Throughout the history of the world, our interest and curiosity in ancient cultures and lives continue to increase day by day. Based on the curiosity of human beings, the researchers took a serious step towards illuminating a first.
According to the studies of Egyptologists from Bonn University, the world’s oldest place name may have been determined.
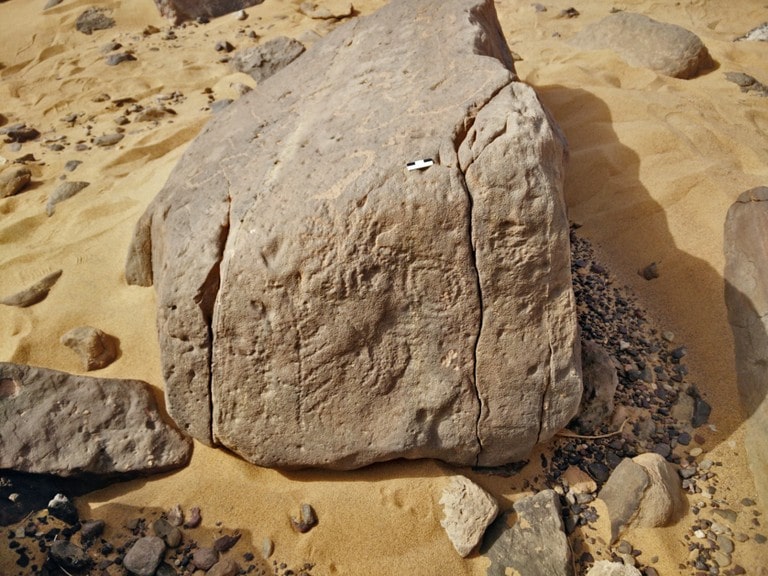
Researchers, who are conducting a joint study with the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities, may have deciphered the oldest place name in the world. There are four hieroglyphs in an archaeologically barely discovered inscription from Wadi al-Malik east of Aswan at the end of the 4th millennium BC after the emergence of the Egyptian state: “The Land of the Scorpion of the King of Horus”.
Egyptologist Prof. Dr. “This ruler, named ‘Scorpio’, was an important figure in the emergence of the first regional state in world history,” says Ludwig D. Morenz. B.C. There is no information about the reign of the living king and how long he lived. The name “Scorpion” was written together with three other hieroglyphs in a rock inscription found in a side valley of Wadi Abu Subeira, east of Aswan, about two years ago: “The Field of the Horus King Scorpion”. A circular hieroglyph indicates that this is a place name. “This makes it the oldest known landmark in the world,” says Morenz.
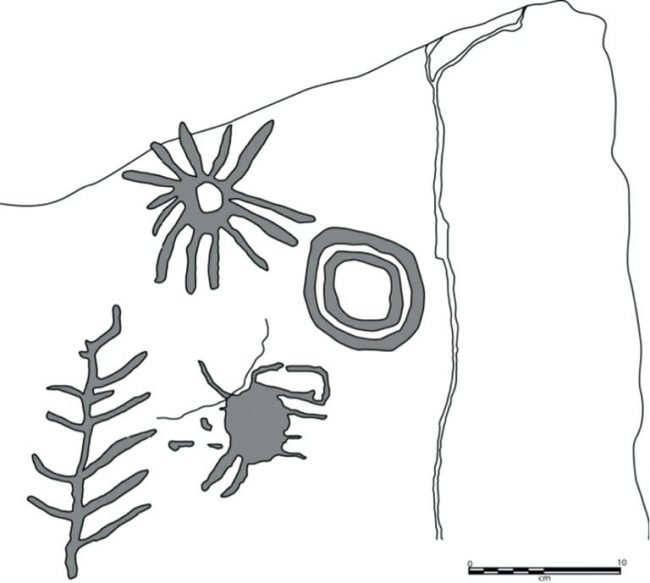
There are few sources available on how people lived more than five thousand years ago, and what the political, social, and economic conditions were. “This is precisely why the discovery of the rock inscription is so valuable,” says the Egyptologist. The very early use of cultural writing practice in this remote place, BC. it is unusual for the fourth millennium. Despite its brevity, this inscription opens a window to the emergence of the Egyptian state and its associated cultures. Morenz: “The internal colonization process in the Nile Valley becomes more was visible write for the first time.” Says.
