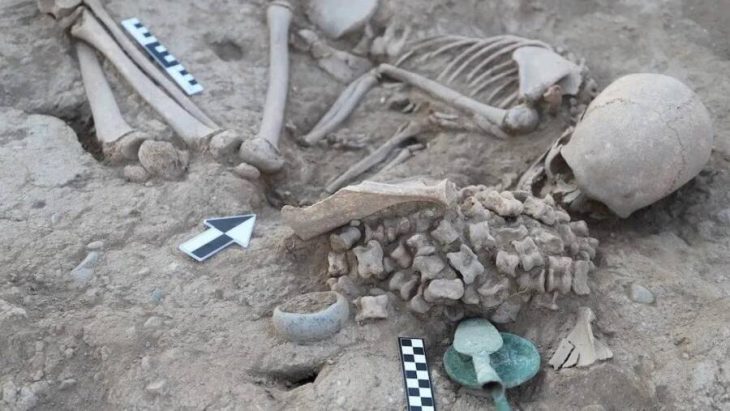
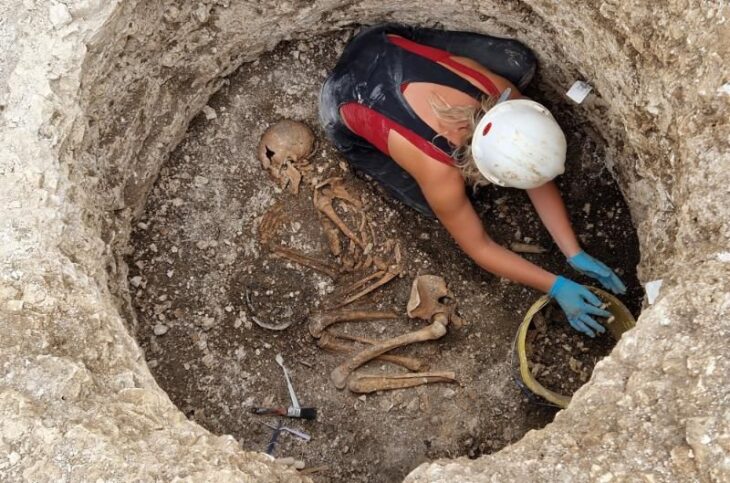
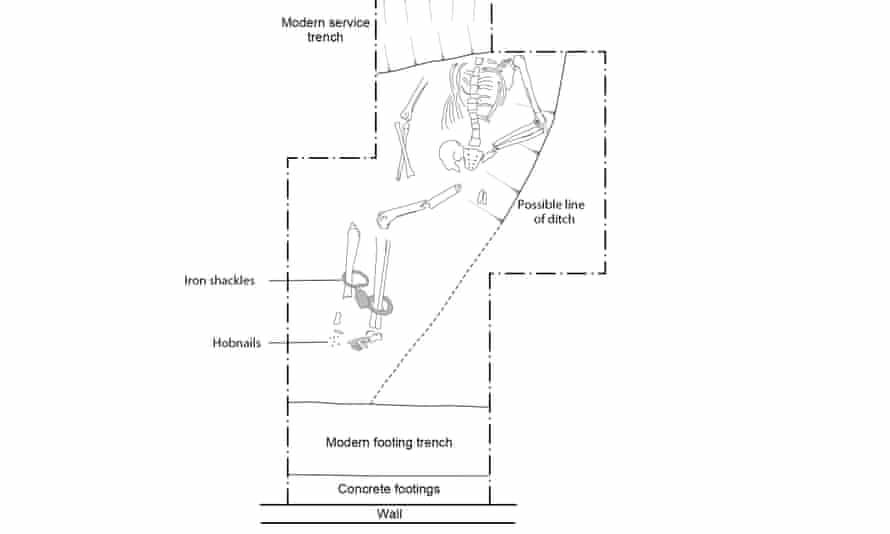
According to specialists, the adult male was discovered buried in a ditch with a locked set of iron fetters around his ankles, indicating ‘ill will’ from those who had control over him at the time of his death.
