Archaeologists in Manching, Bavaria, have made a groundbreaking discovery that offers unprecedented insight into the daily life, craftsmanship, and religious practices of the ancient Celts. Throughout a three-year excavation from 2021 to 2024, the team uncovered more than 40,000 artifacts at the Oppidum of Manching, one of Central Europe’s most extensively studied Celtic settlements. Among these finds, a miniature bronze warrior figurine has captivated experts with its exquisite detail and mysterious symbolism.
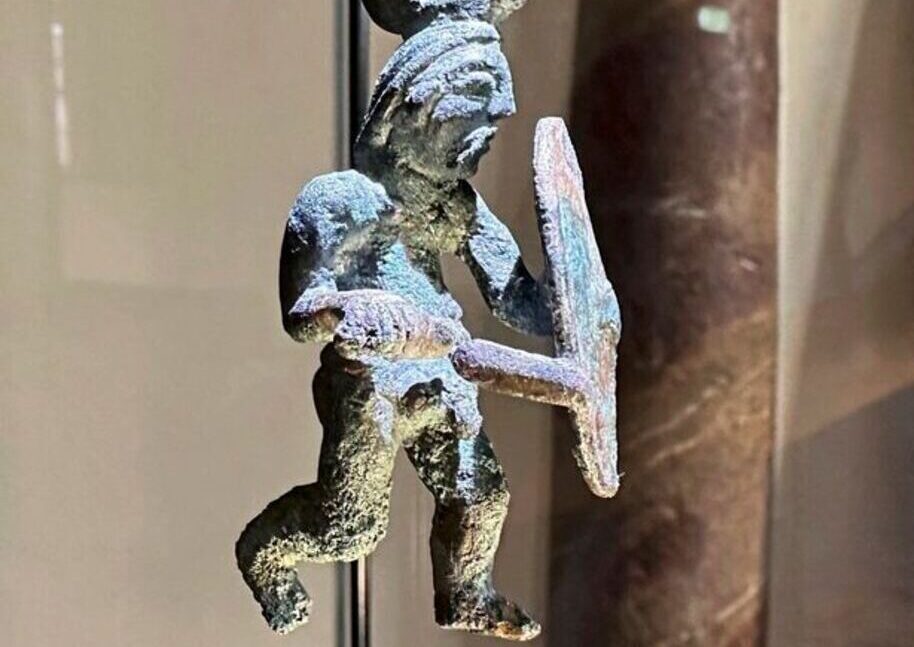
The bronze figurine, measuring 7.5 centimeters in height and weighing 55 grams, depicts a Celtic warrior wearing a chest armor but notably bare from the waist down. This unusual feature has sparked curiosity among historians and archaeologists alike.
“This small bronze warrior looks like something straight out of Asterix and Obelix, but it is authentic,” said Mathias Pfeil, General Conservator at the Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation.
The figure was discovered in a trench within the settlement, and experts believe it may have served either a decorative or ceremonial purpose, possibly hanging from a chain as a pendant, given the small loop on its head.
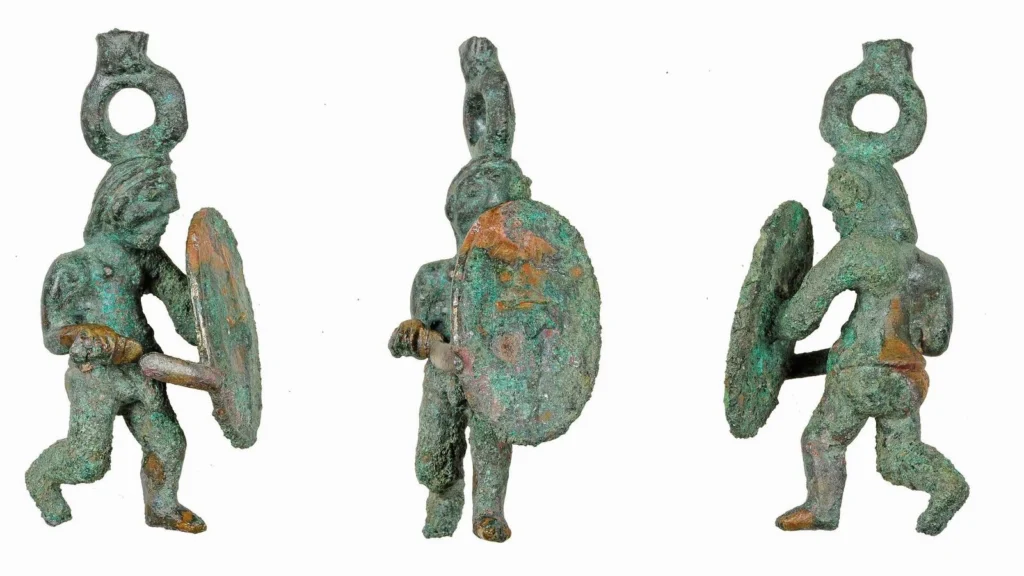

Crafted using the lost-wax casting method, the figurine demonstrates the Celts’ remarkable metalworking skills. In this technique, a wax model is embedded in clay, melted away, and replaced with molten bronze, resulting in highly detailed and durable artworks. According to Thomas Stöckl, a restorer at the State Office, the figurine is “a particularly complex and finely executed work,” highlighting the sophistication of Celtic artisans.