When most people think of Vikings, they imagine fierce warriors charging into battle with axes and shields. But a tiny figurine recently rediscovered at the National Museum tells a very different story — one of carefully styled hair, braided beards, and surprising fashion sense. It seems the Norse weren’t just raiders; they were trendsetters, too.
A newly examined Viking Age gaming piece from the National Museum of Denmark offers rare insights into Viking hairstyles and fashion during Harald Bluetooth’s reign over a thousand years ago.
A Tiny Artifact with a Big Story
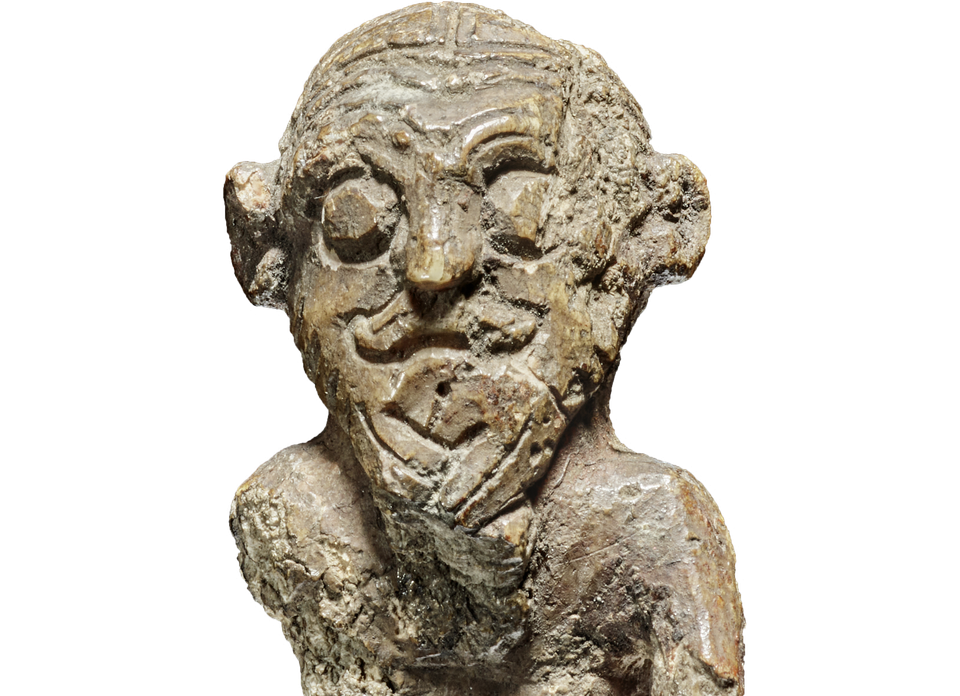
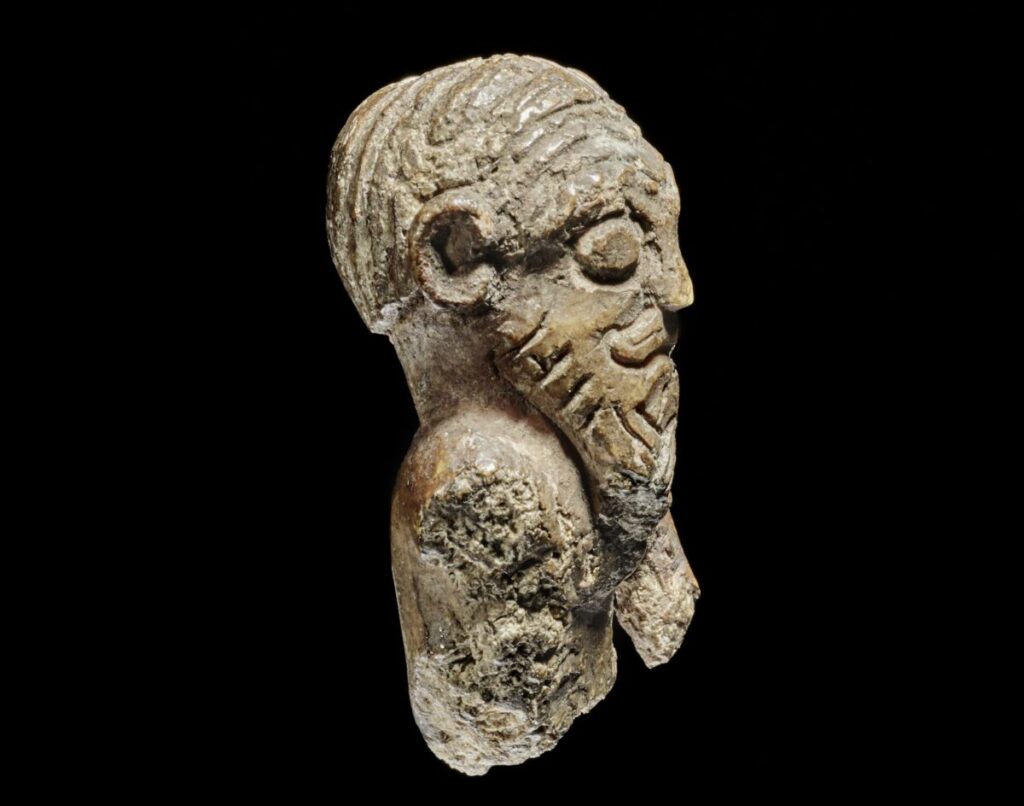
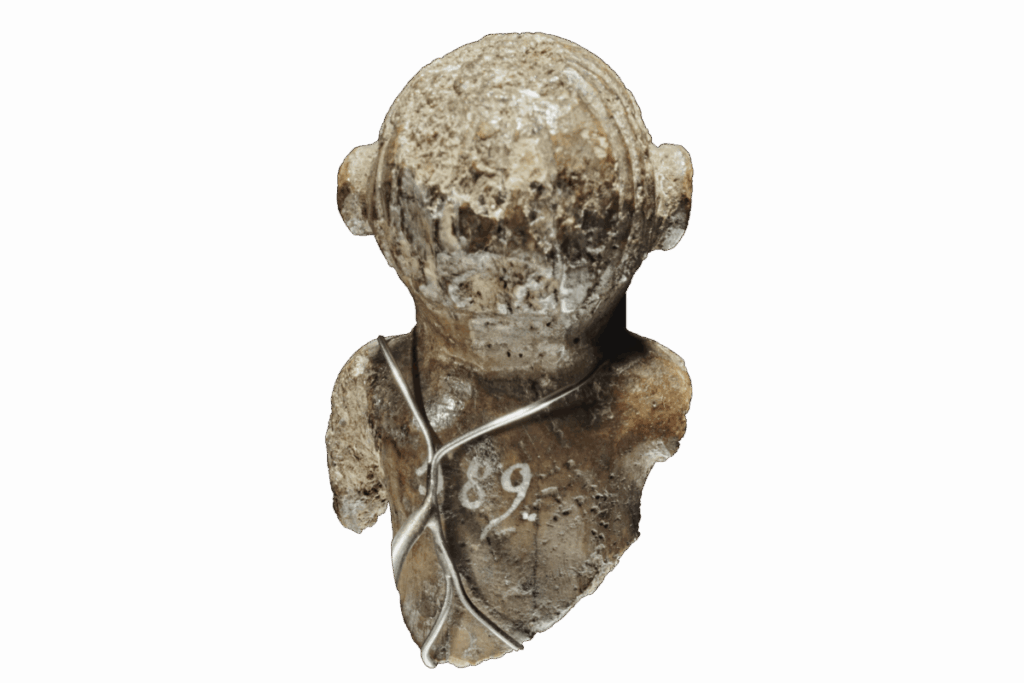
A remarkable discovery from the collections of the National Museum of Denmark has shed light on an overlooked aspect of Viking culture: their hairstyles. A tiny gaming piece, just three centimeters high and carved from walrus ivory, is providing scholars with unprecedented details about Viking grooming trends during the late 10th century.
Though the object has been stored at the museum for more than 200 years, new research highlights its cultural significance. The figurine depicts the bust of a Viking with striking features: a middle-parted hairstyle with a distinctive side wave, cropped hair at the back, a thick moustache, long braided goatee, and neatly trimmed sideburns. These details, scholars argue, may reflect an actual fashion among the Viking elite during the reign of King Harald Bluetooth.
“It’s exceptional that we have such a vivid depiction of a Viking, even a three-dimensional one. This is as close as we will ever get to a portrait of a Viking,” explains Peter Pentz, curator at the National Museum.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

From Storage to the Spotlight
The artifact is far from a new find. Discovered in 1797 within a Viking equestrian burial site in Viken, near the Oslofjord in southern Norway, it was among the first items catalogued by the museum. Registered as object number 589, the piece has largely remained in storage until its inclusion in the museum’s recent exhibition The Wolf’s Warning, which explores Viking Age spirituality and symbolism.
Despite its small size, the ivory figurine holds immense historical value. It was originally part of hnefatafl, a Norse board game sometimes referred to as “Viking chess,” which was widely played from the 8th to 11th centuries. In this strategic game, the depicted figure represented the king — the most important piece on the board.
A Glimpse Into Viking Fashion and Identity
What makes the object particularly valuable to historians is its human detail. Viking art is typically associated with animal motifs and abstract patterns rather than realistic depictions of people. For this reason, the figurine stands out as a rare three-dimensional representation of a Viking.
The hairstyle alone provides unique insight into Viking-era fashion. Until now, little concrete evidence has been available about how men in Scandinavia styled their hair and beards. Pentz notes that the figurine even shows fine details such as a small curl above the ear — features far too deliberate to be coincidental.
“This is the first time we see a figure of a male Viking with his hair visible from all angles. It’s unique,” says Pentz.
