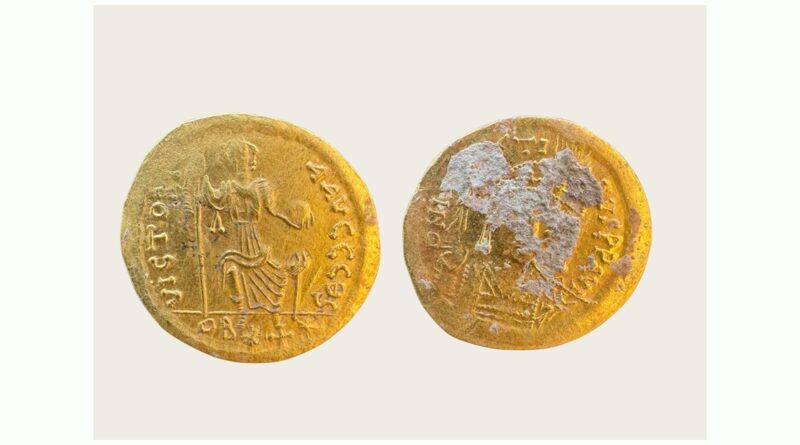
A rare gold coin dating back to the reign of Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Emperor Justin II (r. 565–578 CE) has been discovered at the Tuida Fortress, a strategically important early Byzantine stronghold located in the northeastern part of Sliven, Bulgaria, the Sliven Regional Historical Museum has announced.
This exceptional find marks the fourth gold coin uncovered at the Tuida site and is considered particularly significant due to its rarity and historical context.
Who Was Emperor Justin II?
Justin II was the nephew and successor of Emperor Justinian I, one of the most influential rulers of the Byzantine Empire. Justin II’s reign followed the grandeur of Justinian’s ambitious building projects and territorial expansion, but was instead marked by increasing pressure from the Sassanid Empire in the east and the Lombards in the west. He is also remembered for episodes of mental instability, which led to his wife, Empress Sophia, and his general Tiberius assuming control of the empire during the later years of his rule.
About Tuida Fortress
The Tuida Fortress (also spelled “Tuidda”) stands atop Hisarlaka Hill, a strategic location within the Stara Planina (Balkan Mountains) fortification system. Originally constructed in the late Roman period and rebuilt during the early Byzantine era, Tuida served as a crucial military and administrative center. The fortress played a defensive role throughout Roman, Byzantine, and medieval Bulgarian history, guarding against invasions and controlling key transit routes.
Discovery Details
Initially, the coin was believed to belong to Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565 CE), but after professional cleaning and analysis, experts from the Sliven museum confirmed it dates to the rule of Justin II. The front (obverse) of the coin features a forward-facing bust of Emperor Justin II, depicted holding a globe surmounted by Victoria, the Roman goddess of victory. The inscription reads:
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
D N IVSTINVS P P AVG
(Dominus Noster Justinus Perpetuus Augustus, Latin for “Our Lord Justin, Ever August”)
On the back (reverse), the inscription reads: VICTORIA AVGGG ΘS

According to researchers, the rare gold coin was likely minted in Theopolis, the historical name for Antioch, one of the most significant cities of the Eastern Roman Empire. Today, this ancient city is known as Antakya, located in southern Türkiye near the Syrian border.
Antioch was a major center of administration, commerce, and religion during Roman and Byzantine times. The presence of the mint mark “ΘS” on the reverse of the coin supports the theory that it originated from the Antioch (Theopolis) mint, further enhancing the historical and geographical value of the find.
An Archaeological Season Rich in Finds
So far in this year’s excavation season at Tuida, archaeologists have uncovered 23 coins spanning from the 2nd–3rd centuries to the 12th–13th centuries, offering a broad glimpse into the site’s continuous occupation and significance through centuries of tumultuous history.
Significance of the Find
The discovery of this rare Justin II solidus contributes valuable information to the study of Byzantine numismatics and the economic history of the region. It also reinforces Tuida’s status as a critical node in the imperial defense network during the early Byzantine period.
For history enthusiasts and scholars alike, this golden artifact sheds new light on the enduring legacy of the Byzantine Empire in Southeastern Europe and the vibrant cultural heritage of Sliven, one of Bulgaria’s oldest continuously inhabited areas.
Cover Image Credit: Sliven Regional Historical Museum