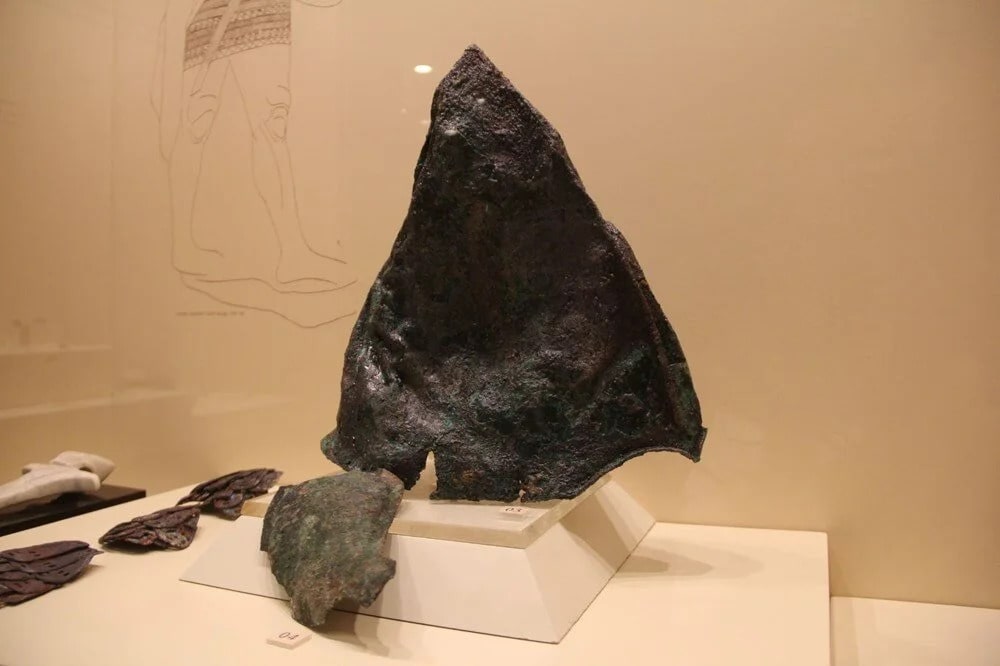
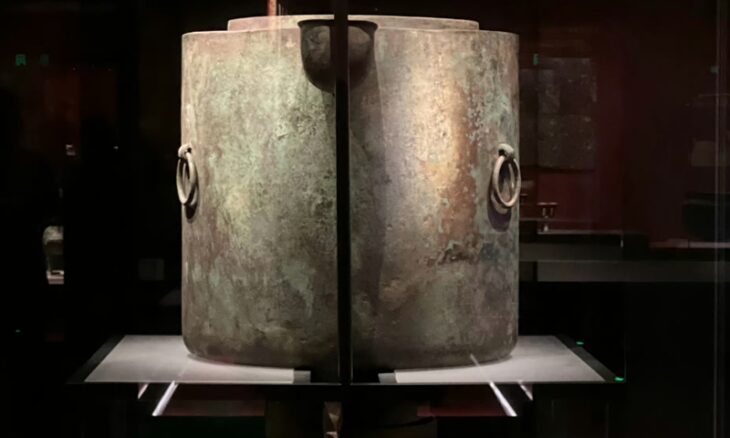
The 3,300-year-old bronze helmet, which was unearthed during the 2002 excavations in Şapinuva, one of the important cult centers of the Hittite Empire, is among the rare artifacts that have survived from the Hittite Empire period.
The Hittite helmet, which was discovered during the excavations at the Şapinuva ruins in the Ortaköy district of Çorum, located in the center of Turkey, have been published by Dr. Mustafa Süel in 2002 and introduced to the scientific world.
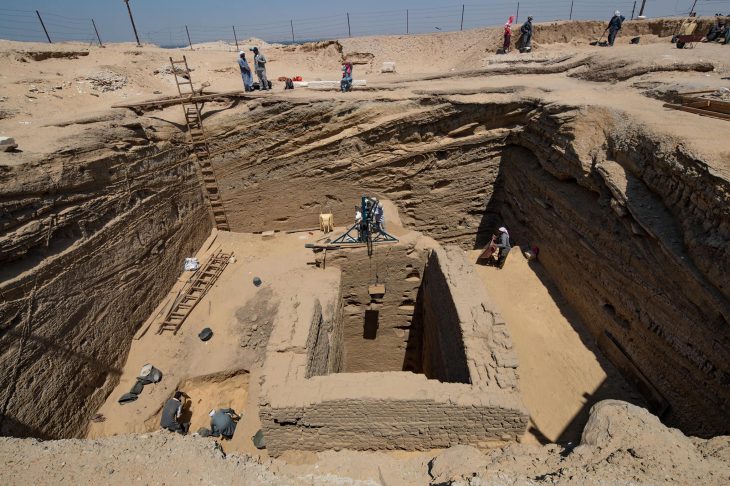
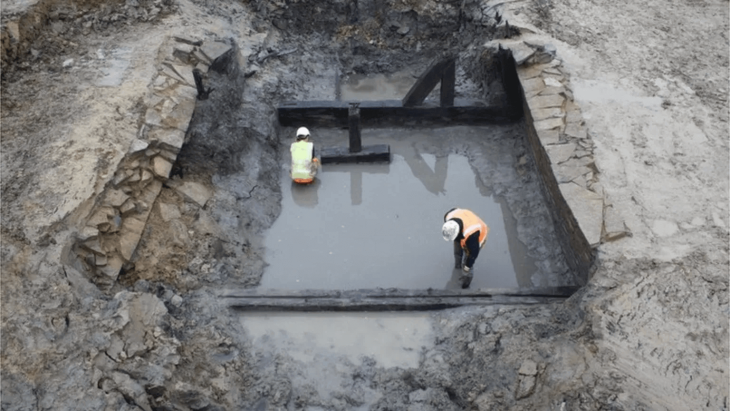
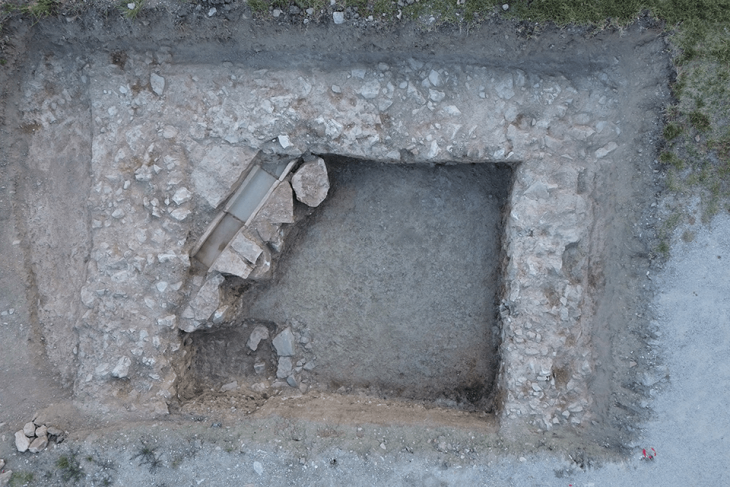
The bronze helmet was discovered in 2002 in the building called Building D. This structure, besides the discovery of this important discovery, is also quite remarkable with its structure that is encountered for the first time in Hittite architecture.
While the building shows a rectangular plan structure with its external appearance, there is an L-shaped hall and spaces arranged inside this hall.
The building, which has a very impressive entrance door, has an entrance corridor of 5.5 meters. Two hearths, on the right and left, were found at the entrance of the corridor. Those who come here enter the interior by passing between these two fires. Undoubtedly, was quite impressive in the conditions of the time.
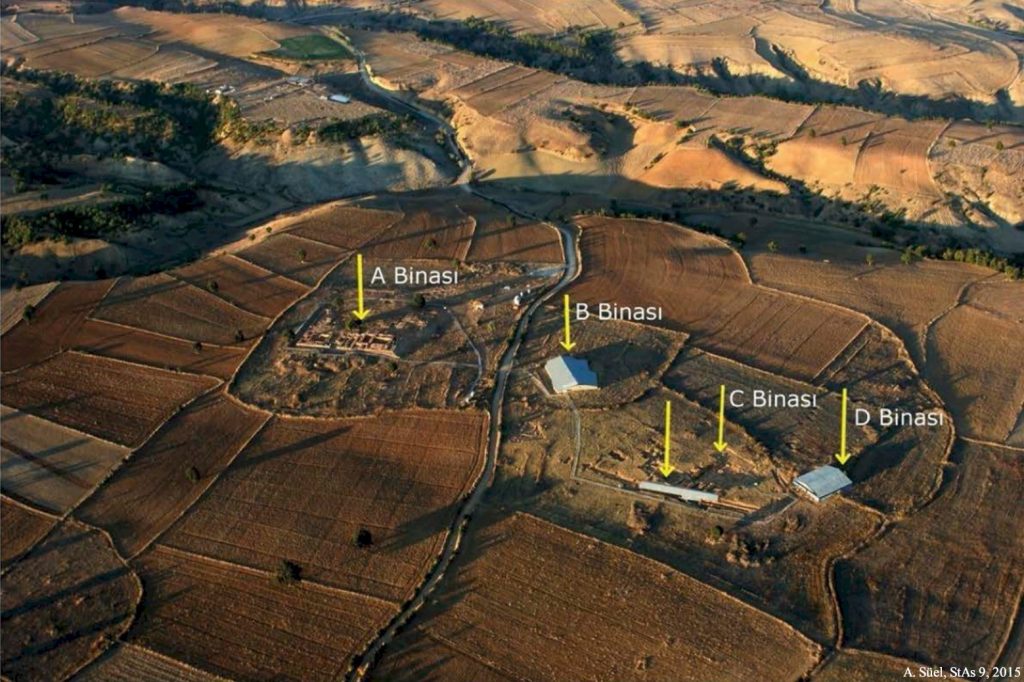
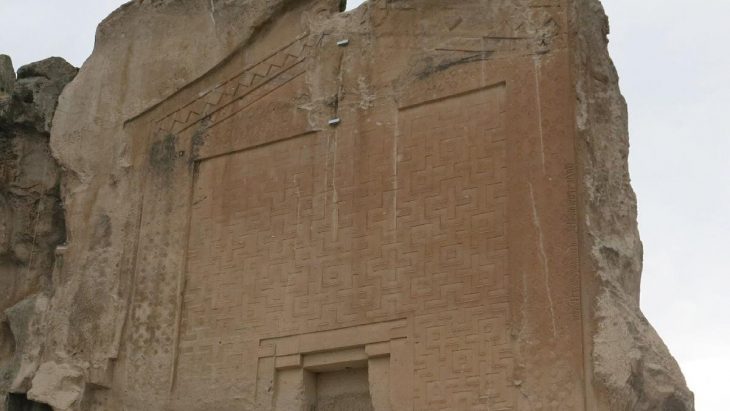
In the last part of the corridor, there are two orthostats placed opposite each other at the door entrance. Especially the orthostat on the left was found in a very well-preserved condition. On this orthostat, there is the figure of the Storm God, whose bow and quiver are hung on his shoulder, which is depicted walking towards the entrance of the building. ( Orthostat is squared stone blocks much greater in height than depth that is usually built into the lower portion of a wall.)
The 30-40 cm purification pool in the building is seen as the definitive proof that the building is a very important place of worship.
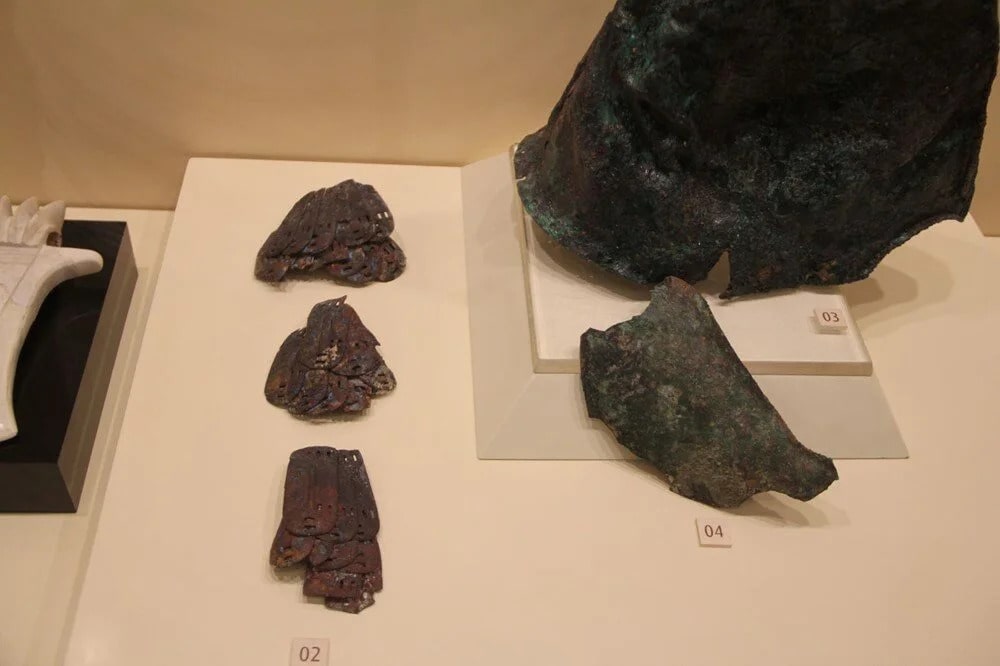
The said helmet must have been presented to this temple as an offering. It is similar to the helmets we have seen on the heads of the figures in many Hittite reliefs. This work was found here for the first time as a whole in its original form.

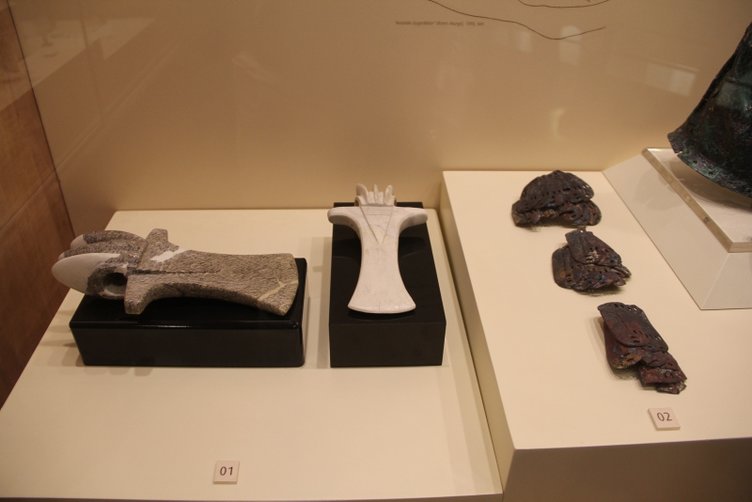
Bronze axes, pieces of armor, and spearheads were found near this helmet, which was left as an offering to the storm god.
The helmet, which has a conical body structure, has a head circumference of 66 cm and a height of 33 cm. The part that comes to the middle of the conical part is slightly inflated by beating outwards to fit the head more comfortably. It is seen that the helmet was formed by cutting and folding the bronze plate based on a certain mold and combining the two curved edges.
It is observed that the back part is kept longer to protect the nape, and the part coming towards the forehead extends from the middle towards the nose. The blows that the warrior can take on his head seem to have been carefully calculated.
The helmet, which was given as an offering to the Hittite Storm God, began to be exhibited at the Çorum Archeology Museum this year.

Özge Eren, one of the archaeologists of the Çorum Museum, “The bronze helmet, which has a conical form with a pointed crest, has rivet holes on the neck and cheeks. Apparatuses that protect the cheeks and neck are attached to these parts,” she said.
Bronze helmets were among the most important royal gifts of the period
Explaining that the Bronze helmet found under the rubble of the religious building called “D” building, which was destroyed as a result of a great fire about 3,300 years ago, was crushed, Eren said, “Due to the fact that bronze war materials were taken as booty in wars and the bronze was melted and reused in other productions, very few of them have survived to the present day. For this reason, this helmet found in Ortaköy Sapinuva is a very important artifact that has survived from the Hittite Empire period to which it belongs, although it was crushed and destroyed.”

Explaining that the work, whose Hurrian name is “gur-sip-pi” and Hittite name is “hupruşhi”, is one of the gifts presented to him in a temple dedicated to the ‘Storm god’, which also represents war, Eren said, “Bronze helmets are ancient Egypt, which was another superpower at that time. It is among the precious gifts sent to the pharaoh. This helmet found in Şapinuva is in perfect harmony with the helmet worn by the god, who is depicted with war clothes and weapons on the relief in Boğazköy Hattuşa King Gate. This shows that the sculptors of the period were able to apply the high relief technique on limestone in a very realistic way and that they were at a level that could visually reflect some sections of the Hittite world from 3,300 years ago,” she said.
In our article, excerpts are made from Dr. Mustafa Süel’s article titled “Ortaköy-Şapinuva’da Bulunan Bronze Bir Miğfer”.
