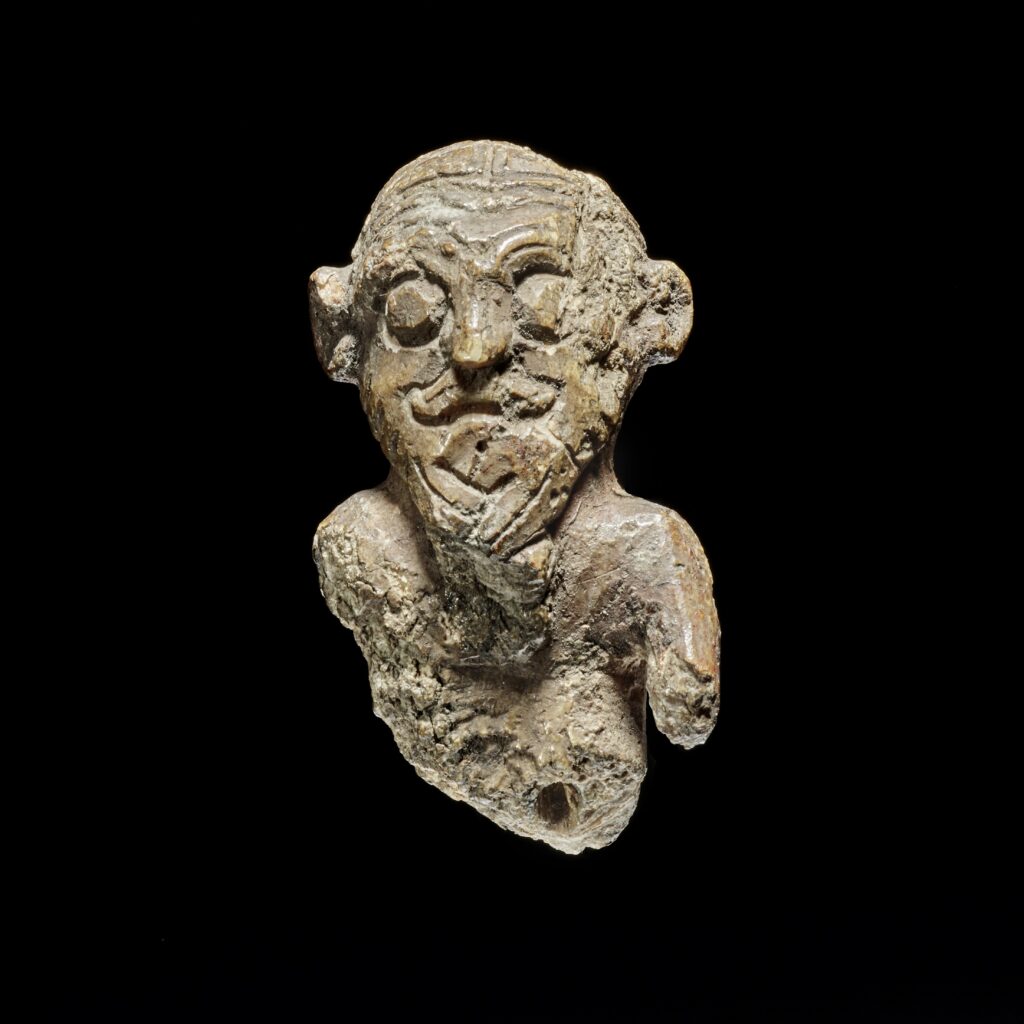

Symbolism Beyond Style
The figurine’s posture and beard also carry symbolic meaning. Despite some damage to its arms, researchers suggest it belongs to a group of carvings known as “beard-stroking” or “beard-pulling” figures. Such imagery, scholars argue, was not merely decorative but conveyed deeper cultural values tied to masculinity, fertility, and kingship in Norse society.
This interpretation aligns with its role in hnefatafl. Just as the king was the central figure in the board game, the act of pulling the beard reinforced authority and leadership in the Viking worldview.
Linking Past and Present
Today, the figurine is not only a curiosity for archaeologists but also a cultural touchstone that helps modern audiences imagine the personal lives of Vikings. Far from the stereotypical image of untamed warriors, this artifact shows that grooming, appearance, and self-expression played an important role among the elite.
The fact that it was crafted from walrus ivory — one of the costliest materials of the era — further highlights its prestige. Such objects were status symbols in their own right, signaling wealth and power within Viking society.
Reconstructing the Viking World
As the National Museum continues its research into Viking figurines, the little ivory king stands as a reminder that history often hides in plain sight. A piece once catalogued and forgotten now enriches our understanding of how Vikings saw themselves, not just as warriors or seafarers, but as individuals who valued style, symbolism, and social identity.
For historians and the public alike, this miniature portrait bridges the gap between myth and reality, offering an extraordinary glimpse into the everyday aesthetics of the Viking Age.
Pentz, P. (2025). Understanding the Flygstad (Fløgstad) Figurine: Gaming Pieces, Kings, Gender and Fertility Rites. Medieval Archaeology, 69(1), 169–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00766097.2025.2518811
Cover Image Credit: Roberto Fortuna, the National Museum of Denmark.
















