The archaeological excavation site at Boker Tachtit in Israel’s central Negev desert offers evidence to one of human history’s most momentous events: the expansion of modern humans, Homo sapiens, from Africa into Eurasia, and the subsequent extinction of Neanderthal populations in the region.
Researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science and the Max Planck Society, directed by Prof. Elisabetta Boaretto, returned to Boker Tachtit over 40 years after it was initially unearthed, together with Dr. Omry Barzilai of the Israel Antiquities Authority. They offer a new chronological framework for this key chapter in our anthropological evolution by using advanced sampling and dating technologies.
The study, which was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, indicates that Homo sapiens and Neanderthals were not strangers.
According to the “recent African origin” theory, Homo sapiens originated in Africa as recently as 270,000 years ago, and at various times took either the northern route to Eurasia via the Levant or several possible southern routes to remote corners of Asia and even Oceania—reaching as far as Australia by land.
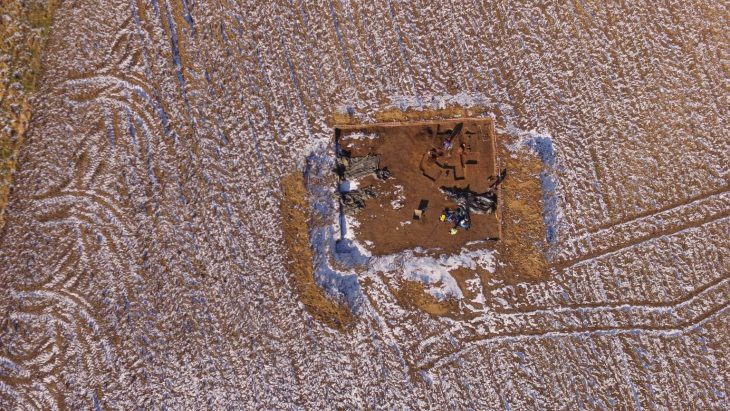
![The excavations at the 50,000-year-old Boker Tachtit site in the Negev Desert Photo: Prof. Elisabetta Boaretto, Weizmann Institute of Science]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/The-Boker-Tachtit-min.jpeg)
Boker Tachtit, in the Wadi Zin basin, in what is now the Ein Avdat National Park, is regarded as an important location for tracing this migration. It is a significant Levantine site for recording an important time in human prehistory: the transition from the Middle to Upper Paleolithic—that is, from a prehistorical society dominated by Neanderthals to the beginning of modern humans’ dominion. This period was distinguished by technological advancements such as blade manufacturing and the introduction of standardized implements made of bones and antlers.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Boker Tachtit is a transitional industry from the Middle to the Upper Paleolithic, according to American archaeologist Anthony Marks, who first excavated and published his analysis of the site in the early 1980s. Marks defines the site as a transitional industry from the Middle to the Upper Paleolithic and dates it to 47,000 years ago based on a single radiocarbon date. However, other dates found from the site, some of which date back to 34,000 years ago, made the transition’s timing extremely difficult.
“If we are to follow this timeline, then the transitional period could have lasted more than 10,000 years, and yet artifacts excavated from northern sites in Israel, Lebanon, and even Turkey suggest that the transition occurred much faster,” says Prof. Boaretto, who heads the Dangoor Research Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (D-REAMS) Laboratory at the Weizmann Institute, which specializes in advanced archaeological dating methods. “Marks managed to date only a few specimens from Boker Tachtit, owing to the limitations of radiocarbon dating then, and the range of his proposed dates is not consistent with evidence gathered from other—old and new—excavation sites in the region,” Prof. Boaretto says. “Radiocarbon dating, the method that he used in his study, has evolved tremendously since his time.”
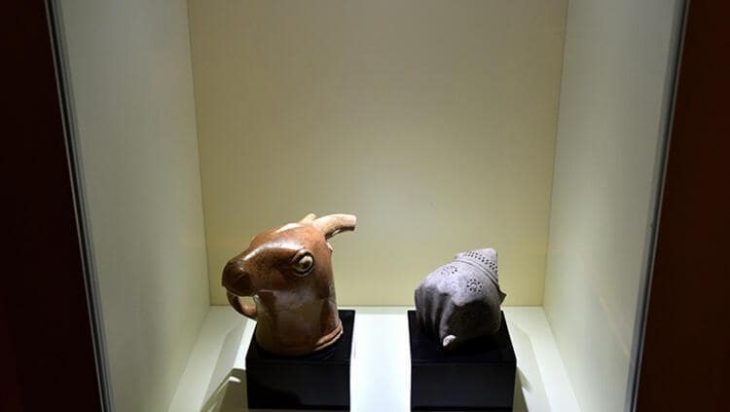
![(L-R) View of the Boker Tachtit excavation site. Circled: a group of unearthed flint stone artifacts; Flint point representative of the Upper Paleolithic in Boker Tachtit Photo: Clara Amit, Israel Antiquities Authority]](https://arkeonews.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/human-origins-min.jpeg)
Prof. Boaretto, Dr. Barzilai, and their interdisciplinary team used advanced dating methods on specimens acquired from Boker Tachtit during their excavations in 2013-2015 to answer these concerns. The Weizmann Institute and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, respectively, used cutting-edge techniques including high-resolution radiocarbon dating of single charcoal fragments found at the site and optically stimulated luminescence dating of quartz sand grains. The researchers also integrated detailed studies of the sediments, using microarchaeological methods to understand how the site was formed physically, contributing necessary data for the construction of its chronological framework.
“We are now able to conclude with greater confidence that the Middle-to-Upper Paleolithic transition was a rather fast-evolving event that began at Boker Tachtit approximately 50-49,000 years ago and ended about 44,000 years ago,” says Prof. Boaretto. This dating allows for a certain overlap between the material transition that occurred at Boker Tachtit and that of the Mediterranean woodland region (Lebanon and Turkey) between 49,000 and 46,000 years ago. Still, it shows that Boker Tachtit was the earliest site for this transition in the Levant and that, based on the materials found, it is a testimony to the last dispersal event of modern humans from Africa.
The early phase of Boker Tachtit also overlaps with the preceding Middle Paleolithic society in the area, the Neanderthals, according to the new dating system. “This goes to show that Neanderthals and Homo sapiens in the Negev coexisted and most likely interacted with one another, resulting in not only genetic interbreeding, as is postulated by the ‘recent African origin’ theory, but also in cultural exchange,” Prof. Boaretto and Dr. Barzilai conclude.
Cover Photo: Wikipedia-Negev Desert