Researchers have found the oldest known reference to a candidate aurora in a celestial event, described in an ancient Chinese text (the Chinese Bamboo Annals) dated around the 10th century BCE.
An event described in the Chinese Bamboo Annals is considered at almost 3,000 years old, this would be the earliest account of such an event whose date might be established. Such a discovery could be of scientific, as well as historical value, since the location of the source implies a particularly powerful geomagnetic storm.
From early stories through 299 BCE, the Bamboo Annals describe the story of China’s development. The Annals were buried for about 600 years until being unearthed in the third century CE, along with several other classic texts. One section alludes to a fascinating celestial object in the north sky.
An event described in the Chinese Bamboo Annals is considered by some a description of a bright aurora. If so, at almost 3,000 years old, this would be the earliest account of such an event whose date might be established. Such a discovery could be of scientific, as well as historical value, since the location of the source implies a particularly powerful geomagnetic storm.
The Bamboo Annals tell the story of China’s development from early legends to 299 BCE. The Annals were buried in a tomb for almost 600 years, and rediscovered, along with several other classic texts, in the third century CE. One portion refers to an object of great interest in the north sky.
Dr. Marinus van der Sluijs of the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archeology and Anthropology and Dr. Hisashi Hayakawa of Nagoya University have analyzed this text in Advances in Space Research. They conclude that not only is this probably a description of an aurora, but they can identify the place and two possible dates at which it was observed.

Van der Sluijs and Hayakawa claim the aurora occurred in either 977 or 957 BCE, in each case plus or minus one year, based on references to it being seen in either the 19th or final year of the reign of King Zhāo. If they’re right, this predates the previous oldest accounts of auroral activity by about 300 years.
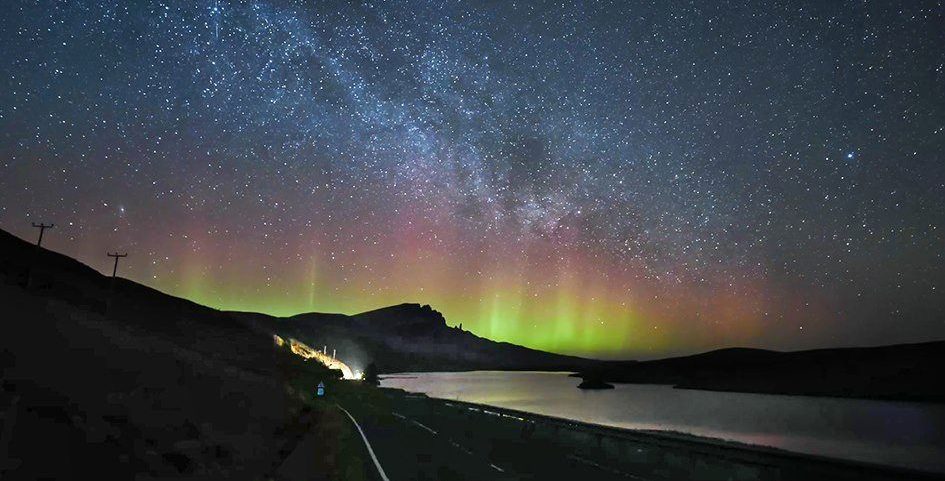
“We have located the observational site around Hàojīng (N34°14′, E108°46′),” they write. Although the north magnetic pole was considerably closer to China in the 10th century BCE than it is now, this would still be almost 40 degrees from the pole. Only a major outburst on the Sun would produce something bright enough to be visible at that distance from a pole. An aurora matching the description in Hàojīng would not be unprecedented, but it would be rare – which is presumably why it was thought worth recording.
Solar storms interacting with the atmosphere produces distinctive radioactive isotopes. Studies of their concentration in sediments indicate a major lull in solar activity, similar to the 17th century Maunder Minimum, between 810 and 720 BCE and sometimes known as the Grand Minimum. Likely descriptions of auroras start appearing in Assyrian and Babylonian texts not long after, along with a possible reference in the Bible.
If van der Sluijs and Hayakawa are right, the Bamboo Annals provides the only datable account we have from before the Grand Minimum. It could help us date the per-minimum timing of solar peaks, since isotopic measures only provide us with decadal activity levels for the era.
The account in the Bamboo Annals has been investigated for astronomical significance before, but some have interpreted it as referring to a comet, not an aurora. Even those who did think it referred to the polar lights have not previously been confident of date or location. Identification has also been confused because there are two versions of the Annals, which respectively refer to the event as a “fuzzy star” or a “five-colored light” in the northern sky. Van der Sluijs and Hayakawa consider the latter reference more authentic. The description has similarities to the ways other writers described bright auroras when they reached latitudes where they are rarely seen.
One of the only places in China you can see the northern lights today is Mohe, nicknamed “Chinas’ Arctic Town”. Bordering Russia, it’s so far north it’s the only place in China you can experience both the aurora borealis and the midnight sun phenomenon depending on the time of year.
Van der suijs has previously published a paper on rock art images proposed to represent depictions of auroras. However, while these almost certainly predate the Bamboo Annals, there is little prospect of dating them precisely, even if the interpretation is correct.
Cover Photo: Ollie Taylor