Egypt as the first regional state in the World
According to the researcher, Egypt was the first regional state worldwide. “Earlier there were already manager systems elsewhere, but these were much smaller,” says Morenz. It has been known for ıts time that Egypt’s north-south extension was around 800 kilometers at that time. “Actually several rival population centers merged with the new central state,” says Morenz. Royal estates, known as domains, It was formed around the empire to strengthen the pharaoh’s empire.

As can be seen from civil servant titles, taxes and fees, an administration had already developed in the fourth millennium. These tasks are evidence of socio-economic dependencies and are based on control, hierarchy, and a special power of the ruler as Horus-God, as well as its earthly equivalent. “The boundaries between symmetrically and asymmetrically designed dependencies seemed pretty fluid at the time,” says Morenz. This meant that the symmetrical exchange principle could shift to an asymmetric principle of powerful exploitation.
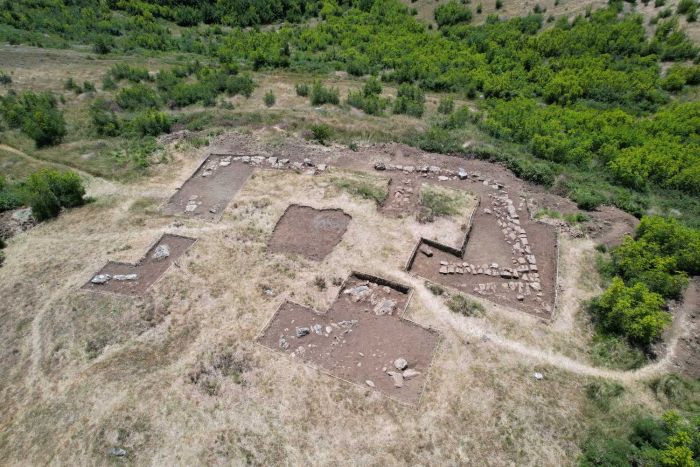
Various economic asset names (fields) are known from smaller text carriers such as labels, cylinder seals and container labels for goods deliveries. Rock inscriptions make such a royal site a concrete archaeological site for the first time. Apart from various rock carvings, other early rock inscriptions were discovered here and were found along with pottery from this period. “This area is still in the early stages of archaeological research,” says Morenz. Researchers see this as an opportunity to take a closer look at the important process of the emergence of the first state in the world.
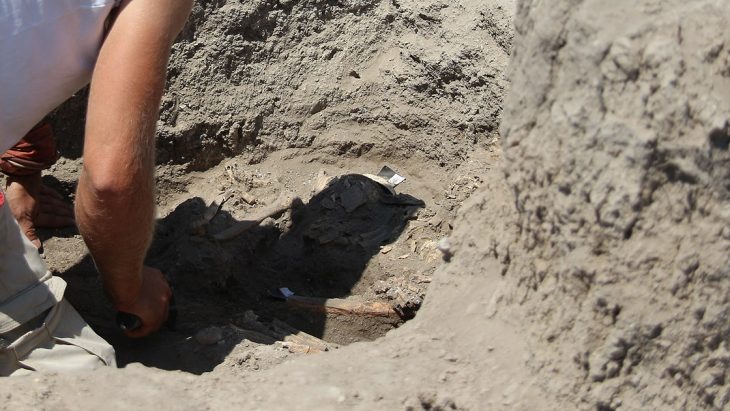
For several years, scientists from the Department of Egyptology at the University of Bonn have been working with the Aswan Office of the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities (“Taftish”) Abdelmonem Said and Mohamed Abdelhay. The research team had documented several rock carvings dating back to the Neolithic period.
The study is presented as the first volume of the newly established “KATARAKT. Aswan Archaeological Worksheets” by the Department of Egyptology of the University of Bonn.
Ludwig D. Morenz, Abdelmonem Said, Mohamed Abdelhhay: Binnenkolonisation am Beginn des ägyptischen Staates. Eine Fallstudie zur Domäne des Königs SKORPION im späten Vierten Jahrtausend – Chr., EBVerlag, 188 page, 29,80 Euro. The book is written in German and includes an Arabic translation.
