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
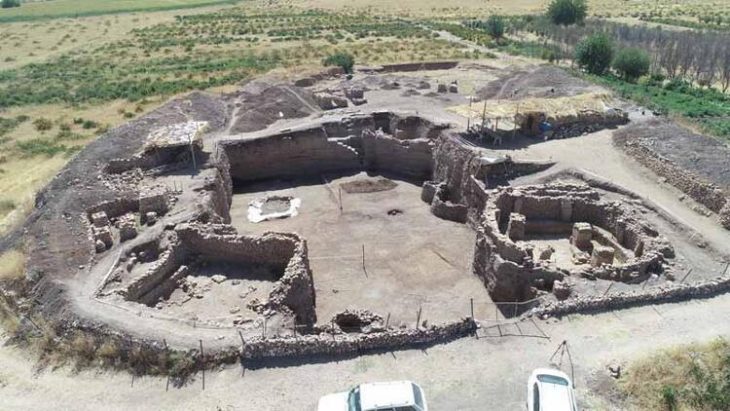
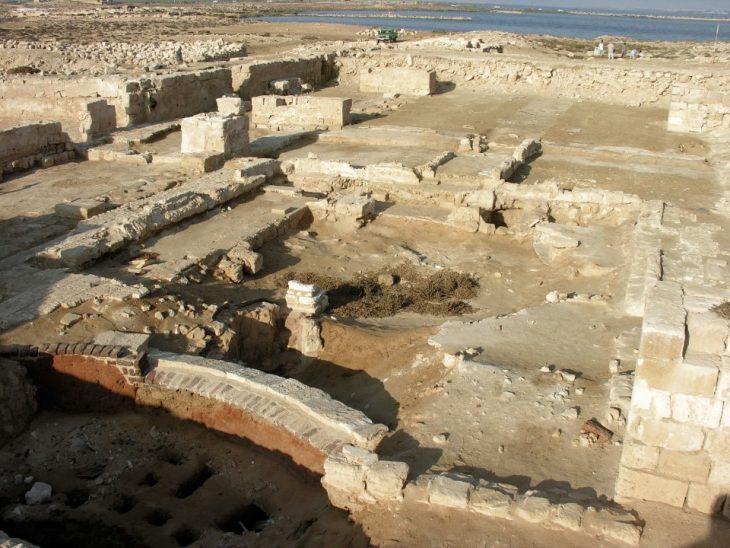
The Oppidum of Manching, founded in the 3rd century BCE and abandoned by the mid-1st century BCE, was a major political and economic center north of the Alps. Covering roughly 400 hectares, it could have housed up to 10,000 people, more than medieval Nürnberg.
Excavations revealed urban planning with streets, central squares, workshops, and residential areas. Artifacts recovered from the site include tools, ceramics, metal objects, and even evidence of fish consumption, indicating a varied diet of domesticated animals, grains, and dairy products. Recycled materials and organized craft districts suggest a society both resourceful and technologically advanced.
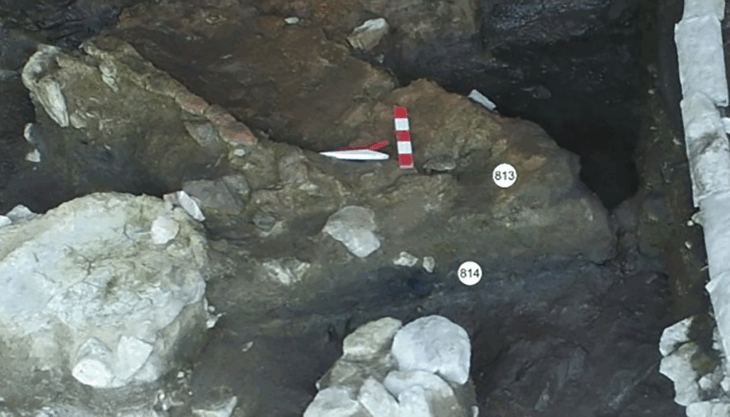
Some finds suggest ritualistic practices, including human and animal remains in a ritual well along with 32 metal objects and over 50 ceramic vessels. These discoveries, combined with the intricately crafted bronze warrior, hint at the spiritual or symbolic significance such figures may have held in Celtic society. “The figurine could have had a cultic function, reflecting the Celts’ elaborate and sometimes bizarre ritual practices,” Pfeil explained.
