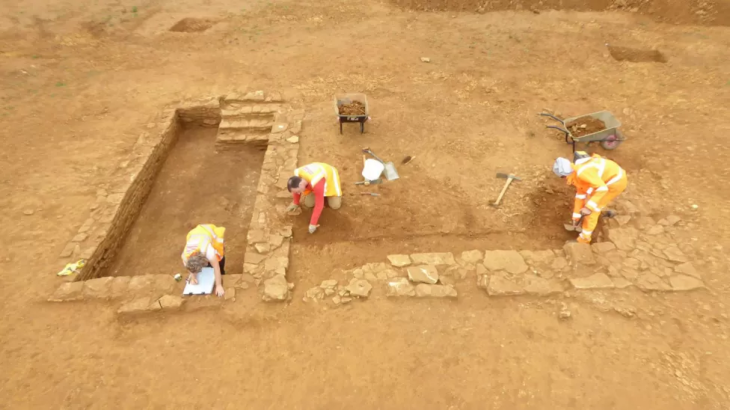
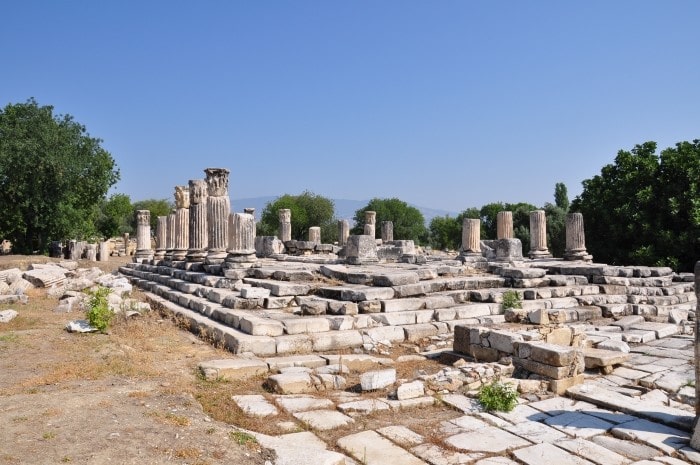
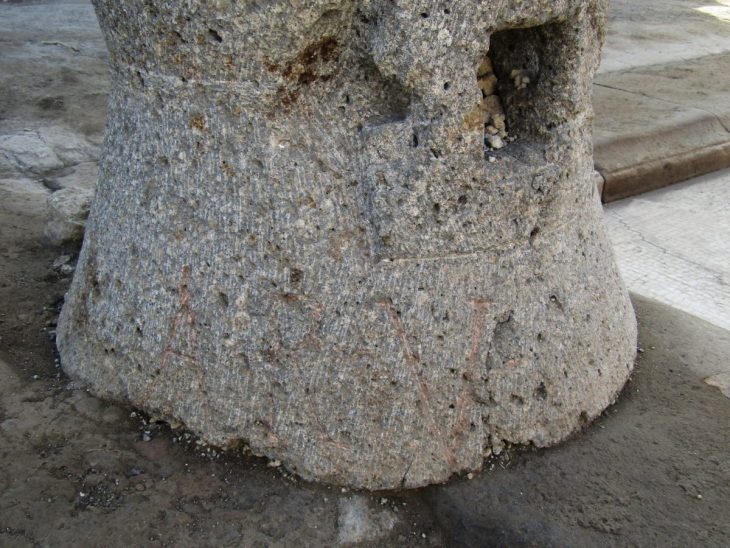
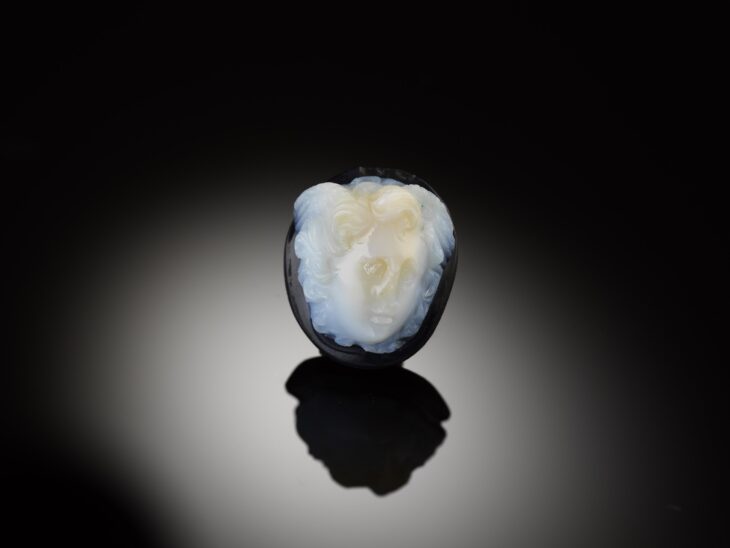
Archaeological excavations in Egypt’s eastern desert provide new data. Excavations in the Egyptian Eastern Desert delivers proof of emerald mines in Roman Egypt at Wadi Sikait.
