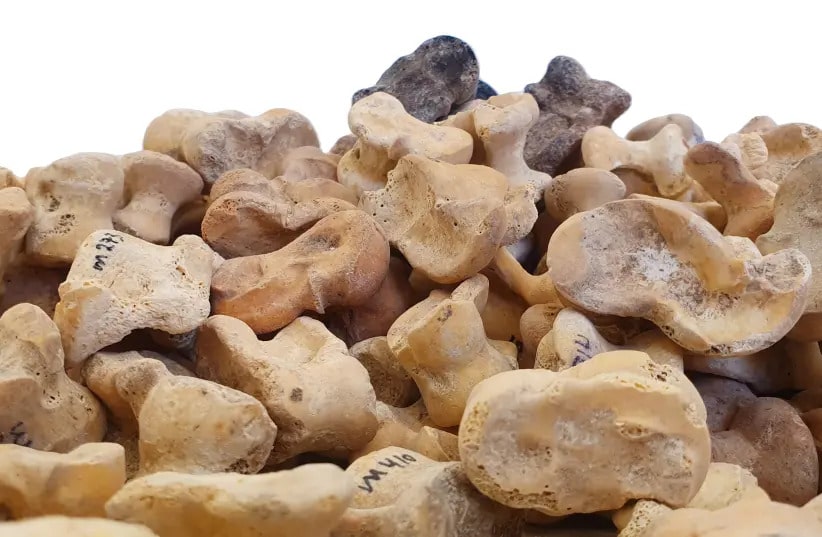
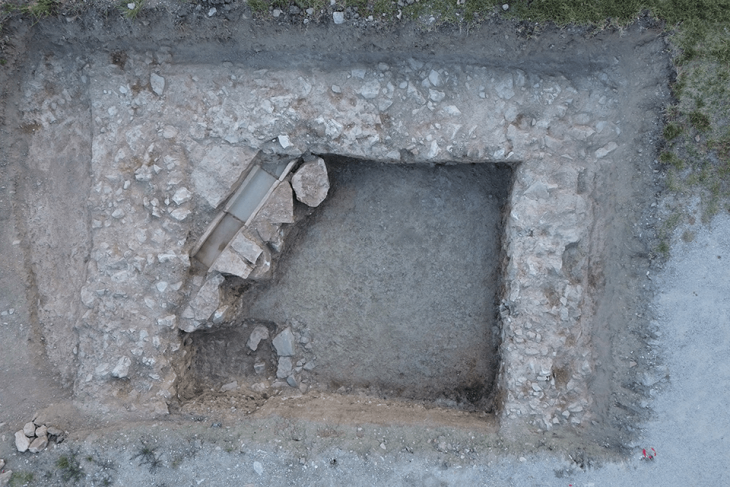
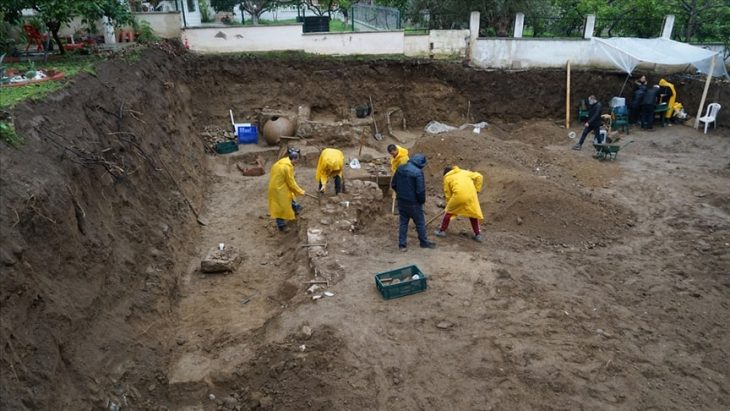
Archaeologists have found a rare assemblage of animal knucklebones known as astragali used in ancient Greek games and divination in Beit Guvrin-Maresha National Park in Israel’s Judean Shefelah region.
Ancient societies made extensive use of astragali, or knuckle bones, particularly those of caprine or cattle. In addition to other uses, they served as toys and tokens for rituals and divination.
Known as astragali, the practice of astragalomancy is of ancient indeterminate origin and has probably been independently invented several times. It is found throughout various cultures worldwide. It was a game of chance or divination played by the Greeks and Romans in ancient times, drawing some inspiration from the Etruscans and nearby Eastern civilizations.
Astragalomancy was practiced in Ancient Greece by rolling astragaloi and then consulting “dice oracles.” To obtain an oracle, either five astragaloi were rolled at the same time, or one astragalos (also known as astragali) was rolled five times in a row.
Astragalos from the Hellenistic era, which dates back 2,300 years, were discovered by University of Haifa researchers working under the direction of Dr. Ian Stern during excavations in the Maresha-Bet Guvrin National Park.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The study, conducted by archaeologists from various institutes around Israel, was published in the peer-reviewed Levant journal.
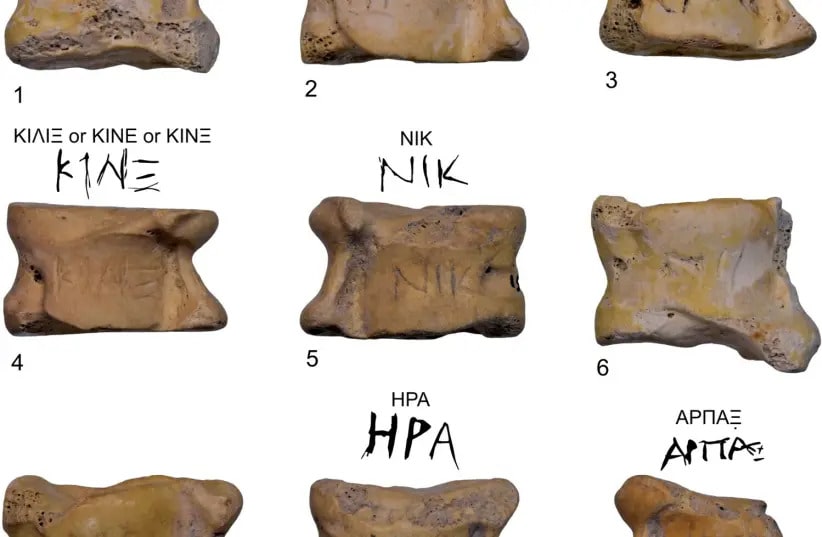
Many of the bones were engraved with the names of Greek gods that are associated with wishes and desire, such as Aphrodite, goddess of sexual love and beauty; Eros, god of love; Hermes, god of travelers, thieves, and merchants; Hera, goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women in childbirth, Nike, goddess of victory. Some of the pieces also have inscriptions such as “Robber”, “Stop, and “You are burnt” engraved.
Astragali were also used as charms and tokens. They were frequently buried beneath the foundations of a house to bring prosperity and peace, and there are records of young women using them as marriage tokens to mark their transition from maidens to married women.
It was discovered that the astragali that were the subject of the study had their shapes altered and were filled with lead.
According to Dr. Lee Perry-Gal, Israel Antiquities Authority, in the University of Haifa: “The extensive collection of astragaloi from Maresha is exceptional in terms of both quantity and quality as well as the numerous inscriptions. The collection shows that, just like today, those in need turned to spells, divination, and other extraterrestrial means of assistance. Men and women struggled in an environment where death, childbirth, and health were unpredictable, and they tried to use magic to protect themselves.”
Cover Photo: Ancient Greek bones known as astragali were used for games and divination. (YULI SCHWARTZ/IAA)
