He was discovered in an ‘awkward’ burial posture — somewhat on his right side, with his left side and arm elevated on a slope – indicating he was disposed of in a ditch rather than a proper grave.
The chained male skeleton discovered by workmen in Rutland – likely to be in his late twenties or early thirties – has now been identified as uncommon and vital evidence of slavery in Roman Britain, as well as “an internationally significant find”.
Radiocarbon dating undertaken by Leicestershire Police showed the remains date from somewhere between AD 226 to 427.
It was also desperately grim, said Chris Chinnock, one of the archaeologists working on the project, but was important because it “forces us to ask questions that we wouldn’t ordinarily ask”.
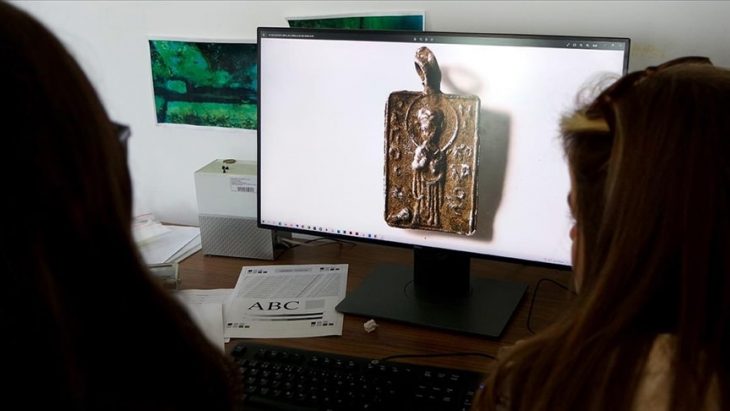
Archaeologists from the Museum of London Archaeology (MOLA) have been enlisted to thoroughly examine the internationally noteworthy find using X-rays and other techniques.
‘For living wearers, shackles were both a form of imprisonment and a method of punishment, a source of discomfort, pain and stigma which may have left scars even after they had been removed,’ said Michael Marshall, a finds specialist at MOLA.
‘However, the discovery of shackles in a burial suggests that they may have been used to exert power over dead bodies as well as the living, hinting that some of the symbolic consequences of imprisonment and slavery could extend even beyond death.’
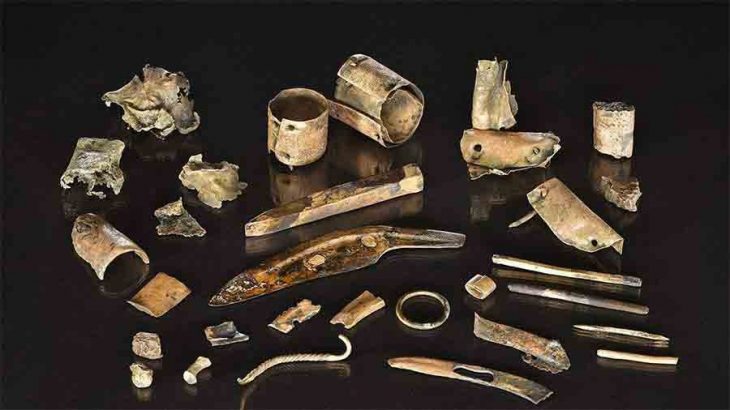
Examination of the skeleton suggests the man led a physically demanding life, according to MOLA.
A bony spur on one of the upper leg bones may have been caused by a traumatic event, perhaps a fall or blow to the hip, or else a life filled with excessive or repetitive physical activity.
The team has been investigating a number of ideas, including the possibility that the shackles were put after the guy died to degrade or mark him as a criminal in the afterlife. The rare bones discovered with shackles in other nations are usually victims of natural calamities who were not buried. Archaeologists say that this is not the case in Great Casterton.
Source: Daily Mail
