Throughout history, people have not managed to keep themselves away from precious stones. Stone always occupies a valuable place in human life. Precious stones are a source of reputation for every person and country. They had fought throughout history for these precious stones and objects. Emerald is one of these stones.
“New evidence of the importance of the Roman Mons Smaragdus settlement within the emerald mining network”
The area is known for its Roman-era emerald mines chronicled by authors such as Pliny the Elder and Claudius Ptolemy and was rediscovered by French mineralogist Fréderic Cailliaud in the 19th century.
The researchers – J. Oller Guzmán, D. Fernández Abella, V. Trevín Pita, O. Achon Casas, and S. García-Dils de la Vega – detail what was found in three buildings in the Mons Smaragdus area in their new work. The researchers published their new articles in the Journal of Near Eastern Studies.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
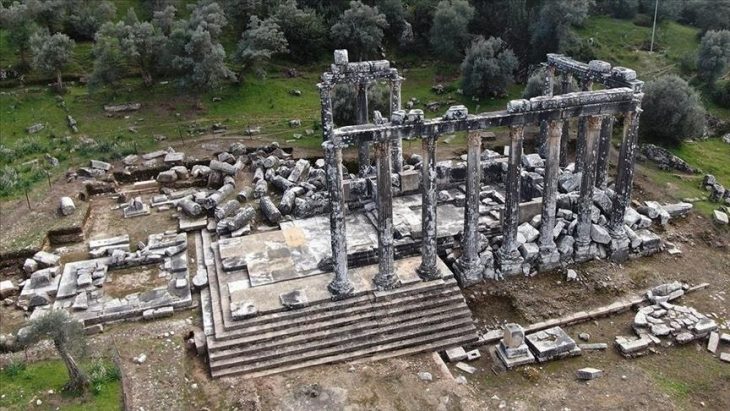
The first building was called the “administrative building” and was probably a temple used between the first and fourth centuries. Bronze and steatite figurines, incense burners, and nineteen coins were captured in this area.
The “large temple,” one of the most well-preserved structures standing in Sikait, also contained religious artifacts like bones, terracotta body parts, and amulets, and was likely occupied between the fourth and fifth centuries AD, although inner shrines were possibly used earlier, based on surviving traces of Egyptian hieroglyph and other materials.
Finally, the “six windows building” complex, possibly a residential space, included an older inner cavity, which may have been related to mining activity.
However, concerning this type of structure, common in Sikait, the authors write, “After analyzing most of these spaces, we can conclude that almost none of them can be identified as beryl mines, and mainly we are dealing with storage or living spaces.” Nevertheless, the study of the underground structures presents in Sikait and the surrounding areas allowed the documentation of several beryl mining spaces.
The detailed analysis of some mines showed relevant evidence concerning their structure, typology, and evolution, including the discovery of the first register inscription ever found in an ancient emerald mine.
These excavation seasons, the authors write, add to knowledge about emerald production in Roman Egypt. “First, it confirmed the significance of the religious aspect in mining settlements like ancient Senskis.” This shows the importance of the settlement within the emerald mining network, as no other site in which a similar concentration of cult spaces has been recorded.
“This links Sikait to other productive regions in the Eastern Desert, which also offer plentiful evidence of the importance of cult and religion, as the imperial quarries.”
The authors propose this work will provide key evidence in the future for determining how, exactly, the mines were exploited. Future seasons will focus on documenting the mining complexes to get a complete overview of the process of extraction and commercialization of emeralds, which will provide greater historical context.
“According to literary sources such as Olympiodorus, in the fifth century AD, a permit from the king of the Blemmyes was required to enter the emerald mines.” Considering that most of the surviving structures in Sikait date to this period, archaeological information from such sites is fundamental for understanding the progressive abandonment of the Roman/Byzantine control in this area and the gradual substitution by the Blemmyan power.
