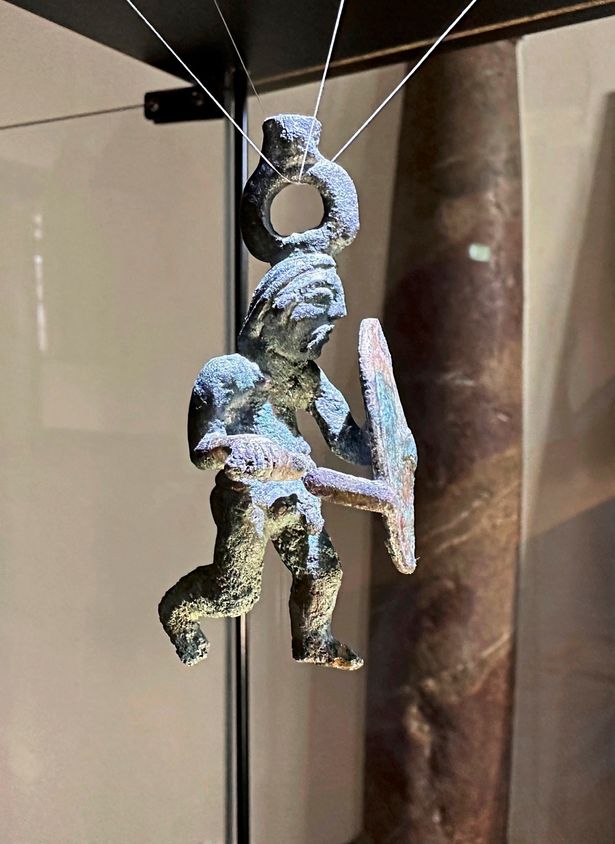

The unique depiction of nudity in the bronze warrior is particularly intriguing. While the warrior wears armor on the chest, the lower body is exposed, emphasizing masculinity. This representation aligns with historical records of Celtic warriors serving as mercenaries in Greek armies, where nudity in art symbolized strength and valor. Whether the figurine was used as personal adornment, a votive offering, or a ceremonial object remains uncertain, but its craftsmanship indicates it was highly valued.
The significance of Manching extends far beyond individual artifacts. The settlement provides unparalleled insight into Celtic urban life, trade networks, and cultural practices. With 87% of the site still unexcavated, archaeologists anticipate further discoveries that could reveal additional treasures and deepen understanding of this enigmatic civilization.
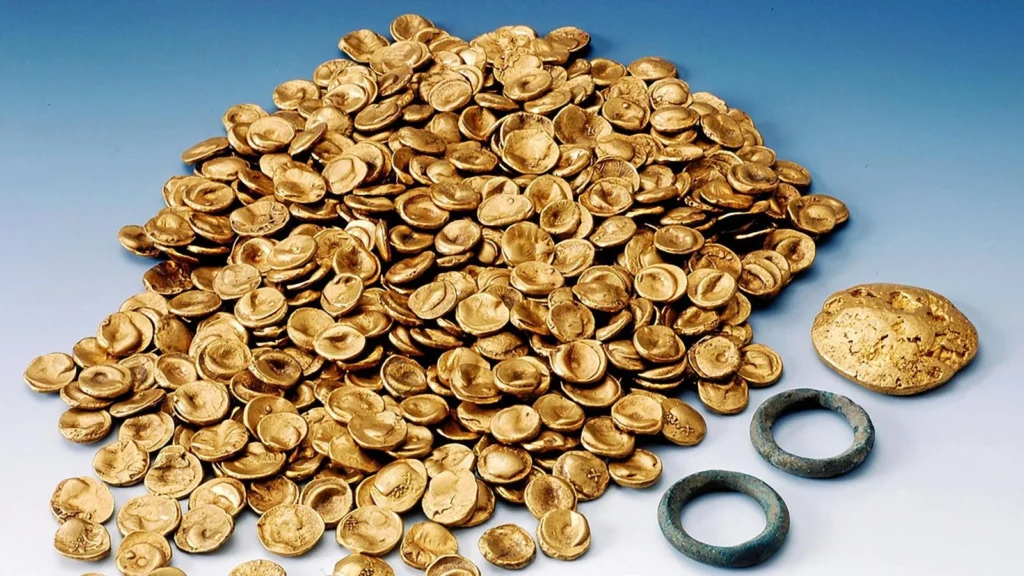
The Legendary Manching Gold Treasure
Previous major finds in Manching include the legendary Celtic gold hoard, which weighed nearly 3.7 kilograms and was the largest collection of Celtic coins ever discovered in the region. Found in 1999, the treasure included 483 high-value gold coins and a 217-gram gold ingot, totaling roughly 3.7 kilograms of Celtic gold—the largest Celtic coin hoard discovered to date.
In a dramatic turn, much of the treasure was stolen from the Manching Museum in November 2022. While three of the four accused were sentenced to multi-year prison terms, most of the gold remains missing, likely melted down. Pfeil notes, “If such a treasure has already been found there once, one cannot rule out finding another—but why would such a valuable item be left behind? Usually, people take it with them.” This underlines both the historical significance and the mystery surrounding Manching.

A Window into Ancient Europe
The Manching bronze warrior figurine exemplifies the combination of artistry, ritual, and social structure that defined Celtic society. As researchers continue their work, such finds not only enrich our knowledge of ancient Europe but also emphasize the importance of preserving archaeological heritage for future generations.
The Oppidum of Manching remains a critical site for Celtic studies, providing rare and detailed glimpses into a civilization that left no written records but expressed its identity through art, craftsmanship, and ritual.
Das Bayerische Landesamt für Denkmalpflege (BLfD) (Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation)
Cover Image Credit: Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation