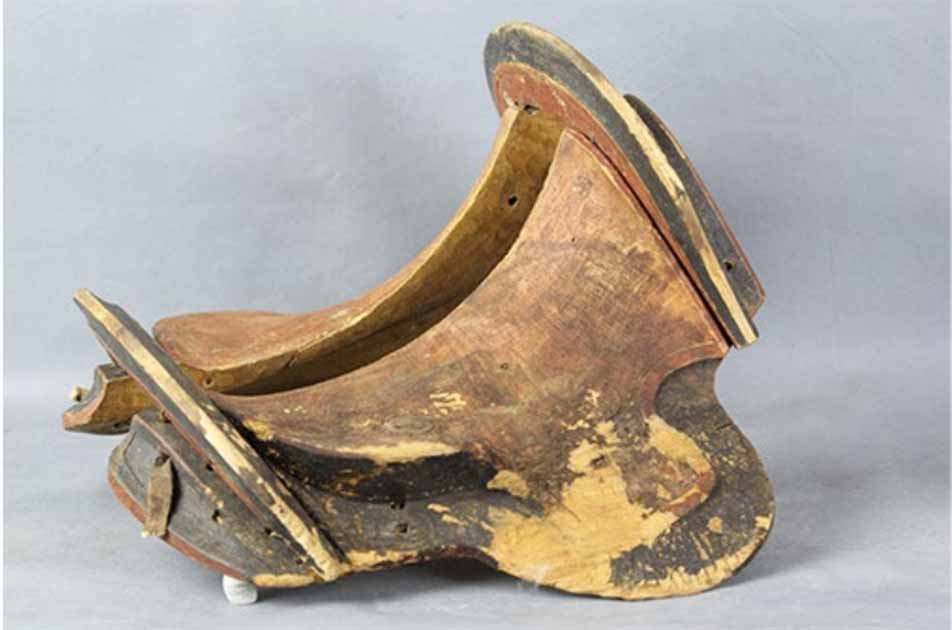
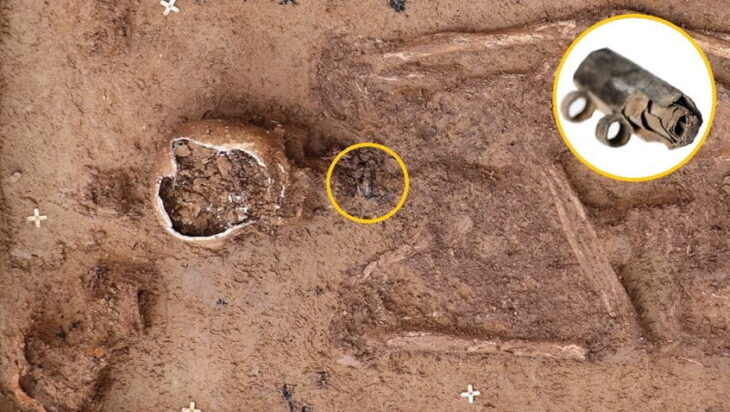
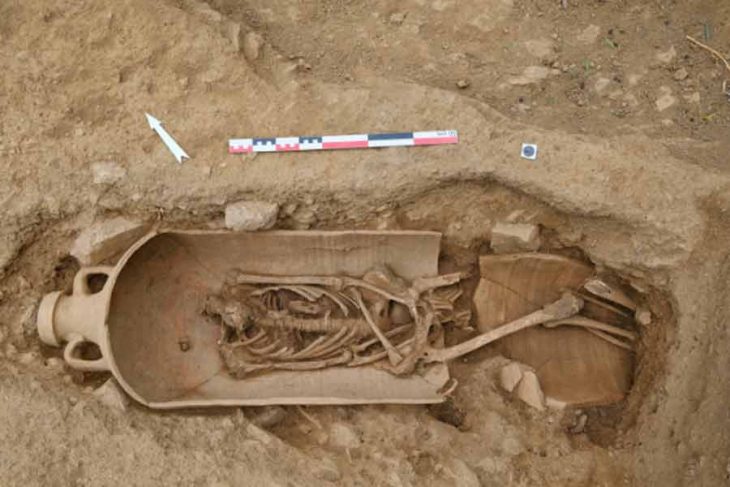
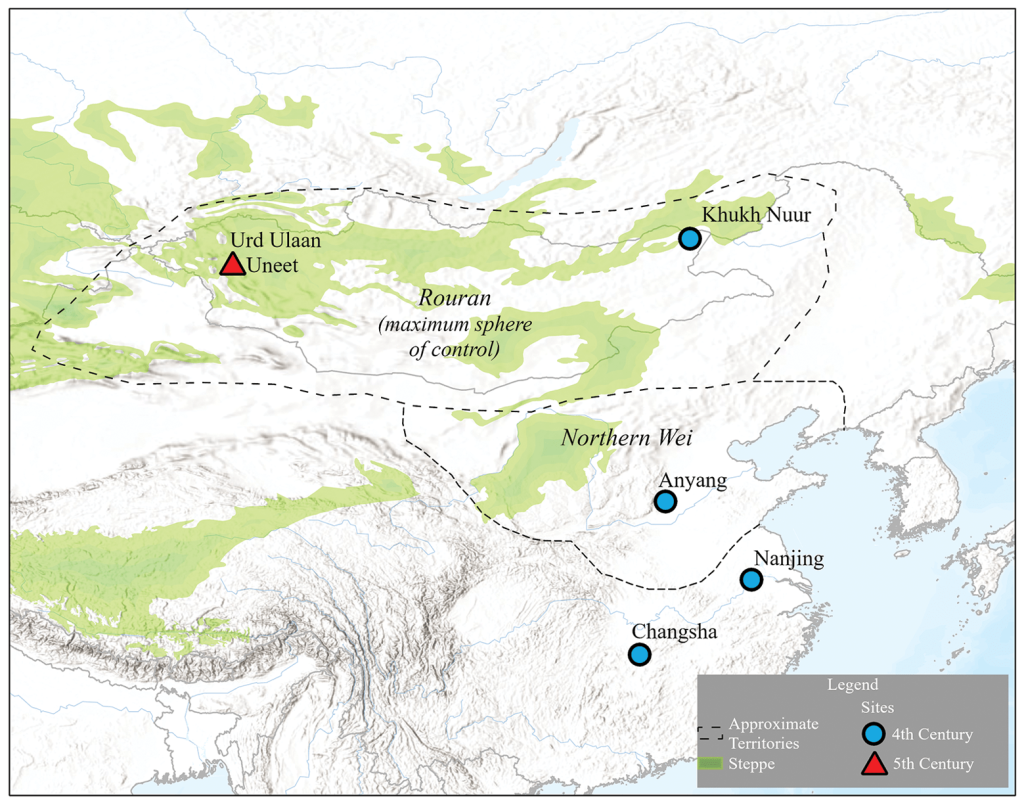
Researchers unearthed a wooden saddle framed with iron stirrups in a tomb in Urd Ulaan Uneet, popularly known as the “horsemen’s cave” in the rugged terrain of Mongolia’s Khovd province. This artifact, dating back to approximately 420 A.D., is hailed as the oldest of its kind.
Archaeologists employed radiocarbon dating to analyze the find, placing it between 267–535 AD, and revealing how the rise of Mongolian steppe cultures was likely aided by advances in equestrian technology.
This breakthrough discovery aids in piecing together the evolution of horseback riding from its humble beginnings to the complex military strategies of the medieval period. The earlier equestrian techniques involved a more primal approach, with riders clutching the mane for stability during bareback riding. With time, bridles and soft pads were adopted until the significant transition to saddles and stirrups, which greatly enhanced the warrior’s effectiveness by offering unmatched stability and upper-body freedom.
Rigid saddles with stirrups used to be an important part of cavalry equipment, and they are considered as a much more recent invention. It has been a mystery as to when these saddles were invented since organic material does not always preserve well in the harsh climate of grassland plains.
The discovery sheds new light on the role of equestrian technology in the rise of Mongolian steppe cultures. The durability of a wooden-framed saddle on horseback, particularly with the addition of stirrups, allowed for increased weight-bearing capacity and greater control, allowing for various forms of mounted combat.
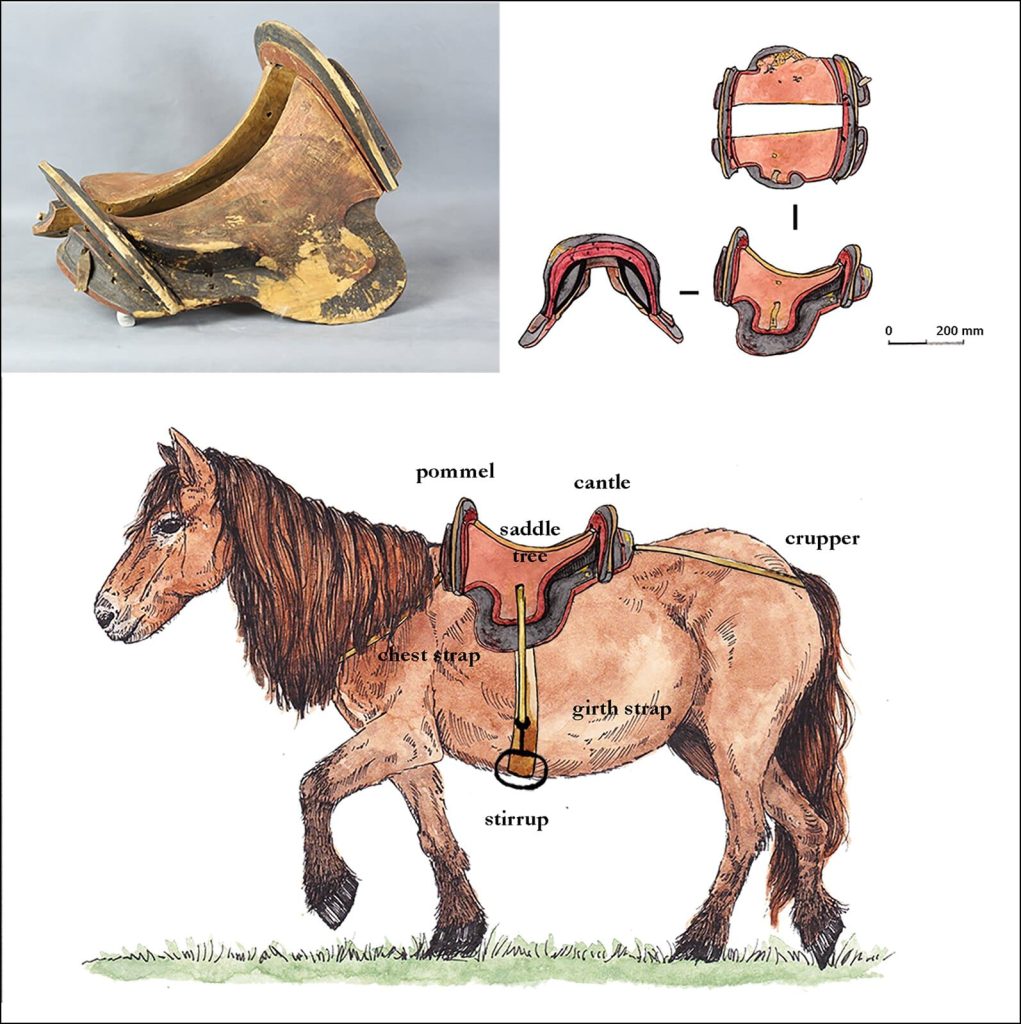
“Despite their ubiquitous presence within modern equestrian activities, saddles and stirrups were not used during the early centuries of horse-back riding,” state the authors. “Their development revolutionized mounted warfare and contributed to far-ranging social change across Eurasia but the origins of this technology remains poorly understood.”
A team of archaeologists from Asia, Europe, and North America examined the saddle, which was discovered in a burial involving a human and a horse at the Urd Ulaan Uneet cave in western Mongolia, to determine the origins of this revolution. Their results are published in the journal Antiquity.
Calibrated radiocarbon dates place the saddle between AD 267–535, making it the oldest example of a true frame saddle from East Asia.
Through DNA testing, researchers confirmed that the human remains were those of a man and that the mummified animal was a male domestic horse. Additionally, further analysis of the materials that make up the saddle found that they were sourced nearby. The leather is from a domestic horse, which were bred in the area, and the wood from local birch trees.
This suggests that the horse cultures of the eastern Eurasian steppe not only used this new riding technology but were also instrumental in its development and manufacture.
The Khaganate took control of Inner Asia through military victories, so its rise may not have been possible without this advanced saddle technology. As such, this specific discovery may have profound effects on how we perceive the history of East and Central Asia.
















