Underwater archaeologists have discovered rare, well-preserved textiles, basketry, and cordage from the early Neolithic period in an area near Rome, Italy.
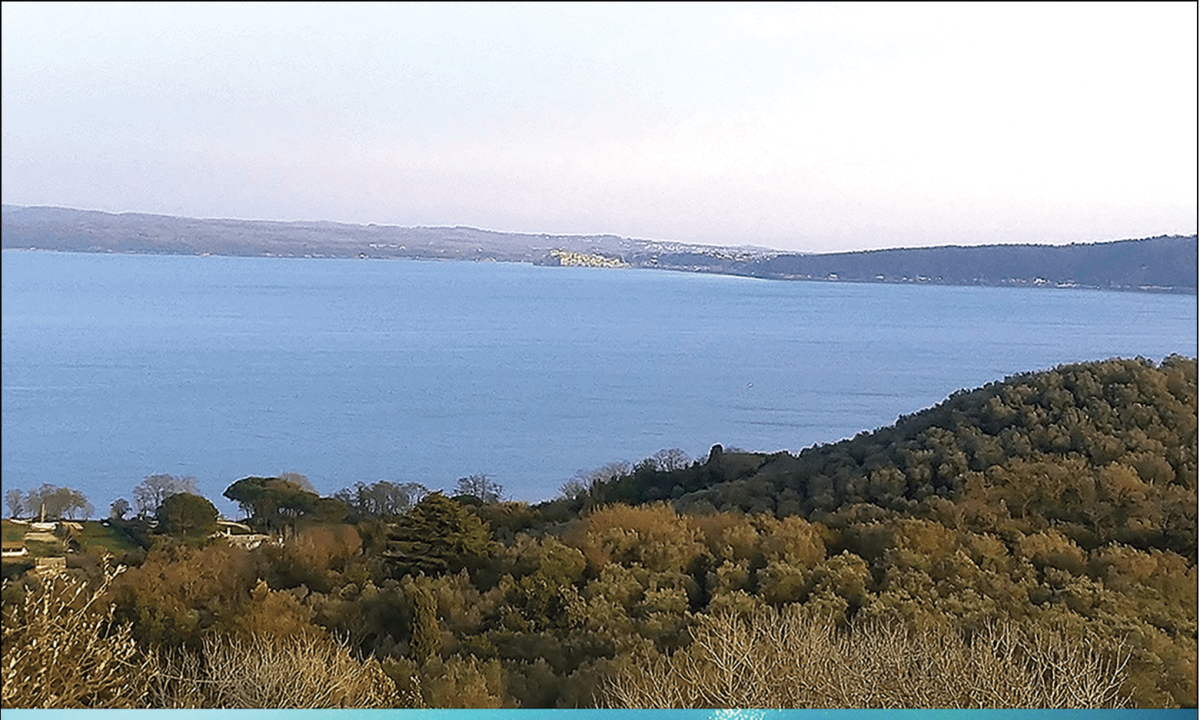
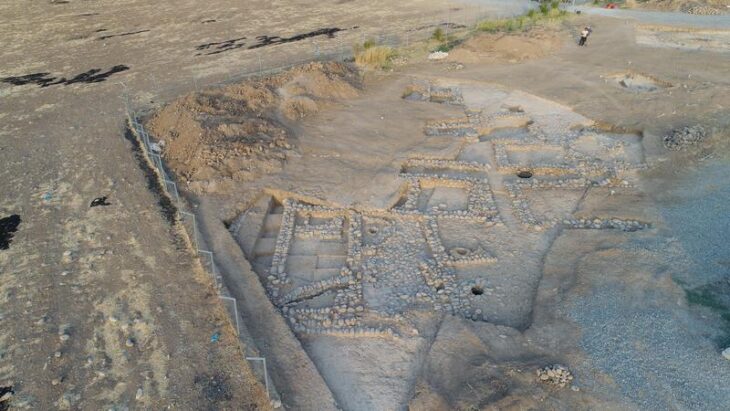
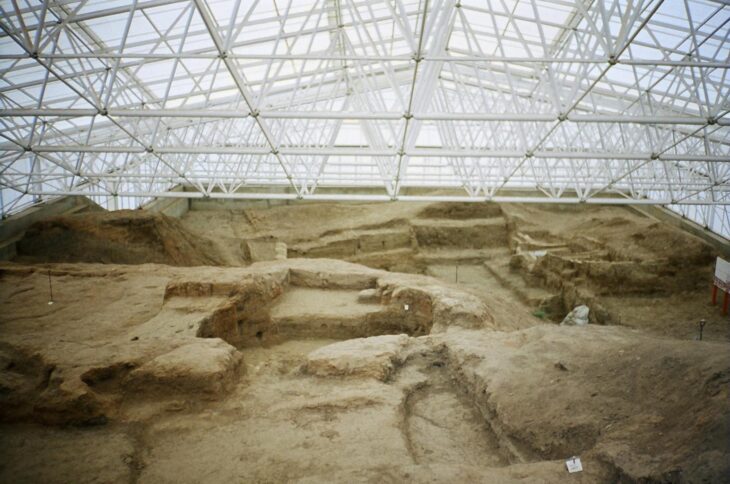
The submerged settlement of La Marmotta in the comune of Anguillara Sabazia, about 30 kilometers northwest of Rome, was discovered in 1989. A lakeshore settlement was established during the Early Neolithic Period, and it now lies approximately 300 meters from the modern shoreline, submerged at a depth of 11 meters.
“Archaeological research on Circum-Alpine lake or pile dwellings has provided unprecedented insight into Neolithic and Bronze Age societies.”
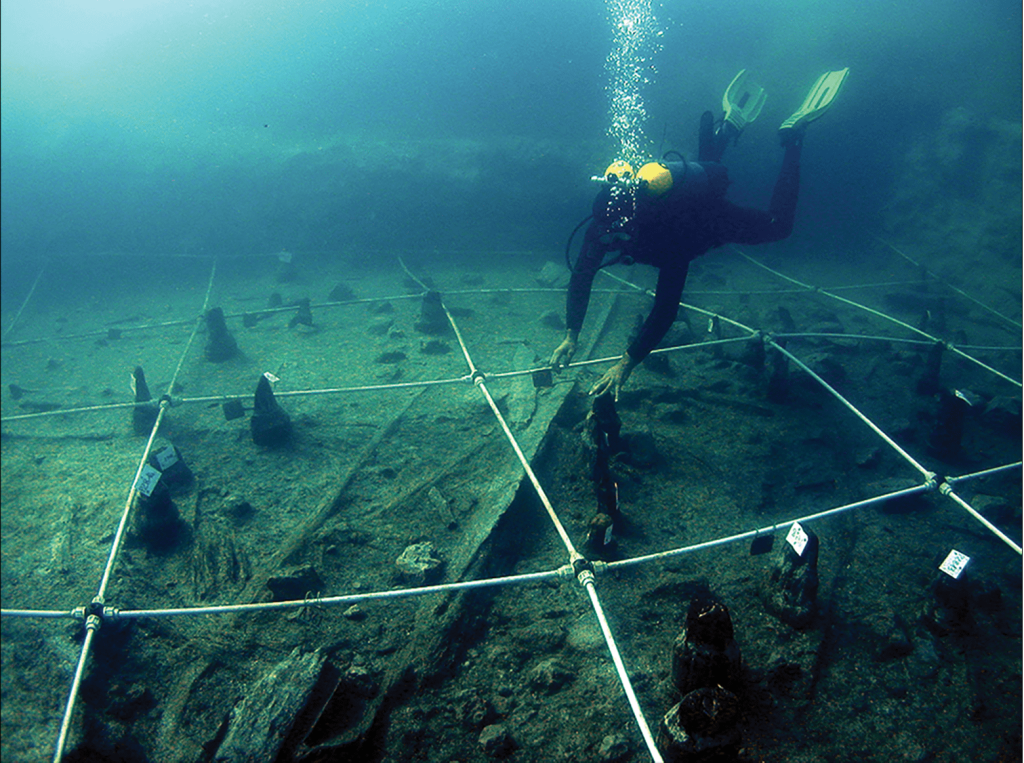
More than a dozen dwellings and a massive assemblage of organic remains have been discovered at La Marmotta after two decades of excavation. The authors present an overview of the recovered textiles, basketry, and cordage, as well as the tools used to make them.
“The assemblage paints a more complete picture of Neolithic societies’ technological expertise and ability to exploit and process plant materials to produce a diverse range of crafts,” the research team writes in the journal Antiquity.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
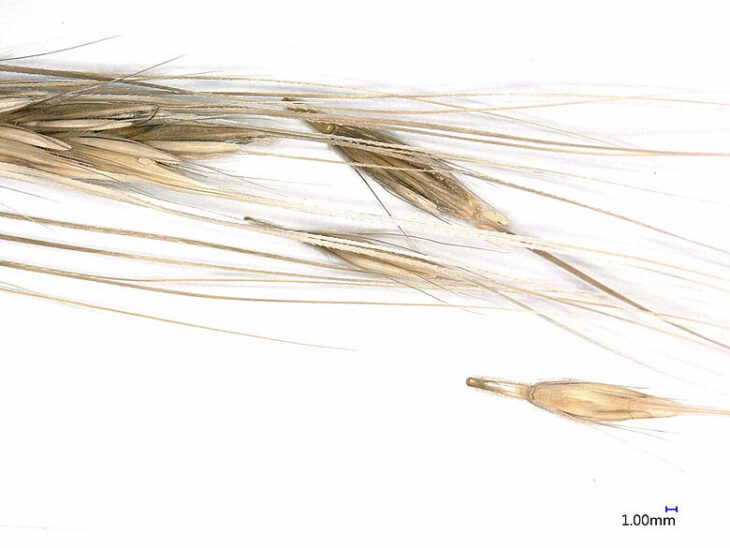
A team from the University of Copenhagen is currently analyzing textile fragments that are thought to have been made from plant fibers. A closer examination using a binocular microscope indicates flax fibers, a common material used by ancient cultures for making textiles until the 19th century AD.
In addition to 43 fragments of basketry, 28 fragments of cord and two lengths of thread have been identified. The discovery of 78 loom weights, three spindle whorls, and 34 complete or fragmented wooden tools that were likely used during weaving to ensure that each new weft thread was tightly packed down provides additional evidence of textile production.
It is unknown why the La Marmotta settlement was abandoned, but it is possible that a sudden rise in the lake’s water level forced people to leave their homes.
“Whatever the reason, the inhabitants left behind all their possessions, including tools, food-preparation vessels, and canoes. Numerous building elements and wooden objects were also found to have been burnt, similar to what has been observed in other submerged villages, such as in some Alpine lake sites (Neolithic, Switzerland) and Must Farm (Bronze Age, UK). Future geomorphological studies may help to determine precisely what happened at the end of the site’s occupation,” In their study, the researchers write.
A minimum of 13 house structures were identified on the Neolithic shore thanks to the spatial distribution of the thousands of wooden piles or support posts that have been discovered during underwater surveys of the settlement. These rectangular homes had an internal partition wall, and a central hearth, and were 8 to 10 meters long and roughly 6 meters wide.
Five wooden canoes, some found next to the houses, are currently the only known examples from the Neolithic Mediterranean.
Examining the raw materials recovered from the site reveals that the La Marmotta community was part of extensive and complex exchange networks with populations hundreds of kilometers away.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2023.21
Cover Photo: Antiquity

















